SYNAPSES AND NEURONAL INTEGRATION
advertisement

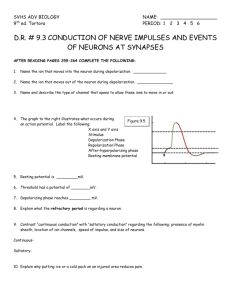
SYNAPSES AND NEURONAL INTEGRATION DR. ZAHOOR ALI SHAIKH LECTURE –10 1 SNAPSES AND NEURONAL INTEGRATION A Neuron may terminate on one of THREE structures: 1) MUSCLE 2) GLAND 3) ON ANOTHER NEURON – JUNCTION BETWEEN TWO NEURON IS CALLED SYNAPSE 2 SYNAPSE SYNAPSE – Junction between two neurons. SYNAPSES TWO TYPES 1) Electrical Synapses 2) Chemical Synapses Depending upon how the information is transferred between TWO neuron. 3 ELECTRICAL SYNAPSES In electrical synapses, two neuron are connected by Gap Junction which allow ions (charged particles) to flow between the two cells . Therefore Action Potential travels from one cell to another. Electrical signals are rare in Human Nervous System. 4 ELECTRICAL SYNAPSES [CONT] Example of Electrical Synapses --- Pulp of tooth --- Retina of the Eye --- Cardiac Muscle --- Smooth Muscle 5 CHEMICAL SYNAPSES In human CNS , most of the synapses are Chemical, where chemical messenger transmits information from one neuron to another . WE WILL DISCUSS CHEMICAL SYNAPSE 6 CHEMICAL SYNAPSE A chemical synapse involves: 1) Pre-synaptic Neuron 2) Post-synaptic Neuron In chemical synapse, there is junction between axon terminals of One Neuron known as ‘PreSynaptic Neuron’, and Dendrites or Cell body of Second Neuron, known as ‘Post-Synaptic Neuron’. 7 8 CHEMICAL SYNAPSE Mostly Dendrites or Cell body receive thousands of synaptic inputs from axon terminals of many other neurons 9 ANATOMY OF CHEMICAL SYNAPSE 10 ANATOMY OF CHEMICAL SYNAPSE REMEMBER PRE-SYNAPTIC NEURON SYNAPTIC KNOB SYNAPTIC VESICLES NEUROTRANSMITTER SYNAPTIC CLEFT POST-SYNAPTIC NEURON 11 ANATOMY OF CHEMICAL SYNAPSE [CONT] Pre-synaptic Neuron—It conducts the impulse and ends in a slight swelling, the SYNAPTIC KNOB. The synaptic knob contains SYNAPTIC VESICLES. Synaptic vesicle store chemical messenger ,a NEUROTRANSMITTER, that is synthesized by pre-synaptic neuron. 12 ANATOMY OF CHEMICAL SYNAPSE [CONT] SYNAPTIC CLEFT– Space between the pre-synaptic and post-synaptic neuron. POST-SYNAPTIC NEURON– it takes Action Potential away from the synapse. 13 SIGNAL TRANSMISSION ACROSS A SYNAPSE A Neurotransmitter carries the signals across the synapse. HOW ? By following mechanism 1. Action Potential reaches axon terminal of presynaptic neuron. 2. Ca2+ channels open, Ca2+ enters synaptic knob [presynaptic axon terminal]. 14 SIGNAL TRANSMISSION ACROSS A SYNAPSE (CONT) 3. Neurotransmitter is released by exocytosis into synaptic cleft. 4. Neurotransmitter binds with the receptors on the synaptic membrane of post synaptic neuron. 5. Binding of neurotransmitter to receptors opens the specific channel [Na+, K+, Cl-]. 15 16 SYNAPTIC DELAY Transmission of electrical impulse [AP] by chemical means from presynaptic neuron to post-synaptic neuron takes time. It is called ‘Synaptic Delay’. It is 0.5 to 1 millisecond. 17 TYPES OF SYNAPSE 1. There are two types of Synapse: 1. Excitatory Synapse 2. Inhibitory Synapse Excitatory Synapse Here neurotransmitter released act on receptors to open Na+ and K+ channels. When Na+ enters, it causes small depolarization [-70 to -60 mv]. It is called ‘Excitatory Post-Synaptic Potential’ [EPSP]. 18 TYPES OF SYNAPSE [CONT] 2. Inhibitory Synapse Neurotransmitter released acts on receptors and causes the opening of K+ or Clions. It causes Hyperpolarization [more negative inside of post-synaptic neuron] when K+ leaves or Cl- enters. Therefore membrane is less excitable now. This small hyperpolarization of post-synaptic cell is called ‘Inhibitory Post-Synaptic Potential’ [IPSP]. 19 20 COMMON NEUROTRANSMITTERS 21 ‘IMPORTANT’ Glutamate – Most common excitatory neurotransmitter in the brain. It causes EPSP. GABA [Gamma amino butyric acid] – Most common inhibitory neurotransmitter in brain. It causes IPSP. 22 NEUROTRANSMITTER REMOVAL FROM THE SYNAPTIC CLEFT 1. 2. 3. Neurotransmitters are quickly removed from the synaptic cleft by various ways: Inactivated by enzymes present on post synaptic membrane. Diffuse away from synaptic cleft. Actively taken back into axon terminal. 23 POST-SYNAPTIC POTENTIAL EPSPs and IPSPs are graded potential [local]. They can be summated [added]. Types of Summation 1. Temporal Summation 2. Spatial Summation 24 TEMPORAL SUMMATION When single presynaptic neuron is stimulated many times after short intervals, to summate several EPSP, it is called ‘Temporal Summation’. Up to 50 EPSPs might be needed to bring postsynaptic membrane to threshold level. 25 SPATIAL SUMMATION When two or more excitatory neurons are stimulated together at the same time, to get the action potential. It is called Spatial Summation. 26 27 CONVERGENCE AND DIVERGENCE Convergence On a given neuron, many other neurons come and synapse on it. It is called ‘Convergence’. Due to convergence input, a single neuron is influenced by thousands of other cells. 28 CONVERGENCE AND DIVERGENCE [CONT] Divergence It refers to the branching of axon terminals so that single cell synapses with many other cells. 29 30 ‘IMPORTANT INFORMATION’ There are about 100 billion neurons in the brain. A single neuron maybe connected to 5000 to 10,000 other neurons. Brain is responsible for different activities like sensations, movements of muscle, thought, emotion, memory – all these depend on electrical and chemical signaling between neurons along wired neural pathways. 31 WHAT YOU SHOULD KNOW FROM THIS LECTURE What is Synapse? - Connection between two neurons What are types of Synapse? - Electrical - Chemical Chemical Synapse - Presynaptic Neuron – Axon terminal (output unit) - Postsynaptic Neuron – Dendrites or Cell Body (receiving or input unit) Anatomy of Chemical Synapse Mechanism of release of Chemical transmitter from the synaptic vesicles. Action of Chemical transmitter (neurotransmitter) on postsynaptic neuron (dendrites of Cell Body) Excitatory and Inhibitory synapse depend on type of neurotransmitter – EPSP, IPSP Most common excitatory neurotransmitter in brain – glutamate Most common inhibitory neurotransmitter in brain – GABA How chemical transmitter are removed at the synaptic cleft? Types of Summation - Temporal – single presynaptic neuron stimulated many times after short intervals - Spatial – when two or more excitatory neuron stimulated same time to get AP 32 THANK YOU 33