Material Requirement Planning (MRP)
advertisement

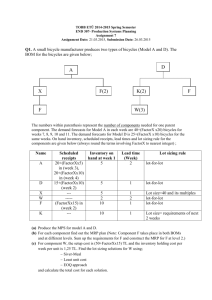
Material Requirement Planning (MRP) Chapter 16 Feb 9, 2006 1 Material Requirement Planning (MRP) ______________________________________ ______________________________________ Key Outputs of MRP Calculate demand for component items Determine requirements for subassemblies, components, and raw material Determine when they are needed Generate work orders and purchase order Consider lead time 2 When to use MRP ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Dependent / Independent Demand? 3 Demand Characteristics Demand Characteristics for Finished Products and Their Components Dependent demand Independent demand 100 x 1 = 100 tabletops 100 tables Discrete demand Continuous demand 400 – 300 – No. of tables No. of tables 400 – 100 x 4 = 400 table legs 200 – 100 – 1 2 3 Week 4 300 – 200 – 100 – 5 M T W Th F M T W Th F 4 MRP Input & Output Material Requirements Planning (MRP) Work orders Purchase orders Rescheduling notices 5 Major Inputs to MRP Process: 1. Bill of Material Product structure file Determines which component items need to be scheduled Product Structure Record Level 0 Clipboard Pressboa rd (1) Top Clip (1) Clip Assembly (1) Bottom Clip (1) Rivet s (2) Piv ot (1) Level 1 Sprin g (1) Level 2 6 Major Inputs to MRP Process: 2. Master Production Schedule (MPS) Drives MRP process with a schedule of finished products Quantities represent production not demand Quantities may consist of a combination of customer orders & demand forecasts Quantities represent what needs to be produced, not what can be produced Example MPS ITEM Clipboard Lapdesk Lapboard Pencil Case 1 2 85 0 75 125 95 50 120 125 PERIOD 3 120 0 47 125 4 5 100 50 20 125 100 0 17 125 7 Major Inputs to MRP Process: 3. Inventory Record _________________________________________________ Contains an extensive amount of information on every item that is produced, ordered, or inventoried in the system _________________________________________________ DESCRIPTION Item Item no. Item type Product/sales class Value class Buyer/planner Vendor/drawing Phantom code Unit price/cost Pegging LLC INVENTORY POLICY Pressboard 734 Purch Comp B RSR 07142 N 1.25 Y 1 Lead time Annual demand Holding cost Ordering/setup cost Safety stock Reorder point EOQ Minimum order qty Maximum order qty Multiple order qty Policy code 1 5000 1 50 0 39 316 100 500 8 3 MRP Processes – 4 Basic Steps 1. Exploding the bill of material 2. 3. 4. ___________________________________ Netting out inventory ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Lot sizing rule – How many units ___________________________________ ___________________________________ ___________________________________ Time-phasing requirements ___________________________________ 9 Lot Sizing Rule Comparison The FOQ rule ___________ _______________________ The POQ rule ___________ _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ The L4L rule ___________ _______________________ _______________________ _______________________ 10 MRP Matrix Gross Requirement Derived from planned order releases of the parent Actual / estimated demand, in case of final product Schedule Receipts Items on order Scheduled to arrive in the future time period Projected on hand Current inventory, or anticipated inventory at the end of period Projected on-hand Inventory at end of period t = Inventory onhand at end of period t - 1 + Scheduled / planned receipts in period t - Gross requirements in period t 11 MRP Matrix Net requirements Actual quantity to produce based on projected on hand and on-order quantity Planned Order Receipts Quantity, when orders need to be received Consider lot sizing rule: Planned Order Release When order need to be placed to receive on time Consider lead time 12 MRP Matrix (You can download the template from our class webpage) ITEM NAME OR NO. LOT SIZE LT 1 PERIOD 2 3 4 5 Gross Requirements Derived from MPS or planned order releases of the parent Scheduled Receipts On order and scheduled to be received Projected on Hand Net Requirements Beg Inv Anticipated quantity on hand at the end of the period Gross requirements net of inventory and scheduled receipts Planned Order Receipts When orders need to be received Planned Order Releases When orders need to be placed to be received on time 13 Example MRP Matrix ITEM: CLIPBOARD LLC: 0 LOT SIZE: L4L 1 2 3 4 5 Gross Requirements 85 95 120 100 100 Scheduled Receipts 175 Projected on Hand LT: 1 PERIOD 25 Net Requirements Planned Order Receipts Planned Order Releases 14 MRP Example 1 Given the following information, determine when orders should be released for A, C, and D and the size of those orders C(3) LT=4 Parts On hand Scheduled Receipts Lot Size Demand A C D 10 140 200 0 0 250, period 2 L4L Mult 50 Mult 250 100, period 8 A LT=3 D(2) LT=2 15 MRP Example 2 Given the following information, determine when orders should be released for A, B, C, and D and the size of those orders. A LT=3 C(3) LT=4 B LT=2 D(2) LT=2 Parts On hand Scheduled Receipts Lot Size Demand A B C D 10 5 140 200 0 0 0 250, period 2 L4L L4L Mult 50 Mult 250 100, period 8 200, period 6 - D(3) LT=2 16 Evolution of MRP MRP (material requirements planning) was the precursor to ERP Primarily a production planning and control system MRP evolved to MRP II (manufacturing resource planning) ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) and ERP II continue to extend the links through all business processes 17 Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) An Overview Organizes and manages a company’s business processes by sharing information across functional areas Connects with supply-chain and customer management applications ERP in the nutshell* Client server software Integrates majority of business processes Processes majority of transactions Enterprise wide database Real time data access * adapted from e-courseware, MIT Sloan 18 ERP Modules [Figure 12.1 Organizational Data Flow] 19 ERP Modules [Figure 12.2 ERP’s Central Database] Finance & Accounting Sales & Marketing ERP Data Repository Production & Materials Management Human Resources 20 ERP Implementation Process First step is to analyze business processes Which processes have the biggest impact on customer relations? Which process would benefit the most from integration? Which processes should be standardized? Use of Internet portals can aid implementation 21