Creating a Screening Algorithm for
Sexually Transmitted Infections:
Baiye N. Orock, MPH, U of S School of
Public Health
Dr. Mark Vooght, MHO, FHHR
April 2015
Chlamydia Rates (All Ages) per 10,000 Population for FHHR and SK,
2009-2014, Target 2013/14
Updated: Feb 2, 2015
60
50
Target is based
on average rate
for 2009-14,
and a 5%
Rate per 10,000
40
30
20
10
0
FHHR
SK
Target
2009
28.5
46.8
24.5
2010
22.9
48.8
24.5
2011
28.0
52.1
24.5
2012
26.0
52.4
24.5
Senior Leader
Dr. Vooght
2013
19.7
53.5
24.5
Chart Maintenance
Epidemiologist
2014
29.5
24.5
Chart Developer
Epidemiologist
FHHR Chlamydia Positivity Rate (%) - Tests Done,
Updated: Jan 6, 2015
Q3 2012/13 to Q3 2014/15
Target is based on average rate
for Q1 2012/13 to Q4 2013/14,
and a 20% decrease
1000
8.0
900
7.0
800
6.0
5.0
600
500
4.0
400
3.0
300
2.0
200
1.0
100
0
Q3
2012/13
Q4
2012/13
Q1
2013/14
Q2
2013/14
Q3
2013/14
Q4
2013/14
Q1
2014/15
Q2
2014/15
Q3
2014/15
Number tests done
752
679
665
710
782
858
842
891
810
Positivity rate (%)
3.3
4.6
4.2
3.5
3.3
2.9
5.0
4.9
6.9
Target (%)
3.3
3.3
3.3
3.3
3.3
3.3
3.3
3.3
3.3
0.0
Senior Leader Chart Maintenance
Dr. Vooght
T. Schellenberg
Positivity rate (%)
Number of Tests
700
HIV Rates per 100,000 Population for FHHR and SK, 2001 to 2014
Updated: Feb 12, 2015
25
Rate per 100,000
20
15
10
5
0
2001
2002
2003
FHHR HIV Rate
SK HIV Rate
4
2.6
4
2004
2005
2006
2007
2008
2009
2010
2011
2012
2013
2014
1.8
0
1.9
1.9
1.8
3.7
3.6
9
5.5
1.8
1.8
5.5
8.1
10.2
12.7
17.1
19.4
16.2
17.2
16.2
12
9.6
Sponsor
Owner
Dr. Vooght
C. Ward
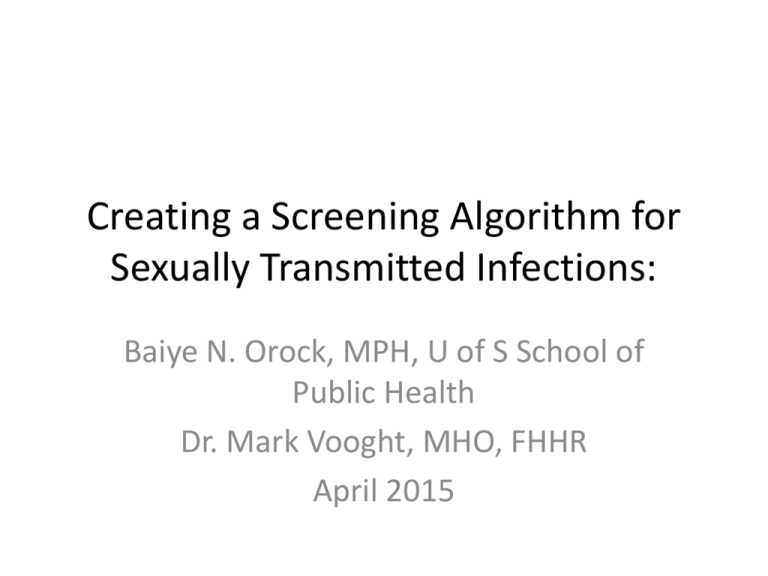
Issue: Develop an Evidence-based STI
Screening Decision Tool
• The development of an STI screening decision
tool to be used by healthcare providers
• Screening to be risk-based ?
• This to be informed by conducting a literature
review
RESEARCH QUESTIONS:
• 1. What are the evidence-based algorithms for
identifying sexually transmitted infection risk
factors and testing requirements in adult patients
presenting to primary care?
• 2. What are the evidence-based guidelines
regarding optimal risk grouping, age cohorts, risk
categories, and timing of screening for sexually
transmitted infections in adult patients?
Asymptomatic Patients:
Symptomatic Patients
Utilizing the Evidence:
• We predominantly used 6 STI Guidelines, to
create a screening algorithm
• Risk-based
SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED INFECTION/BLOOD BORNE PARTHOGEN (STI/BBP) SCREENING ALGORITHM
Offer routine screening (Chlamydia, Gonorrhea, HIV & Syphilis) to ALL sexually active clients.
Yes
Is this visit related to a sexual health concern?
Are there any STI-related
Signs & Symptoms?
No
As part of investigation,
consider routine screening
plus risk based screening
below
Yes
Syndromic
management1 .
Routine
screening plus2
HBV, HCV.
Female
Male
Is client pregnant?
Yes
No
< 30 & sexually active?
ALL
< 25 &/or at high risk* ?
Yes
No
Routine
screening
plus3 HBV
Routine
screening
plus4 HBV, HCV.
Routine
screening
Risk - based
screening
Risk-Based Screening:
Important: Go through ALL questions as the
client may be in more than one risk
category:
Using IV drugs or other addictive substances?
Add HBV5, HCV.
Same-sex partner( MSM6/WSW) or bisexual?
Add HAV5, HBV5, HCV.
Sex trade workers and/or their clients?
Add HBV5 .
Recently in an STI endemic area8?
Add HBV5 ; consider Chancroid#, LGV#, Granuloma inguinale #
Are there any other risk factors9?
Routine screening & Other2
Client requests STI screening
consider Parasitic7 STI
STI /BBP Screening Algorithm
SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED INFECTION/BLOOD BORNE PARTHOGEN (STI/BBP) SCREENING ALGORITHM
SUPERSCRIPT:
1 - Focused primary and secondary prevention counselling; treatment as necessary and partner follow up .
2 – Offer routine screening and/or screening based on institutional or local prevalence of STI.
3 – For all pregnant women, Chlamydia and Gonorrhea screening recommended for first prenatal visit. If positive, re-test within 3
– 6 months.
4 – For all pregnant women at high risk, Chlamydia and Gonorrhea screening recommended for first and third trimesters. Also
repeat HIV serology during labour for those at high-risk.
5 - Offer serological screening and immunize accordingly following Hepatitis A and B immunization recommendations as per the
Saskatchewan Immunization Manual, available at: http://www.health.gov.sk.ca/sim-chapter10
6 – Sample collection for MSM should be at site of receptive/penetrative oral or anal sex (Pharyngeal, urethral and/or rectal).
7 – Examples of a parasitic STI include trichomoniasis, pubic lice and scabies. Screening may be necessary only for trichomoniasis.
8 – For a list/map of STI endemic regions/countries, refer to:
http://www.who.int/gho/hiv/hiv_013.jpg --- HIV -endemic regions
http://www.cdc.gov/immigrantrefugeehealth/guidelines/domestic/sexually-transmitted-diseases.html -- Syphilis- endemic
regions (see Table 3).
NB: “The largest number of new infections occurs in the region of South and Southeast Asia, followed by sub-Saharan Africa,
Latin America, and the Caribbean” CDC, 2011.
STI /BBP Screening Algorithm
9 - OTHER RISK FACTORS:
-Sexual contact with person(s) with a known STI.
-A new sexual partner or more than two sexual partners in the past year.
-Serially monogamous individuals.
-No contraception or the use of only non-barrier methods of contraception
(i.e. no condoms).
-Any individual engaging in unsafe (i.e. Unprotected) sexual practices
-“Survival sex”: exchanging sex for money, drugs, shelter or food.
-Anonymous or internet sexual partnering.
-Victims of sexual abuse.
-Previous history of STI
-Living in an area with high prevalence of STI.
ABBREVIATIONS
HAV = Hepatitis A Virus.
HBV = Hepatitis B Virus.
HCV = Hepatitis C Virus.
HIV = Human Immunodeficiency Virus.
LGV = Lymphogranuloma venerum.
#- Use professional discretion (i.e. screen based
on prevalence of STIs in the countries recently
visited).
*- presence of one or more risk factors for
STI/BBP.
Utility of the Screening Tool:
• Used in concert with the STI Syndromic-based
risk-assessment tool
STI Risk Assessment in Primary Care Settings
Sexual health-related visit
Presence of
signs/symptoms
Non-Sexual health-related visit
No symptoms
but
concerns
Brief risk assessment (See back of page)
Risk identified
No risk identified
*Routine Asymptomatic screening
Minimal prevention counseling
Maintenance of safer practices
Discussion of future risk avoidance
Focused risk assessment
Focused prevention counseling
Syndromic management
Testing/screening
Treatment and partner follow-up
Testing Code Key
Survey Conclusion & Recommendations:
Of the Physicians, NPs and PHNs who participated in an implementation survey of the
developed tools, (screening algorithm and clinical assessment tool):
- 92% found them easy to use,
- 46% found the algorithm cluttered
- 100% rated the content as good to excellent, and
Recommendations
Development of an accompanying STI risk-based client questionnaire
Creation of a partnership with eHealth to develop a province wide format for the Electronic
Medical Records (EMR) system.
Have strategically located patient-specific posters or monitor displays, with appropriate STI
prevention and control messages (especially risk factors), at waiting areas in physician offices
and health clinics