File
advertisement

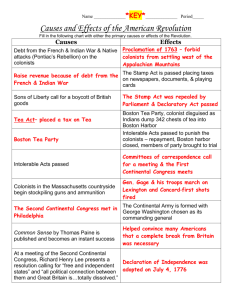
Events Leading to Revolution (1763-1775) Event Yr. /Facts Right violation 1763 1764 1765 1766 1768 1770 1772 1773 1774 1774 1775 Colonists Reaction Events for you to place in order • • • • Proclamation Line Townshend Tax Sugar Act Stamp Act Other words we Vice-Admiralty Cts. • non-importation First Continental Congress agreements • • • • Intolerable Acts Stamp Act Congress Boston Tea Party Gaspee Affair Associations - boycotts Committees of Correspondenc writs of assistance internal tax / direct tax external tax/ indirect tax Did the Colonists Object more to taxes or violations of civil liberties (cause of the forthcoming conflict?) Sugar Act -Lowered tax – 3 pennies to 1 penny, but taxed British sugar as well and was enforced – smugglers tried in Vice-Admiralty Courts -Civil liberty violations (right denied)– -Internal tax (Dulaney’s argument) -No trial by jury – Vice Admiralty Courts Stamp Act - 1765 - Tax on paper products: dice,wills - Civil Liberty violations: - No taxation without representation - Colonial Reactions – Stamp Act Congress Non-importation agreements Violence – tarring and feathering (British response – repeal it, pass Declaratory Act) Townshend Act 1767 • Light, indirect (paid at port) tax on lead, paper, tea - Civil Liberty violations – “No taxation without representation - Colonial reactions – - Sons of Liberty, non-importation agreements - (British response – will repeal all but tea tax) Quartering Act - 1767 • Colonies need to house / feed (quarter British Troops) • Civil liberty violation – right to privacy • British – will disband NY legislature for failure to implement Boston Massacre (1770) • • • • Colonists incite British to fire on civilians British kill 8 Sons of Liberty fan flames Trial – John Adams defends British soldiers (things settle down for 2 years) Gaspee Affair (1772) • Providence townspeople burn British schooner – Gaspee • Bri. Royal Governor Hutchinson – establishes a special commission to investigate • No one found guilty (Hutchinson’s house had been burned in 1767 by a mob) Boston Tea Party (1773) • Colonists dump tea into harbor • British impose Intolerable Acts • Colonists band together – TJ offers a day of fasting, goods are given to Boston, committees of corr., non-importation, • First Continental Congress called Intolerable (Coercive) Acts - 1774 • • • • • Closed Boston Port Disbanded the Mass. Legislature Banned town meetings Martial Law in Boston (curfew, etc) Quebec Act - First Continental Congress • Cause – Intolerable Acts • Elements – Petition for Redress/ »Associations formed/ »Suffolk Resolves »Significance – shows a growing unity amongst the colonies Second Continental Congress • Cause – Lexington and Concord attacks • Elements • - Olive Branch Petition • - Declaration of Causes and Necessity For Taking Up Arms • - Declaration of Independence • Significance – took more than a year to get the divided colonies to respond with unity to Bri. Transgressions. Potential Essay Question • What was the most significant reason for the American Revolution? Analyze any three of the following in your response. • British Taxation policy • British military measures • Legacy of Colonial political and economic practices • Violations of civil liberties Declaration of Independence American Spirit – p. 153 Who was it written to? Why do you think it was written? List the three natural rights. Quote the “Social Contract” within it. State your favorite 2 grievances State any two propaganda devices used • • • • • • • Power Notes – sections of Chap. 6 France Finds a Foothold New France Fans Out Washington Inaugurates War Pitt’s Palms of Victory Restless Colonists War’s Aftermath