Hydropower, Wind, Geothermal, Biomass
advertisement

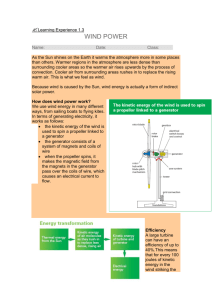
Activities for 5.7C Following are 7 activities for 5.7C. Some of these are basic, others are more difficult. Choose the ones that best fit the needs of your students. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. Renewable vs Nonrenewable—sorting activity. Divide the resource cards into either renewable or nonrenewable. Alternative Energy Sort—sorting activity. Sort the types of renewable resources by matching the description with the picture. Alternative Energy Arrays—(Fig 19). There are four arrays showing pictures and descriptions of alternative energy sources. There are also questions that go with the arrays. Students can work on this in partners, in a station, or as a class. Geothermal and Hydropower Sequencing Cards. Sequence the order of how Hydroelectricity is created. There is also a sort for geothermal energy. Alternative Energy Sorting Chart. Use the chart and sort the cards that represent the different characteristics of the 5 types of alternative renewable energy sources. Renewable and Nonrenewable Energy Questions—answer the multiple choice questions about renewable and nonrenewable resources Mojo Island—alternative energy game. In this game, students play the role of scientists that have been asked to identify the most appropriate energy options for village communities on an island. This game came from Practical Action. Also, don’t forget resources we all have available to us: CINCH science—the lesson on “Alternative Energy Sources”. This lesson has great information and great diagams of the different alternative energy sources and power plants. Quizlet—online flashcards. www.quizlet.com Search for “sets” already made. “Alternative Energy 5.7C” is a set that has 10 questions about the different sources. Students can study, spell, match, or test themselves. They do not need to make an account to use. Kahoot—online quiz game www.getkahoot.com Online quiz game for a whole class. Very similar to the “clicker” system. Teacher creates an account and sets up a game. Students use computers or smart devices to play the game (they don’t make an account, just type in the game code) Search for “Energy Sources: renewable vs nonrewable”. There are also other games on resources you might find and like through the public search. I have all of the master copies(so you can print color versions) of the activities I found and created on my wiki. http://grahamsgalaxy.wikispaces.com/Alternative+Energy+Sources I also have a lot of other resources on my team wiki: sciencewilmeth5.wikispaces.com If you need anything else or have any questions, just ask! Christine Graham cgraham@mckinneyisd.net Array Questions for Alternative Energy Sources • • • • • • • • • • • How does this energy source get transferred into electricity? Why should we use this energy? Where does this energy come from? Is this energy source found everywhere? How do we use this energy source? How is energy converted in the process of making electricity with this energy source? (How does it involve mechanical energy?) Can you describe the tools we use to access this energy source? Is this energy source easy to access? What percent of energy production in the US is made by this energy source? Does this energy create more pollution? Do we need to use this energy source more or less? Why? Hydropower Hydropower depends on rivers and the water cycle. Moving water converts into mechanical energy Swiftly flowing water carries a lot of energy. Water flows through a pipe and turns blades on a turbine that spins a generator that converts this mechanical energy into electrical energy. Hydroelectric power on rivers accounts for 7% of all energy production in US and 20% of electricity production in the world. Hydropower dams can negatively affect the environment by: hindering migration, stopping sediment flow, altering human activities and are very expensive to build. http://www.eia.gov/kids/energy.cfm?page=hydropower_home http://www.romania-insider.com/wp-content/uploads/2011/03/hydro-power-plant.jpg There are only six tidal energy plants in the world. Tidal power is easy to predict, but expensive to harnass. Geothermal Energy is gathered as water is pumped into the rocks below. The hot rocks heat the water. The water is then brought back up to the surface as steam. The hot, moving steam turns a special turbine. This turbine spins a generator. The generator converts this mechanical energy into an electrical charge. The electricity moves through a transformer into wires at the power station. The power station sends it into homes and businesses. http://www.buzzle.com/images/diagrams/geothermal-power-plant.jpg http://www.eia.gov/todayinenergy/detail.cfm?id=3970 Geothermal = geo (Earth) + thermal (heat) Geothermal energy is heat from deep inside the rocky outer layer of Earth http://conserve-energy-future.com/Images/Geothermal_Energy.jpg http://www.technologystudent.com/images5/geo2.gif 26 countries have geothermal power plants. California produces 80% of the geothermal energy for the U.S. Geothermal Energy comes from: hot springs, geysers, and volcanoes. It is usually found near plate boundaries. The area under the surface needs to be 300 to 700 degrees to be hot enough for a power plant. These geothermal plants are expensive to build but inexpensive and environmentally friendly to maintain. WIND POWER What causes wind? Darrieus vertical-axis wind turbine in Martigny, Switzerland http://www.eia.gov/kids/energy.cfm?page=wi nd_home-basics http://www.eia.gov/kids/energy.cfm?page=wind_homebasics http://blog.industrialinterface.com/w pcontent/uploads/2009/11how_wind_t urbine_works-562x334.jpg Wind spins the turbine blades. The blades mechanically turn the shaft and gearbox which spin a generator that creates an electric spark. There are two main kinds of wind turbines. Horizontal axis turbines look like windmills. Vertical-axis turbines look like egg beaters. In 2012, wind turbines generated 2% of all of the electricity production for the US. Small turbines can be used by single families. In some cases, families can sell their extra wind produced electricity back to the city. http://www.eia.gov/kids/energy.cfm?page=wind_home-basics The largest wind farm is in Texas. It has 421 wind turbines and generates enough electricity to power 220,000 homes per year. BIOMASS and BIOGAS Biomass is the energy that comes from plant and animal matter and waste. Biomass contains stored chemical energy from the sun. Plants absorbed this energy in photosynthesis. This energy transfers to animals and people when they are eaten. When the biomass is burned, the stored chemical energy is released as heat. This heat can be used to produce steam to make electricity. It can also be used as methane gas, ethanol, or biodiesel (transportation fuels). The major advantage of burning biomass is that it gets rid of waste material. It is also reliable and available all over the world. In developing countries, people are learning how to use biogas digesters to convert manure into methane gas that can be used to heat their homes and for electricity. http://www.blogmost.com/8-advantages-disadvantages-of-biomass-energy/ Geothermal Energy Sequencing Cut apart the sentences in strips. Put the cards in order of how geothermal energy is used. Use the geothermal reading to help you. Pipes send cold water down into rocks under Earth’s surface. The heat in the rocks heats the water and turns some of it into a high pressure steam. The steam rises in pipes into the power plant on the surface. The pressurized steam moves quickly and spins blades of a turbine. The turbine spins a generator. The generator mechanically converts the energy into an electric charge. The electric charge is sent into a generator and is transferred by electric wires in a circuit. This electricity is sent to homes, businesses, and Geothermal Energy Sequencing • Pipes send cold water down into rocks under Earth’s surface. • The heat in the rocks heats the water and turns some of it into a high pressure steam • The steam rises in pipes into the power plant on the surface. • The pressurized steam moves quickly and spins blades of a turbine. • The turbine spins a generator. • The generator mechanically converts the energy into an electric charge. • The electric charge is sent into a generator and is transferred by electric wires in a circuit. • This electricity is sent to homes, businesses, and other buildings. Hydropower Sequencing Cards Cut apart the statements in strips. Put them in order according to how we use hydropower. Use the Hydropower story to help you. Water moves quickly down a river or through a dam The water moves through pipes in the power plant The moving water turns blades of a turbine The turbine spins a generator The generator converts the moving water into electrical energy This electrical energy moves through power lines from the power plant to consumers who want to use it Hydroelectric Power Sequence • • • • • Water moves quickly down a river or through a dam The water moves through pipes in the power plant The moving water turns blades of a turbine The turbine spins a generator The generator converts the moving water into electrical energy • This electrical energy moves through power lines from the power plant to consumers who want to use it What am I ? • I am a form of energy collected by moving water • Water flows (due to gravity) through pipes • It then turns a turbine and spins a generator • This generator converts the moving water to from mechanical energy to electricity What am I ? • I am a form of energy collected by heat from under the surface of the Earth • Water flows through pipes underground • The heat in the rocks undergrond turns the water into vapor • In Iceland, individual people use this type of energy to heat their homes. • This energy can be found near volcanoes, hot spots, plate boundaries, and geysers.