chp 11-12 packet
advertisement

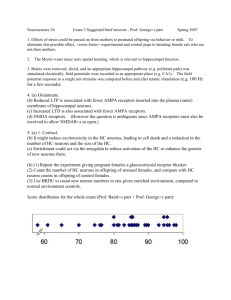
Name: ______________________________ Period: _______ Nervous packet continued… CHAPTER 11: AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM I. COMPARISON OF SOMATIC AND AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEMS OBJ: Compare the main structural and functional differences between the somatic and autonomic parts of the nervous system. Somatic nervous system (SNS) includes both ___________________ and ________________ neurons. Somatic sensory neurons convey input form receptors for the special senses: _________________ _________________ _________________ _________________ _________________ Also receptors for somatic senses: ____________________ ____________________ ____________________ _________________________________ These are all consciously perceived… Sensory motor neurons synapse with _____________________ _______________ and produce ______________________________________________. Skeletal muscles also generate __________________________ movements. Autonomic sensory neurons are associated with sensory receptors that monitor ___________________________. __________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ Autonomic motor neurons regulate _________________ and _______________ muscles, and ______________. These cannot be consciously suppressed or altered. Comparison of somatic and autonomic motor neurons Somatic motor neurons extend from _________ to ____________________________________. Autonomic motor pathways consist of ________ motor neurons. ______________________________ o Has cell body in CNS ______________________________ o Lies entirely in PNS Autonomic also has two main branches: ___________________________________________ ___________________________________________ Define dual innervation: ___________________________________________________________ _______________________________________________________________________________ 10 COMPARISON OF SOMATIC AND AUTONOMIC MOTOR NEURON PATHWAYS TO THEIR EFFECTOR TISSUES. Neurotransmitters: ACh is acetylcholine NE is norepinephrine II. STRUCTURE OF THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM OBJ: Identify the structural features of the autonomic nervous system. Preganglionic neurons, ganglia, and postganglionic neurons and how they relate to the activities of the ANS. READ THROUGH THIS SECTION, PAGES 302-307; EXAMINE THE DIAGRAMS. TAKE NOTES IN THE SPACES PROVIDED, QUESTIONS ON THIS WILL BE MINIMAL ON THE TEST. A. Organization of the Sympathetic Division ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 11 ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ B. Organization of the Parasympathetic Division ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ III. FUNCTIONS OF THE AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM; pages 307-310 OBJ: Describe the functions of the sympathetic and parasympathetic divisions of the autonomic nervous system. A. ANS Neurotransmitters Check the appropriate neurotransmitters in the chart below: Neurotransmitter Sympathetic preganglionic neurons Parasympathetic preganglionic neurons Sympathetic postganglionic neurons Parasympathetic postganglionic neurons Acetylcholine Norepinephrine 12 B. Activities of the ANS 1. Sympathetic Activities—“Fight or Flight” List the “E” situations that could bring on stress: _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ List examples of “Fight or Flight” responses: ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________ 2. Parasympathetic Activities—“Rest and Digest” What are the functions of the parasympathetic responses of the body? ___________________________________________________________________________ What does SLUDD stand for? ___________________________________________________________________________ What type of responses are the five things listed above? _____________________________ 13 CHAPTER 12: SOMATIC SENSES AND SPECIAL SENSES I. OVERVIEW OF SENSATIONS OBJ: Define a sensation and describe the conditions needed for a sensation to occur. A. Definition of a Sensation What four conditions must be satisfied in order to be able to experience a sensation? (1) ______________________________________________________________________________ (2) ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ (3) ______________________________________________________________________________ (4) ______________________________________________________________________________ B. Characteristics of Sensations Explain how we have perceptions. __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ What is the relationship between perception and adaptation? __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ C. Types of Sensory Receptors Look over Table 12.1 on page 315, you will be using this information soon in lab… Label the following sensory receptors in the skin and subcutaneous layer pictured below: a. Meissner corpuscles (Corpuscles of touch) e. Hair Root Plexuses b. Pacinian corpuscles (Lamellated corpuscles) f. Nociceptors c. Ruffini corpuscles (Type II cutaneous mechanoreceptors) d. Merkel Disks (Type I cutaneous mechanoreceptors) II. SOMATIC SENSES OBJ: Describe the location and function of the receptors for tactile, thermal, and pain sensations. Identify the receptors for proprioception and describe their functions. A. Tactile Sensations (Mechanoreceptors) Which sensations are tactile? ______________________________________________________________________________ What are they detected by? ____________________________________ 14 1. Touch Two types of rapidly adapting touch receptors: ______________________________________ ______________________________________ Two types of slowly adapting touch receptors: ______________________________________ ______________________________________ 2. Pressure How is pressure different from touch? ___________________________________________________________________________ Pressure receptors: ___________________________________________________________ 3. Vibration What types of receptors detect lower frequency vibrations? __________________________ Higher frequency vibrations? ____________________________ 4. Itch and tickle How are itch sensations stimulated? ___________________________________________________________________________ What type of receptors sense itch and tickle? ______________________________________ Can you tickle yourself? _______ Why or why not? ___________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ B. Thermal Sensations (Thermoreceptors) What type of receptors are thermoreceptors? ____________________________________ What are the two distinct types of thermal sensations? _________________________________ Temperatures between 10 and 40C (50-105F) activate __________ _________________; located in the ___________________. Temperatures between 32 and 48C (90- 118F) activate __________ _________________; located in the ___________________. Below 10C and above 48C stimulate what type of receptors? _________________________ These receptors produce what type of sensations? _____________________ C. Painful Sensations (Nociceptors) What type of receptors are nociceptors? ____________________________________ Where are nociceptors found? ______________________________________________________________________________ List five different stimuli that can cause pain ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ Describe what is meant by referred pain. ______________________________________________________________________________ Describe what is meant by fast pain. ______________________________________________________________________________ Describe what is meant by slow pain. ______________________________________________________________________________ 15 D. Proprioceptive Sensations (Proprioceptors) Inform you consciously and unconsciously of ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ Receptors for these sensations are called: _________________________________ and they are located in _____________________, ______________________,_________________________, and _____________________. They adapt slowly and only slightly What is kinesthesia? ______________________________________________________________________________ III. SPECIAL SENSES Allow us to detect things in our environment… IV. OLFACTION: SENSE OF SMELL (Chemoreceptors) OBJ: Describe the receptors for olfaction. CHARACTERISTICS OF RECEPTORS: _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ 16 V. GUSTATION: SENSE OF TASTE (Chemoreceptors) OBJ: Describe the receptors for gustation. CHARACTERISTICS OF RECEPTORS: _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ Let’s try something, everyone get a piece of gum. Unwrap the gum, hold your nostrils closed, place the piece of gum in your mouth and chew, and then let go of your nostrils). What Happened? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 17 VI. VISION (Photoreceptors) OBJ: Describe the receptors for vision. Identify the structures of photoreception and how they work. __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________________________ VII. HEARING AND EQUILIBRIUM (Mechanoreceptors) OBJ: Describe the receptors for hearing and equilibrium. The ear has three principle regions: the outer ear, the middle ear, and the inner ear. 18 Physiology of Hearing Describe events 1-8 pictured below involved in simulations of hair cells by sound waves. (1) ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ (2) ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ (3) ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ (4) ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ (5) ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ (6) ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ (7) ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ (8) ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________________ 19 Physiology of Equilibrium Describe static equilibrium and its function. _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ Describe dynamic equilibrium and its function. _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________________________ 20