Expository writing
advertisement

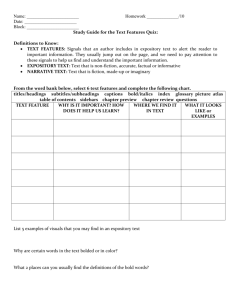
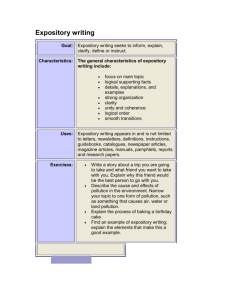
Expository Writing Today’s Agenda: 1. Introduction to Expository Writing Mini-lesson with Guided Notes 2. Newspaper Scavenger Hunt—Identify the Expository Structure 3. Exit Ticket Check for Understanding Expository Writing Unit What is Expository Writing? • Expository writing is nonfiction writing about a topic. • Often called Informative/Explanatory Writing • Expository writing gives facts and information, explains how to do something, or tells readers about real people and events. Expository Writing Unit You can find expository writing in many different places. • Textbooks • Newspapers • Encyclopedias • Magazines • Websites Expository Writing Unit Expository Writing Traits • A clear, focused topic • Relevant facts and concrete details that support and develop the topic • A strong introduction, body, and conclusion • Paragraphs that have a topic sentence and supporting details • Appropriate and varied transitions that connect ideas and show relationships Expository Writing Unit Expository Writing Traits • Appropriate voice for the purpose and audience • An informative, respectful, and consistent tone • Exact, concise language • Domain-specific vocabulary that is used correctly and explained as necessary • Clear sentences with structure that supports the purpose • Sentences that flow together smoothly • No or few errors in grammar, usage, and mechanics Expository Writing Unit How Expository writing is organized depends on its purpose. Here are some common structures: • Cause-and-Effect describes a cause and the result, or effect, of that cause. • Compare-and-Contrast describes the similarities and differences between things. • Explanatory gives the meaning of a topic. • How-To tells readers how something happens or explains a step-by-step process. • Problem-and-Solution describes a problem and offers one or more solutions. • Research Report organizes information about a topic. • Summary describes the main points of a piece of writing. Expository Writing Unit Strong expository writing includes the following features: • Topic • Definitions • Facts • Transitions Let’s look at how we can use these features in strong expository writing. • Precise language • Domain-specific vocabulary • Conclusion Expository Writing Unit Topic A tsunami is a series of giant waves. Tsunamis are created by undersea disturbances, such as earthquakes or giant landslides. As the waves travel away from the point of the undersea disturbance, they grow taller and gain higher speeds. However, tsunami waves do not look like normal waves that curl and crash against the beach. Instead, they look like a moving wall of water. In order to understand tsunamis, it is important to understand how Earth is formed. Tectonic plates, or giant pieces of Earth’s crust, sometimes push against each other. At times this motion can be subtle; other times it can be violent. An earthquake is caused when two plates push and pull against each other and suddenly release a tremendous amount of energy. Expository Writing Unit Definitions A tsunami is a series of giant waves. Tsunamis are created by undersea disturbances, such as earthquakes or giant landslides. As the waves travel away from the point of the undersea disturbance, they grow taller and gain higher speeds. However, tsunami waves do not look like normal waves that curl and crash against the beach. Instead, they look like a moving wall of water. In order to understand tsunamis, it is important to understand how Earth is formed. Tectonic plates, or giant pieces of Earth’s crust, sometimes push against each other. At times this motion can be subtle; other times it can be violent. An earthquake is caused when two plates push and pull against each other and suddenly release a tremendous amount of energy. Expository Writing Unit Facts A tsunami is a series of giant waves. Tsunamis are created by undersea disturbances, such as earthquakes or giant landslides. As the waves travel away from the point of the undersea disturbance, they grow taller and gain higher speeds. However, tsunami waves do not look like normal waves that curl and crash against the beach. Instead, they look like a moving wall of water. In order to understand tsunamis, it is important to understand how Earth is formed. Tectonic plates, or giant pieces of Earth’s crust, sometimes push against each other. At times this motion can be subtle; other times it can be violent. An earthquake is caused when two plates push and pull against each other and suddenly release a tremendous amount of energy. Expository Writing Unit Transitions A tsunami is a series of giant waves. Tsunamis are created by undersea disturbances, such as earthquakes or giant landslides. As the waves travel away from the point of the undersea disturbance, they grow taller and gain higher speeds. However, tsunami waves do not look like normal waves that curl and crash against the beach. Instead, they look like a moving wall of water. In order to understand tsunamis, it is important to understand how Earth is formed. Tectonic plates, or giant pieces of Earth’s crust, sometimes push against each other. At times this motion can be subtle; other times it can be violent. An earthquake is caused when two plates push and pull against each other and suddenly release a tremendous amount of energy. Informative/Explanatory Writing Precise Language A tsunami is a series of giant waves. Tsunamis are created by undersea disturbances, such as earthquakes or giant landslides. As the waves travel away from the point of the undersea disturbance, they grow taller and gain higher speeds. However, tsunami waves do not look like normal waves that curl and crash against the beach. Instead, they look like a moving wall of water. In order to understand tsunamis, it is important to understand how Earth is formed. Tectonic plates, or giant pieces of Earth’s crust, sometimes push against each other. At times this motion can be subtle; other times it can be violent. An earthquake is caused when two plates push and pull against each other and suddenly release a tremendous amount of energy. Informative/Explanatory Writing Domain-Specific Vocabulary A tsunami is a series of giant waves. Tsunamis are created by undersea disturbances, such as earthquakes or giant landslides. As the waves travel away from the point of the undersea disturbance, they grow taller and gain higher speeds. However, tsunami waves do not look like normal waves that curl and crash against the beach. Instead, they look like a moving wall of water. In order to understand tsunamis, it is important to understand how Earth is formed. Tectonic plates, or giant pieces of Earth’s crust, sometimes push against each other. At times this motion can be subtle; other times it can be violent. An earthquake is caused when two plates push and pull against each other and suddenly release a tremendous amount of energy. Informative/Explanatory Writing Conclusion It is impossible to stop a tsunami. However, early warning systems and accurate weather forecasting equipment can warn people of the danger. Special buoys floating in the ocean record waves and send information to scientists on land. These scientists can then warn people to get away from the shore and head to higher ground. Sometimes an early warning can save thousands of lives from the deadly force of a tsunami. Expository Writing Unit Some common types of expository writing include the following: • Research Report • Cause-Effect Report • Problem-Solution Essay • Response to Literature • How-To Essay • Compare-and-Contrast Essay Identify the Expository Structure Directions : Using the Newspaper provided, you and your partners must search and identify the different structures of Expository Writing. Utilize your guided notes for assistance, and fill in your answers on the worksheet. Exit Ticket 1. What is Expository Writing? 2. List at least 3 out of the 7 features included in Expository Writing 3. List at least 3 structures of an Expository Writing piece