Cell Design and Function
advertisement
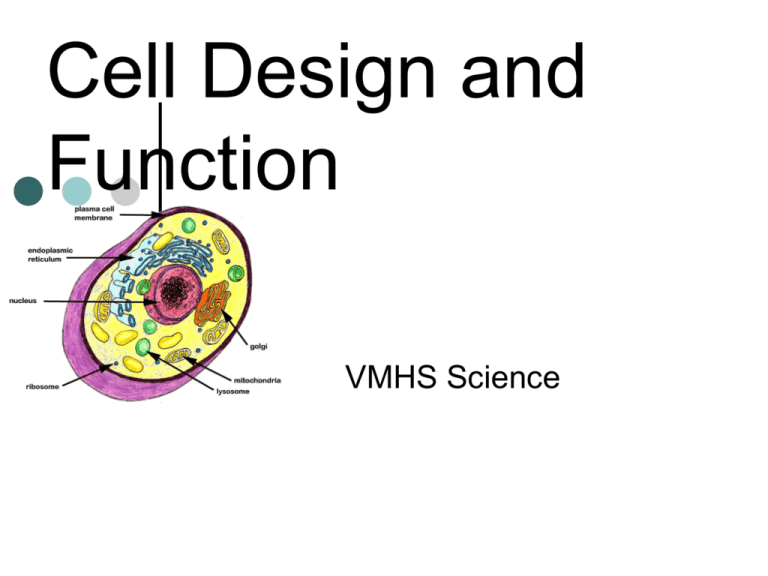
Cell Design and Function VMHS Science Cell Theory The Cell Theory States the Following: 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells. 2. The Cell is the basic unit of life. 3. All cells come from pre-existing cells through Mitosis or Meiosis. The Two Basic Cell Types Prokaryotes: Eukaryotes: Most multicellular the cells of most unicellular organisms like bacteria lacking membranebound structures.image organisms that contain membrane-bound structures. image Prokaryote Characteristics Include Kingdoms: Archaebacteria and Eubacteria. diagram Contains Circular DNA image Genetic material not bound by a nuclear envelope. Divide by fission. image No membrane-bound organelles. Eukaryote Characteristics Include Kingdoms: Plantae, Fungi, Animalia, and Protista. diagram Contains linear DNA condensed into chromosomes image Genetic material is bound by a nuclear envelope image Divide by sexual reproduction--meiosis and mitosis. animation Contains membrane-bound organelles. Microscopes Total magnification is found by multiplying the Eyepiece lens magnification times the Objective Lens. Complete the table below: Eyepiece Objective Lens 10X 40x 10X Total Magnification 500X 10X 100X CELLULAR ORGANELLES AND THEIR FUNCTION The Plasma Membrane Maintains homeostasis creates a barrier for the cell. Protection semi-permeable image The Nucleus Contains the genetic info. (DNA) Assembles Ribosomes Central Processing Unit Nuclear Envelope and pores The Ribosomes A small, NON-membrane bound organelle. Located in the cytoplasm and the rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER). Produced in the nucleolus. rRNA functions to assemble proteins from amino acids. Composed of both DNA and RNA. Ribosomes The Mitochondrion Produces cellular energy for the cell in the form of ATP. (=Adenosine-P-P-P). image Contains highly folded internal membranes called cristae. image Contains it’s own DNA (theorized to have once been a single-celled organism) image Contains an inner and outer compartment image The Mitochondrion (cont’d) Divides asexually (fission) similarly to that of a prokaryotic organism. image The # of mitochondria in a cell is determined by that cell’s energy needs. image (Ex: Muscle cells contain more mitochondria than do skin cells.) The Golgi Apparatus Contains a single membrane. Is a stack of vessicles involved in packaging macromolecules for transport through the cell. Golgi vessicles are involved in transporting material out of cell. The Golgi Apparatus Large Vessicle Small Vessicle AK BACK The Golgi Apparatus Vessicle Contents: 1) hormonal/enzyme contents of lysosomes. 2) Peroxisomes that breakdown toxic hydrogen peroxide. 3) Secretory vessicles that transport material via exocytosis. image The Endoplasmic Reticulum • Attached to the nucleus to form a transportation network for protein distribution. Two Types: 1) Smooth ER: Ribosome-free and produces lipids and membrane proteins. 2) Rough ER: w/ribosomes and produces Endoplasmic Reticulum • Contain digestive enzymes. • Digests excess or worn out organelles, food particles, bacteria, & viruses. • Has a membrane to protect the rest of the cell from the strong digestive enzymes. The Differences Between Plant and Animal Cells • Has a few different organelles than an animal cell. • A plant cell has a cell wall. • A plant cell has chloroplasts. • A plant cell has a vacuole. • An inflexible barrier that protects a plant cell and gives it support. • Composed of cellulose. • Allows materials to enter, but it is not selective like the plasma membrane. •Located in the cytoplasm. • Temporary storage containers. Store food, enzymes, & other materials needed by the cell. • Some vacuoles store waste products. • Capture light energy and convert it to chemical energy. • Has a double membrane • Inside the membranes, the thylakoid gain energy from trapped sunlight. •The thylakoid are arranged in stacks called grana. •The grana is surrounded by a fluid called stroma. • Chloroplasts contain the green pigment, chlorophyll, which gives plants their green color. The Six Kingdoms of Life Plantae Animalia Fungi Protista Eubacteria Archaebacteria The Six Kingdoms of Life Plantae Animalia Fungi Protista Eubacteria Archaebacteria Escherichia coli undergoing cell fission. Image showing Mitochondrial DNA Image of Circular DNA AK BACK Secretion: Expelling via exocytosis Vessicle being expelled into exterior Vessicle fusing with the plasma membrane AK BACK Prokaryotic Cell Click on the image the first time. Click on the image the first time. Eukaryotic Cell Double-Stranded DNA Eukaryote--Nuclear Envelope Sperm entering egg. The Phospholipid Bilayer The ATP Cellular Energy Molecule






