Biology 101L
advertisement

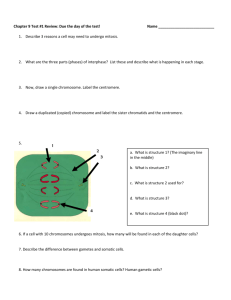
Genetics--Nuclear Division & Inheritance Mitosis & Meiosis Introduction • What is Genetics? • What level of organization is being examined? – molecular, cellular, species, or population • What is the purpose of this lab? Somatic versus Reproductive Cells • Somatic cells: – all except the reproductive cells – 2 copies of each chromosome – diploid – example: in humans, the diploid number is 46 • Reproductive or sex cells: – haploid – 1 copy of each chromosome Nuclear Division • Mitosis – – – – prior to mitosis chromosomes are duplicated nuclear division in somatic cells genetic info from “parent” to daughters cancer: uncontrolled cell division Nuclear Division • Meiosis – prior to meiosis: chromosomes are duplicated – nuclear division in the sex cells – genetic diversity Cytokinesis • • • • division of the cytoplasm occurs at the end of mitosis occurs at the end of meiosis I occurs at the end of meiosis II Interphase Mitosis Interphase • no nuclear or cell division • DNA replication, chromosome duplication, and cell growth • “chromosomes,” not visible inside nucleus • but can see nucleolus inside nucleus Mitosis • Four phases of mitosis: – prophase – metaphase – anaphase – telophase • End result of mitosis: 2 daughter cells Prophase • Duplicated chromosomes condense and become visible as sister chromatids joined at the centromere • nuclear membrane disintegrates; neither the nucleus nor the nucleolus is distinct • spindle apparatus of the cell is formed Prophase • Chromatin condenses into discrete chromosomes Early prophase – two identical “sister chromatids” – joined at the centromere Prophase Metaphase • Chromosomes are aligned along the cell’s equator at their centromeres • spindle fibers are visible Metaphase Chromosomes convene on the metaphase plate, an imaginary “equator” located between the two poles of the spindle. Centromeres are aligned, and sister chromatids of each chromosome straddle the metaphase plate. Metaphase plate Spindle fibers Anaphase • Migration of the chromosomes: – centromeres split – move along the spindle fibers towards opposite poles – pulling the sister chromatid • Each chromatid -- a chromosome Anaphase The sister chromatids separate from each other and move along the spindle fibers towards opposite poles. Each chromatid is now considered a chromosome. Spindle poles Early anaphase Anaphase Anaphase By the end of anaphase, each pole has an equivalent and complete set of chromosomes. Late anaphase Telophase • Chromosomes are aggregated at the poles and begin to thin out and extend in length • new nuclear membrane forms; nucleolus and nucleus begin to reappear • spindle disintegrates • cytoplasm divides (cytokinesis occurs); daughter cells begin to form Telophase • The “daughter” nuclei begin to form at the two poles Telophase • Nuclear membranes begin to form • chromosomes lose their distinct appearance. Cytokinesis begins, separating the cytoplasm into 2 “daughter cells”. Late telophase Telophase • formation of 2 daughter cells • Each daughter cell has same genetic material as parent Daughter Cells Meiosis: Reproductive or Sex Cells • Gametes – female gametes: “eggs” or “ova” (ovum, singular) – male gametes: “sperm” – HAPLOID, have 1 copy of each chromosome (i.e., 1/2 as many chromosomes as somatic cells) – example, in humans, the haploid number is 23. Meiosis in the Lily Anther • Lily anther: – male reproductive organ in flowering plants. – meiosis takes place – result: haploid pollen grains Meiosis in the Lily Anther • A very thin cross-section of a lily anther • stain it • examine with a compound light microscope: Meiosis in the Lily Anther Each anther contains 4 pollen sacs where meiosis takes place. Meiosis in the Lily Anther • Study the various phases of meiosis in prepared slides of the lily anther. • look at the cells inside the pollen sacs • locate the different phases. Stages of Meiosis Meiosis consists of meiosis I and meiosis II and both have 4 stages leading up to the actual cell division. Meiosis I: Meiosis II: Prophase I Prophase II Metaphase I Metaphase II Anaphase I Anaphase II Telophase I Telophase II Meiosis: Prophase I Chromatin condenses into discrete chromosomes. Chromosome is actually composed of 2 sister chromatids. Homologous chromosomes come together as pairs. Meiosis: Metaphase I Metaphase plate • Chromosomes are arranged on the metaphase plate, still in homologous pairs. • Spindle fibers from each pole attach to one chromosome of each pair of the homologue. Spindle fibers Meiosis: Anaphase I • each homologous pair of chromosomes separate and move toward opposite poles. • each chromosome still consists of 2 sister chromatids joined together at the centromere. Meiosis: Telophase I • Chromosomes have moved to opposite poles. • Cytokinesis separates the cytoplasm into 2 daughter cells. • Each cell is now haploid. Haploid Haploid Meiosis: Prophase II In prophase II, the chromatin again condenses so the chromosomes have a distinct shape. Meiosis: Metaphase II In metaphase II, chromosomes align on the metaphase plate. Meiosis: Anaphase II • sister chromatids separate, and move towards opposite poles • sister chromatids are now individual chromosomes. Meiosis: Telophase II • nuclei begin to form at opposite poles, and cytokinesis occurs • 4 daughter cells, each with the haploid number of chromosomes. Haploid Haploid Haploid Haploid Meiosis I: Review Prophase I Anaphase I Metaphase I Telophase I Review: Meiosis II Prophase II Metaphase II Anaphase II Telophase II Chromosomes and Genes • one long strand of DNA • associated proteins – “chromatin” • thousands of genes • gene – discrete unit of heredity • locus – physical location of a gene Homologous Chromosomes, Genes, and Alleles • Chromosome pair: – “homologous chromosomes” • pair has genes at the same loci – “alleles” – may be the same or different Human Genetics • Genotype – heterozygous – homozygous • Phenotype • Observe traits and identify which form you possess • Make a table Heredity and Genetic Disorders • Video, “Healthy, Heredity, and Genetic Disorders” Extra 21st chromosome Mechanics of Mitosis • Answer questions – use instructional materials available • video: Mechanics of Mitosis • posters • Photo Atlas of Biology Mitosis in the Onion Root Tip • Today’s lab exercises – examine the tip of an onion root – find and identify the 4 different phases of mitosis. • Root tips are useful material because the cells are frequently dividing as the root grows. Growth and Mitosis in Onion Root Tips A) Examine onion (Allium) root tip under low power objective (10x) – answer questions B) Examine same slide under high power objective (40x) – follow instructions Meiosis: The basis of Genetic Inheritance and Sexual Reproduction • Mechanics of Meiosis – Answer questions • use instructional materials available – video: Mechanics of Meiosis – posters – Photo Atlas of Biology Meiosis and Gamete Formation in Lily Anthers • Observe first and second meiotic division in demonstration slides Note: •DO NOT move the slides out of position •Use only FINE focus