chapter01
advertisement

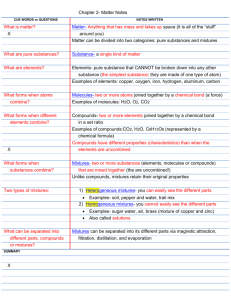
With Dr. Wieser Chemistry can be defined as the study of matter. Matter is anything that has mass and occupies space. So chemistry is the study of pretty much everything. We will focus on the structure of matter and the changes that matter can undergo. A chemical is defined as any substance that has a definite composition. Look around the room-how many chemicals can you observe? There are many different branches of Chemistry. See p4. Also on PP4-5-different types of research are discussed. We can define matter as anything that has mass and occupies space. All matter is composed of atoms. Elements and compounds are made up of atoms. An atom is the smallest unit of an element that has the properties of that element. An element is a pure substance and can not be broken down into simpler substances. A compound is a pure substance that is made of two or more elements that can be broken down into simpler substances. Matter can exist in four states (three are found on Earth) Solid Liquid Gas Plasma (found in the interior of the sun) Note that energy must be supplied to go from one state or phase to another: Solid →liquid→gas Solids-have fixed volume and shape. Liquids-have fixed volume but take on the shape of their container. Gases-have neither fixed volume or shape. In addition to phase changes matter can undergo other physical changes: Physical changes do not produce any new substances: What happens to an ice cube when heat is supplied? What about when sugar is dissolved in water? Chemical changes produce new substances. In a chemical reaction one or more substances, the reactants are converted to one or more new substances, the products. A physical property is one that describes a physical change. When considering phase changes, the melting point of a substance is a physical property. In the case of ice, this temperature is______oC. A chemical property describes the chemical change. Paper undergoes a chemical change when it burns, so the ability to react with oxygen is a chemical property of paper. Compounds and elements are both pure substances. Compounds are a chemical combination of two or more elements. Mixtures are a physical combination of two or more pure substances. Mixtures that are uniform in composition are called homogenous mixtures (sugar in water) Mixtures that are not uniform are heterogeneous mixtures (sand in water) Homework: always due at the beginning of the next class period. P 14 #’s 1-2-4 And p22 #’s 10-12 I mentioned previously that elements are composed of atoms. The periodic table lists all the known chemical elements. The columns are called groups or families – there are 18 of them. The rows are called periods. (see p 17). There are three types of elements shown on the table. Metals Non-metals Metaloids or semi-metals Pages 18-20 give examples. Homework for section 3 Page 20 #’s 1-4 END of Chapter 1 a test will follow. Observation Hypothesis Observation or experiment Theory Observation or experiment Law See page 31 15 Scientists ask questions and make observations. A hypothesis is a possible explanation for an observation. A hypothesis must be testableusually by performing an experiment and analyzing the result. Experiments are conducted under controlled conditions. If the results of an experiment may support the hypothesis- which will lead to more experiments or not support it-then you need to look for a new hypothesis or the result may lead you in a whole new direction. If over a relatively long period of time many experiments support the hypothesis then the hypothesis can become a theory. A theory is the best current explanation for a series of observations. If new information becomes available in the future then the theory may be modified or even replaced. This is all part of the scientific method! In the course of performing experiments, sometimes a cause and effect relationship is observed. This relationship is a scientific law-scientific laws do not explain observations but point out connections between observations. For example later in the year we will study the Gas Laws-one says that when the temperature of a gas goes up so does its volume-the theory that explains this observation is called the Kinetic Theory of gases. One of the key parts of the scientific method is the ability to make measurements. If I told you a measurement was 59.7. What would be your response? The metric system is the one used in science. The units are called SI units-we will see that not all the units we will use are SI units. SI base units are listed on p 34. Some for you to try: a. 1.34 g to kg b. 15.2 cm to m c. 2580. mg to kg Derived units: many measurements use more complicated units derived from the base units. For example volume (l x w x h) requires a cubic unit, if the measurements were in meters the unit would be m3. The non-SI unit we commonly use for volume is the liter which is equivalent to a dm3 or 1000 cm3 (1000 mL) One important physical property of matter is density . Density = mass/volume Every substance has its own unique density. See p 17 for a list. Since the density formula has 3 variables, 3 types of problems are possible. 1. given mass and volume-find density a substance has a mass of 23.2 grams and a volume of 18.5 cm3. Find its density. 2. given density and volume, find mass (g) D = m/V so m=D x V The density of silver is 10.5 g/cm3. Find the mass of a block of silver with a volume of 40.0cm3. 3. Given the density and mass, find the volume of a substance. D= m/V so V= m/D Find the volume of a piece of iron that has a mass of 147grams. (from p 17 density of iron = 7.86 g/cm3) Substances (pure) - matter in which all samples have identical composition and properties. Elements ◦ substances that cannot be decomposed into simpler substances via chemical reactions Elemental symbols ◦ found on periodic chart 27 28 Compounds ◦ substances composed of two or more elements in a definite ratio by mass ◦ can be decomposed into the constituent elements Water is a compound that can be decomposed into simpler substances – hydrogen and oxygen 29 The properties(chemical and physical) of compounds are unique and are totally different from the elements that make up the compound. Sodium chloride for example. NaCl Mixtures ◦ composed of two or more substances ◦ homogeneous mixtures ◦ heterogeneous mixtures 31