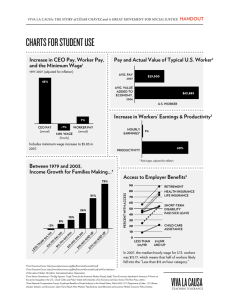
POM-Formulas-e3
advertisement

Exam 3 Formulas
Chapter 13 Aggregate Planning
Production rate/day/worker = Hours per day/ Labor hours per unit
Production rate/period/worker = Production rate/day/worker x No. of days per period
Wage/worker/day = Wage rate/hour x hours/day
Wage/worker/period = Wage rate/worker/day x days per period
OT cost/unit = Standard hours x OT wage per hour
No. of workers needed = Production Required ÷ Production per worker (Rounded up)
Cost summary for aggregate planning:
Cost summary
Regular wages
OT cost
SC cost
Hiring cost
Firing cost
Carrying cost
Total cost
No. of workers x no. of periods x wage rate per period per worker
OT quantity x OT rate/unit (Only for mixed strategy)
SC quantity x SC rate/unit (Only for mixed strategy)
Workers hired x hiring cost per worker
Workers fired x firing cost per worker
Sum of ending inventory x inventory carrying cost/unit/period
Chase:
Production 1st period = Forecasted Demand - (Initial inventory - Safety stock)
Production for all other periods = Forecasted demand
Period
Demand
Production
Workers
Hire
Fire
Hire/fire cost may be based on production rate changes or number of workers hired/fired.
Level:
(Sum of demand−(Initial inventory−Safety stock)
Initial estimate of production rate =
Number of periods
Number of workers = Production rate/Production rate per worker
Period
Demand
Production
Ending inventory
Mixed:
Production Capacity = number of workers * production rate/worker/period
Regular time production = Minimum{Requirement, Capacity}
Shortage = Requirement – Regular time production
Over time capacity = OT Limit % x Regular time capacity
Over time production = Minimum{Shortage, Over time Capacity}
Subcontracting production = Shortage – Over time production
Period
Demand
Requirement
Capacity
RT
Production
Shortage
OT
Capacity
OT
SC
Chapter 14 Material Requirements Planning
Gross requirement:
= Number of units required per unit of Parent (from BOM) x MPS quantity if parent is at
Level zero of BOM
or
= Number of units required per unit of Parent (from BOM) x Planned Order Release (PORL,
the last row) if parent is at an intermediate Level of BOM
Projected on-hand for week t+1
POHt+1 = POHt + SRt – GRt
POH is always > Safety stock, if not there is net requirement
Net requirement
If POHt+1 < Safety stock, then NRt = GRt – (POHt + SRt)
POHt = Projected on hand for week t
POHt+1 = Projected on hand for week t+1
SRt = Scheduled Receipt for week t
GRt = Gross requirement for week t
NRt = Net requirement for week t
Lot sizing: Lot-for-lot:
Total cost = No. of setups x Setup cost + Total ending inventory x Holding cost/week
EOQ:
Q
2dS
H / week
d = Average demand per week
S = Setup cost
H = Holding cost per week
Total cost/week = (d/Q)S + (Q/2)*Holding cost per week
Total cost for n weeks = Total cost/week x n
Periodic Order Quantity
POQ interval = EOQ/Average weekly demand rounded to whole number
Chapter 15 Short-term Scheduling
Input Output Control Chart
Cumulative deviation of input = Previous cumulative deviation + actual input – planned input
Cumulative deviation of output = Previous cumulative deviation + actual output – planned output
Cumulative backlog = Previous backlog + Actual input – Actual output
Job due date = Days till due date = Due date – Today’s date
Completion time (Flowtime) of a job = Completion time of the previous job + processing time
Average completion (flowtime) time =
Sum of total flow time
Number of jobs
Average job lateness =
Total late days
Number of jobs
Average number of jobs in the system =
Utilization =
Sum of total flow time
Total job processing time
Total job processing time
Critical Ratio =
Sum of totl flow time
Time remaining
Workdays remaining
=
Days till due date
Work time remaining in days