Unit 9 - Let us entertain you
advertisement

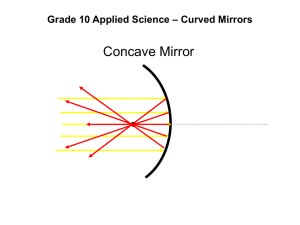
Unit 9: Let Us Entertain You Essential Questions What are the relationships among wavelength, frequency, and speed of a wave? How are vibrations and pitch varied in a string to produce different sounds? How does vibrating air produce sound? How do plane and curved mirrors affect the image that is produced? How can the colour of an object appear to be different by shining different colour light on it? Chapter Challenge You will work with your partner to create a 2-4 minute light and sound show This can be performed “live” or shown as a video Along with it, there will be a written report that explains the physics concepts used in the show and explains why each concept is important The sound must come from instruments or noise makers you make yourself Due date: Monday, June 3 (During exam time) Day 1: Making Waves Learning Objectives: Observe the motion of a pulse Measure the speed of a wave Observe standing waves Investigate the relationship among wave speed, wavelength, and frequency Make a model of wave motion Starter Tsunamis are giant ocean waves caused by an underwater earthquake Waves can reach extremely high heights, for example in Thailand (2004), the waves reached 30m How does water move to make a wave? How does a wave travel? Time: 10 minutes Video: Japan Earthquake Activity 1 Draw a picture of a wave that includes the following terms: Amplitude Wavelength Crest Trough Time: 15 minutes Activity 2 For you to do, pg. 327 Steps #1-10 Write down observations, record data Data table will be provided for you Make a concluding statement about the relationship of frequency, wavelength and speed of a wave Time: 45 minutes Activity 3 Discussion of results and conclusion Draw a picture that shows what happens to the frequency of a wave if you increase or decrease the wavelength Time: 10 minutes Homework For you to read, pg. 331 Physics talk, pg. 333 Physics to go, pg. 337 #1, 7, 10, 11, 12 Day 2: Sounds in Strings Learning Objectives: Observe the effect of string length and tension upon pitch produced Control the variables of tension and length Summarize experimental results Calculate wavelength of a standing wave Organize data in a table Starter When the ancient Greeks made stringed musical instruments, they discovered that cutting the length of the string by half or two-thirds produced other pleasing sounds. How do guitarists or violinists today make different sounds? Time: 10 minutes Video: The Physics of Sound Activity 1 For you to do, pg. 340 in lab groups Steps #1-7 Record the data table and answer the questions/observations to go along with the steps Hand in 1/lab group at the end of the period All equipment is on back table Time: 45 minutes Activity 2 Physics to go, pg. 344 #7 There are wood blocks in the back storage area that have strings on them Work with your lab group to produce different sounds and answer the following: Explain how different sounds are being produced using wavelength, frequency, pitch, and standing waves in your explanation Describe how the instrument works using wavelength, frequency, and standing waves in your description Hand in with the “for you to do” activity Time: 20 minutes Homework Please take your roller coaster models home For you to read, pg. 343 Physics to go, pg. 344 #1, 2, 3 Day 3: Sounds from Vibrating Air Learning Objective: Identify resonance in different kinds of tubes Observe how resonance pitch changes with length of tube Observe the effect of closing one end of the tube Summarize experimental results Relate pitch observations to drawings of standing waves Organize observations to find a pattern Starter The longest organ pipes are about 11m long. A flute, is about 0.5m long and makes musical sound in the same way. How do a flute an organ pipes make sound? Time: 15 minutes Video: Sound in pipes Video: Fresh Prince Season 1, Episode 1 Time: 13:51 Activity 1 For you to do, pg. 347 Steps 1-3 Data table is provided for you Write a concluding statement about straw length and the pitch obtained Time: 20 minutes Activity 2 For you to do, pg. 347, steps 4-5 Write a concluding statement about the amount of water in the test tube and the sound you hear. How can this be changed to use in your sound and light show? (i.e. what materials could you use?) Time: 20 minutes Activity 3 Create an “instrument” that uses at least one of the principles that we have discussed thus far Wavelength Frequency Pitch Create an advertisement that tries to sell your instrument to the rest of the class Time: 30 minutes Homework Physics Talk, pg. 348 For you to read, pg. 349 Physics to go, pg. 351 #1, 2, 3, 4 Day 4: Reflected Light (60 min) Learning Objectives: Identify the normal of a mirror Measure angles of incidence and reflection Observe the relationship between the angle of incidence and the angle of reflection Observe changes in the reflections of letters Identify patterns in multiple reflections Starter Astronauts placed a mirror on the moon in 1969 so that a light beam sent from Earth could be reflected back to Earth. By timing the return of the beam, scientists found the distance between Earth and the Moon. They measured within 30cm. How are you able to see yourself in a mirror? If you want to see more of yourself, what can you do? What type of image is produced? Time: 10 minutes Video: How do Mirrors Work? Activity 1 You and your lab group are to design a short video clip to be posted on Youtube This clip needs to explain to students how plane mirrors work Use your text book and/or internet to help you Think about how to present your video in a fun and meaningful way (i.e. think about what type of video you would want to see) Time: 30 minutes Activity 2 Present your clips to the class Homework For you to read, pg. 357 Physics to go, pg. 359 #1, 2, 4, 5, Day 5: Curved Mirrors Learning Objectives: Identify the focus and focal length of a curved mirror Observe virtual images in a convex mirror Observe real and virtual images in a concave mirror Measure and graph image distance vs. object distance for a convex mirror Summarize observations in a sentence Starter Curved mirrors can be concave or convex Draw a picture of what these two types of mirrors look like Where do you find concave and convex mirrors? How are the images produced different from that of a plane mirror? Time: 15 minutes Video: Curved Mirrors Activity 1 With your lab group, complete the table Time: 15 minutes Type of Mirror Plane Concave Convex Image Upside Down/Rightside Up Real/Virtual Image Size of Image Activity 2 Draw a ray diagram for the following types of mirrors: Plane mirror Concave mirror, image in front of focal point Concave mirror, image behind focal point Convex mirror We will do one together first Time: 20 minutes Plane Mirror Convex Mirror Concave Mirror Activity 3 Use this time to create a concept map for the various topics we have covered so far This will be useful when you are writing the explanation component of your chapter challenge It is a good idea for everyone to have one of their own Time: 15 minutes Homework Physics Talk, pg. 366 Reflecting on the Activity and the Challenge, pg. 377 Complete concept map Physics to Go, pg. 367 #1, 2, 3, 4 Day 6: Refraction of Light Learning Objectives: Day 7: Colour