Unit 1: Cell Biology Review Questions
advertisement

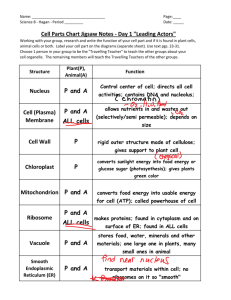
Biology Journal 8/27/2015 The DNA of a prokaryote is called “naked.” Why is that? What’s different about the DNA of a eukaryote and a prokaryote? Unit 1: Cell Biology Review Questions What kinds of cells make up… 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. A human A bacteria An ant E. coli A bananna Eukaryote Prokaryote Eukaryote Prokaryote Eukaryote What kinds of cells would have… 1. A chloroplast 2. 70s Ribosomes 3. A plasma membrane 4. Mitochondria 5. Reproduce by binary fission 6. Cell wall (any kind) Plant cell Prokaryote (bacteria) Every kind of cell! Every eukaryote Prokaryote (bacteria) Prokaryote, Plant cell, fungi cell Make a drawing of a prokaryote cell and label the following structures: cell wall, pili, flagella, and plasma membrane enclosing cytoplasm that contains 70S ribosomes and a nucleoid with naked DNA. . Nucleoid Region where naked DNA can be found; may have plasmids (loops of “extra” DNA, which can introduce new genes) Cytoplasm Jelly-like substance Flagella Whip like; allows the cell to move Cell Membrane Made out of phospholipids; controls what enters and leaves cell Cell Wall Made out of peptidoglycan (mesh of amino acids and sugars) Pili Allows cells to connect and exchange DNA (sexual reproduction) 70S Ribosomes make protein Make a drawing of a eukaryotic plant cell and label the following structures: plasma membrane enclosing cytoplasm that contains 80S ribosomes and a nucleus, mitochondria, chloroplasts, vacuole, and cell wall. Plasma membrane Mitochondria Free 80S ribosomes Lysosomes Cytoplasm Nucleus Golgi apparatus Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Nucleus DNA in a membrane Mitochondria Makes energy by doing cellular respiration Vacuole Large compartment for storage of water or other molecules 80S Ribosomes They make protein; sometimes attached to ER Cytoplasm Jelly-like substance Endoplasmic Reticulum Transports molecules; can have ribosomes attached (rough) or none (smooth) Golgi Complex Makes vesicles for molecules to enter or leave the cell Chloroplast Makes glucose by doing photosynthesis Cell Wall • In plant cells, it is made out of cellulose (a carbohydrate) • In fungi, it is made out of chitin (a carbohydrate) • Animal cells don’t have one Explain why there is a limit to the size of a cell. Cells are limited by a surface-tovolume ratio. This is because all areas of the cell need to be close enough to the surface area to efficiently exchange nutrients and wastes. Thus, cells must stay small to survive. What is a stem cell? Describe how they might be useful in the treatment of a particular disease. A stem cell is a cell that has the ability to differentiate, becoming other types of cells in the body. They can replace any damaged tissues in the body. • • • Replace retina tissue to cure failing sight (Stargardt’s disease) Replace damaged heart tissue from a heart attack Replace killed bone marrow (leukemia) A cell is 10 µm across. A student draws it as 250mm wide. What is the magnification? You don’t have to draw it, but you can if that helps! Measured length Actual size = Magnification 250 mm 10 µm = 10 µm = x 250,000 µm Solve for x x 25,000 times X= 25000 magnified Convert to the same 1000 µm units before you divide! 250 mm x 1 mm = 250,000 µm What 2 organelles are believed to have originated as a result of the Endosymbiotic Theory? Mitochondria and Chloroplasts! Identify the structures in this false-colored microscopic image of a human liver cell 2 1 3 7 4 5 6 Identify the structures in this false-colored microscopic image of a human liver cell 1. Cytoplasm 2. Mitochondria 3. Ribosomes (free) 7. Plasma membrane 4. Nucleus 5. Endoplasmic Reticulum (rough) 6. Lysosome Identify the structures in these false-colored microscopic images 3 1 4 5 6 2 Identify the structures in these false-colored microscopic images 3. Cell membrane 1. Cell wall 4. Cytoplasm (the darker spheres are ribosomes) 5. Pili 6. Flagella 2. Nucleoid region (where DNA is located) A microscope has the objective lenses of 4x, 10x, and 40x. The ocular eye piece has a magnification of 10x. What is the maximum magnification of this microscope? 40 x 10 = 400 times magnification Here is a human hair magnified 400 times. What could be 3 pieces of evidence that support the endosymbiotic theory? Mitochondria / chloroplasts have… 1. a double membrane 2. Their own DNA and ribosomes 3. Are the same size and bacteria 4. Reproduce via binary fission when their cell divides What kind of cell is this? What are 3 reasons you know that? It’s a plant cell. (it’s also a eukaryote because it has organelles) It has a large vacuole It has chloroplasts It has a cell wall Compare and contrast eukaryotes and prokaryotes in a Venn diagram. Eukaryotes Both Prokaryotes Compare and contrast eukaryotes and prokaryotes in a Venn diagram. Eukaryotes Both Prokaryotes •Large and more complex •Have a cell membrane and cytoplasm •Small and simple •Has a nucleus and organelles •Reproduce through asexual cell division •Lacks a nucleus and lacks organelles •DNA is linear and in many pieces (chromosomes) Have ribosomes (but they •DNA is circular and in are different) one piece (usually) •Cells divide through mitosis •Cells divide through binary fission •Have 80s ribosomes •Have 70s ribosomes •Attaches and transfers DNA through pili Compare and contrast plant and animal cells in a Venn diagram. Plant Both Animal Compare and contrast plant and animal cells in a Venn diagram. Plant Both Animal •Often are high in lysosomes •Have chloroplasts •Are eukaryotes •Has a plant cell wall •Have other organelles in •Can have great common (mitochondria, ability to move ER, golgi bodies…) •Has a large vacuole •Are similar in size •No / very limited ability to move •Cells asexually reproduce through mitosis A sperm cell has a tail that is 50µm long. A student draws it as 75mm. What is the magnification? You don’t have to draw it, but you can if that helps! Measured length Actual size = Magnification 75 mm 50 µm = 50 µm = x Convert to the same units before you divide! 75 mm x 75000 µm Solve for x x 1500 x X= 1500 magnified 1000 µm 1 mm = 75000 µm 1. Which focus knob should you use under the low magnification objective lens? Coarse focus knob (it changes the focus a lot) 2. The image appears too dark. What should you do? The diaphragm controls how much light passes through the slide 3. The image appears too dark. What should you do? The diaphragm controls how much light passes through the slide. Also, make sure the light is on!