Stream Table Lab. #1
advertisement

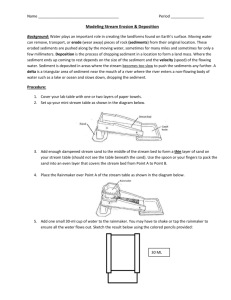
Stream Table Lab. #1 The stream's ability to transport materials depends on its gradient, discharge, and velocity. Typically a stream erodes more near its headwaters where it’s gradient is highest. These factors change as the stream approaches its mouth or base level. Objective: To recognize patterns of erosion and deposition. Materials: stream table, sediment, water, textbooks, colored pencils Procedure * Clean up any spills IMMEDIATELY. 1. Pack the sand into the top third to one half of the tray. Be sure the sand is smooth, gently sloping towards the downstream end of the tray. 2. Place 6-8 pieces of gravel on the sand in random places. 3. Be sure everyone in close proximity has goggles on. 4. Allow each member of your group to have a CLEAN straw. Blow on the top of the stream table for approximately 4 seconds moving across entire width of tray. DO NOT touch the straw to the sand. 5. Carefully observe the changes produced by the “wind”. 6. Draw a before and after sketch below. The sediment BEFORE the “wind” The sediment AFTER the “wind” 7. Repeat the same experiment raising the gradient of the stream table by adding 2 textbooks. GRADIENT ANSWERS WILL VARY 8. Draw a before and after sketch below. The sediment BEFORE the “wind” The sediment AFTER the “wind” 9. Answer the following questions A. How does wind affect erosion? The wind helps erode the land by moving smaller sediment. B. How does gradient affect erosion? The higher the gradient, the greater the amount of erosion. C. Circle the graph below that makes sense after your experimenting. 1. 2. Slope Slope Rate of Erosion Rate of Erosion D. Circle the graph below that makes sense after your experimenting. 1. 2. Sediment Sediment Size Size Rate of Erosion Rate of Erosion Stream Table Lab. #2 Watch how the stream channel changes over time. Note where sediment is being picked up and where they are deposited (dropped) by the stream. Objective: To recognize patterns of erosion and deposition. Materials: stream table, sediment, water, textbooks, colored pencils Procedure * Clean up any spills IMMEDIATELY. 1. Pack the sand into the top third to one half of the tray. Be sure the sand is smooth, gently sloping towards the downstream end of the tray. 2. One group member, pour water onto the stream channel for two minutes. Then stop. 3. In the boxes below, draw what the stream looks like initially and after two minutes. Show the main channel and any smaller channels. 4. Include arrows to show the direction of stream flow. Use different colors to represent where sediment started and where it moved. Use a third color to show areas where the sediment was undisturbed. 5. Create a key for the colors you use. Use this key for all your sketches for this lab. KEY: Started Moved BEFORE the water was poured Undisturbed AFTER the water was poured Books should have affected it more. 6. NOW increase the gradient and repeat. Be sure to note the changes, so you can answer questions that follow. GRADIENT WILL VARY A. Look at your diagrams. Describe what changes happened to your stream over time. These answers will vary B. Where does erosion seem to occur most? Erosion occurs the most on outside of the bend C. Where along the meanders does most deposition occur on the inside or outside of the bend? Inside Where does most erosion occur? on the outside D. Areas of erosion are called cutbanks place a star on a cutbank on your last diagram. Areas of deposition along a meander create point bars (deposits of sandy material) Point to one point bar on your last diagram by drawing an arrow. E. As slope increases the velocity increases F. As slope increases the rate of erosion increases G. As slope increases the amount of deposition increases H. On the picture below. Place "E"'s next to areas that erosion would occur and mark the letter "D" where material would be deposited based on what you saw of slow-moving meandering rivers. E D D E I. In general what size sediment does a stream carry? J. Sediments tend to be (eroded/deposited?) eroded Small on the outside of a meander bend and deposited on the inside of meanders in stream channels. Thinking further…How do we adjust the discharge rate of the stream? You could increase the slope to increase the discharge rate. Decreasing the slope would decrease the discharge rate. Stream Table Lab. #3 Objective: To recognize patterns of erosion and deposition. Materials: stream table, sediment, water, textbooks, colored pencils Procedure : * Clean up any spills IMMEDIATELY 1. Pile the wet sand all up in the center of the flat stream table. 2. Spray the spray bottle at multiple areas of the pile representing rain hitting a mountain. 3. Compare the rate of erosion by using the same set up, this time with toothpicks representing vegetation. 4. Sketch below your findings. Erosion without vegetation Erosion with vegetation Before water/erosion After water/erosion 5. Answer the questions below. A. How does vegetation affect the rate of erosion? The less erosion. more vegetation, the B. Circle the number of the graph below that best shows the results from your experiment 1. Vegetation 2. Vegetation Rate of Erosion Rate of Erosion Determining Discharge Rate These numbers are all rounded to the nearest tenth** 1. The width of the stream at point A is 8m. The depth at this point is 4m and the velocity of a leaf traveling down the stream at this point is 20m/s. What is the discharge rate? 640 cms 2. The width of the stream at point A is 22m. The depth at this point is 18m and the velocity of a leaf traveling down the stream at this point is 16m/s. What is the discharge rate? 6336 cms 3. The width of the stream at point A is 28m. The depth at this point is 10m and the velocity of a leaf traveling down the stream at this point is 12 m/s. What is the discharge rate? 3360 cms 4. The area of the stream at point A Is 45m and the velocity of a leaf traveling down the stream at this point is 14m/s. What is the discharge rate? 630 cms 5. The discharge rate for Alum Creek at Africa Rd. is 170 CFS. The Velocity at Africa Rd. is 25 F/S, what is the area of this section of Alum Creek? 6.8 ft *Remember the formula for gradient is rise/ run. 6. A stream’s final elevation is 2000 m. It takes the stream 300km to reach its final altitude. What is the gradient of the stream? 6.7 m/km 7. A stream’s final elevation is 1000 m. It takes the stream 600km to reach its final altitude. What is the gradient of the stream? 1.7 m/km 8. A stream’s final elevation is 8000 m. It takes the stream 400km to reach its final altitude. What is the gradient of the stream? 20 m/km 9. A stream’s final elevation is 1,200 m. It takes the stream 100km to reach its final altitude. What is the gradient of the stream? 12m/km 10. The gradient of stream #139 is 50.9 ft/mi. The final elevation is 4ft. How many miles must stream #139 run? 12.7 miles Stream Table Lab. #4 Objective: To measure the gradient of a stream Materials: Stream table, textbooks, floats, ruler, beaker to pour water Procedure: * Clean up any messes/ spills IMMEDIATELY 1. Prop the stream table up on 3 books and fill it with 1 beaker full of water and let it drain out until it stops flowing into the sink. 2. Use the ruler to measure the distance a) between the blue tape and the red tape b) the width of the stream table and c )the depth of the water at the red tape. 3. Place the float behind the blue tape. 4. Pour 1 beaker full of water down the stream table near the propped books. 5. Record the velocity of the float from the blue tape to the red tape. 6. Find the discharge rate of the stream table. *Remember Discharge Rate= Velocity X Area A. What is the area of your stream? Depth @.3cm X Width @29 cm = Area 8.7 cm Remember that Velocity is Speed = D/T with direction. Look around the room and note what direction your stream is flowing. B. What is the velocity of your stream? 3.7 cm/s The distance the float moved @11cm divided by the time it took to get there @3 s plus the direction it was traveling East C. Now take the answer from part A and multiply by the answer from part B. My stream discharge rate is 32.2 cubic cm/s. Try it again, D.What is the discharge rate of your second trial? 40 ccs