enlightenment notes
advertisement

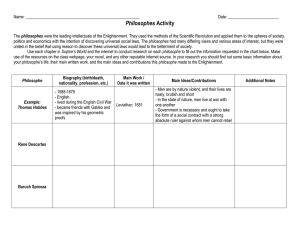
Agenda • • • • • • Bell ringer/Parliament Video Review Questions/Review HW Notes: Enlightenment Philosophes Index Cards/Exit Tix assessment Reading Jigsaw Guess Who Announcement • Quiz Friday! Review Questions • Define Divine Right – God given right to rule, similar to Mandate of Heaven • Why did Spain become bankrupt under Ferdinand? – Inflation, too much $ from colonies, spent $ on colonies • Who led the Roundheads in the English Civil War? – Oliver Cromwell • Who was Martin Luther? – German Monk, 95 theses, began protestant reformation Review HW • Let’s discuss p. 7 in packet The Enlightenment Objectives • Students will demonstrate an understanding of how the Enlightenment resulted from the Scientific Revolution, Identify at least 2 philosophes and their ideas, and describe how the Enlightenment influenced world-wide revolutions. Where is Europe? Remember… • It is crucial to remember that the scientists, artists, and authors of the scientific revolution and renaissance questioned existing authorities (catholic church). By questioning authority – they set a trend. Because they did it, others will now do it. But these guys aren’t going to do it through science or art, they are going to question politics, government, and human nature. Their philosophies are going to change the way people view the word around them for the rest of history….. Enlightenment • Enlighten: the act of being enlightened or the state of enlightenment. Having full comprehension of a situation. A “light bulb” goes off…. Enlightenment • The Enlightenment: was a period of time when intellectuals questioned existing governments, leaders, and human nature based on individualism and reason. • Absolute rulers and officials of the Church were most opposed to the ideas of the Enlightenment (duh) The Scientific Revolution and the Enlightenment • During the Scientific Revolution people began to question old ways through observation and reason (Bacon! Descartes! Scientific Method!) • Reason was applied to these studies during enlightenment: – Economics – Political Science/Government – Industry (eventually….with industrial rev) – Sociology (study of society, how people act) Enlightened Thinkers…. • We call the fellers that became “enlightened” philosophes (weird way to say philosopher) • There are 5 big ones. You must try to memorize at least TWO! • Why? They changed the world as it existed and created the world you live in today. Philosophes…. • Make sure you write down each of their names and what they did…. Thomas Hobbes • He wrote the book Leviathan, which stated that people are naturally evil, and need an absolute ruler otherwise there would be chaos and disorder • Obvi absolute leaders LOVED them some Hobbes …. He thought they should maintain absolute power. • But some people disagreed…. John Locke • He believed people should rule themselves. Humans are totally capable of that. • Locke also believed that people have three natural rights: life, liberty, and property. – If a government does not protect these rights, Locke said that the people should overthrow the government. • Wrote "Two Treatises of Government” • His philosophy becomes the basis for the US Constitution. Our founding fathers loved this guy… Voltaire • “I may disagree with what you have to say. But I will fight to the death defending your right to say it” – Voltaire • Firm believer in freedom of speech • US Bill of Rights…. Jean-Jacques Rousseau • Social Contract Theory!! – People give up power and freely form a government in exchange for the protection of natural rights as defined by Locke – I allow my government to make decisions for me. I give them my money. In return – they protect my life, liberty, and property – Basis for US Government • Wrote "The Social Contract” Baron de Montesquieu • Flip the “M” in Montesquieu upside down and what number do you get? – 3! • Believed in Separation of Powers. • Legislative branch, Executive branch, and Judicial branch (3 branches!) • Basis for US Government • Wrote "Spirit of the Laws.” Agenda • • • • • Bellringer Review Questions Finish/Study Index cards Whiteboard activity Jigsaw readings (Locke and Rousseau) Review • Absolute rulers believed they could do whatever they wanted because they ruled by: – Divine Right • John Locke said everyone is entitled to Life, Liberty and property. These are called: – Natural Rights • What classical civilization collapsed leading to feudalism in Europe? – Rome • What law code was based on an “eye for an eye”? – Code of Hammurabi Index Cards • Write the name of a philosophe on the front of an index card (should have 5 total) • On the back of the card, write their most important contributions/ideas • We will continue adding to this “Pile of People” as the year progresses… • You have 3 minutes to study your philosophes with your partner • What Philosophe believed in natural rights of life, liberty and property? • What Philosophe believed in freedom of speech? • What Philosophe argued in favor of absolute rulers because people are naturally bad? • What Philosophe argued in favor of multiple branches of government? • What Philosophe believed that in order for government to work their must be a social contract between the people and their government? Jigsaw Readings • If you are given the number “1” – Read/listen to the selection from Locke’s book on p. 10 – Highlight key ideas, be prepared to share Locke’s thoughts with the rest of the class • If you are given the number “2” – Read/listen to Rousseau’s excerpt on p. 11 – Highlight key ideas, be prepared to share locket’s thoughts with the rest of the class. Bellringer • Study index cards with your partner to prepare for quiz… Agenda • • • • • Bellringer Study time (index cards) Quiz Jigsaw Locke/Rosseau readings Decode US Constitution Study • Take 3-5 minutes to study your index cards with your partner prior to our quiz • You must know ALL philosophes! Quiz • What are natural rights as defined by Locke? • What was Montesquieu's theory of government? • Define social contract as outlined by Rousseau • What did Thomas Hobbes believe about human nature? • Define Divine Right • What was the result of Henry VIII’s Act of Supremacy? • Voltaire believed everyone had a right to free _____________________ Jigsaw All “2’s” stand up! You are going to be paired with a “1” Discuss your respective readings with each other for 5 minutes US Constitution • In your packet, page 8 • Read the US Constitution and underline any enlightenment ideas you find • You must have at least THREE underlined ideas with the name of the philosophe written next to it Meanwhile in America… • America was a collection of colonies under the control of Great Britain • Great Britain profited from our resources and labor (mercantilism) • Truthfully – GB did nothing out of the ordinary. We were not treated unfairly. • They defended us in French and Indian war. Cost them a lot of money Meanwhile in America… • To recover some of the money that GB spent defending us from the French and the Indians they passed new taxes • Stamp act, Tea act, etc… • Some pretty patriotic fellas got real mad…. • WHY? Meanwhile in America… • BECAUSE THEY DID NOT WANT THEIR TAXES RAISED WITHOUT REPRESENTATION IN PARLIAMENT • THE PEOPLE SHOULD HAVE A SOCIAL CONTRACT WITH THEIR GOVERNMENT • THE GOVERNMENT SHOULD HAVE CHECKS ON ITS POWER • I CAN SAY WHAT I WANT BECAUSE I HAVE FREEDOM OF SPEECH Where did these ideas come from? • Enlightenment philosophes • All of those books they wrote were printed on the printing press and shipped to America • Americans read them, agreed with them, got mad at GB, and revolted. Influence on the American Revolution • Domino Effect: First Americans revolt, then the French will, then Latin America….. Constitution of the U.S. • Read p. 8 • Underline everything you believe in an enlightenment idea. • Next to it, write the philosophers name Activity • You will each have five index cards. • On each, write the name of an enlightenment philosophe on one side and their beliefs on the other • You have 10 minutes to quiz the person next to you, then we will have a pop quiz. Exit Ticket: Quiz! • Which philosophe believed that all people have natural rights of life, liberty, and property? • Which philosophe believed that there should be 3 branches of government? • What did Voltaire advocate? • Why did absolute leaders like Hobbes? • What was the social contract theory created by Rosseau? • What was the first revolution inspired by the enlightenment? • What time period inspired enlightenment philosophes?