Right
advertisement

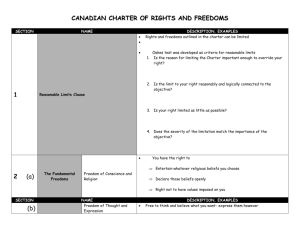
Rights, Freedoms, and Responsibilities Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms • Right: a legal, moral, or social entitlement that citizens can expect, mainly from the government. • Freedom: the right to conduct one’s affairs without governmental interference. • Inalienable rights: guaranteed entitlements that cannot be transferred from one person to another. Do You Know Your Rights? • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MNnKPUyg boA Civil Rights • In Canada, our civil rights are set out in an important part of our constitution called the Charter of Rights and Freedoms. • Civil Rights protect us from unfair treatment by the government. • They are different from Human Rights, which protect us from discrimination by other people. Sources of our Civil Rights and Freedoms • In 1960 the Canadian Government passed the Canadian Bill of Rights. It was later added to the Constitution in 1982 in the Constitution Act. • In order to change the Constitution of Canada two-thirds of the provinces representing 50 percent of the population must vote to make a change. The Supremacy of Parliament • In our system of government, legislative bodies (Parliament and the provincial legislatures) are the supreme lawmakers. So our system is based on the supremacy of Parliament. • The Charter of Rights and Freedoms gives power to the Canadian court system to strike down any law that is seen as violating the rights of Canadians. Therefore the Supreme Court has the final say on laws that affect our rights. The Notwithstanding Clause: Section 33 • Under certain circumstances Parliament or a provincial legislature can pass a statute (law) that violates a right guaranteed by the Charter of Rights and Freedoms. Jurisdiction • The Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms protects you and your rights from discrimination from the Government and it’s agencies and organizations. • The Charter does not protect your rights if discrimination or other injustices (wrongs) occur that do not involve the government. Enforcement • The Supreme Court of Canada – guardian of the Constitution. • The Supreme Court of Canada has 9 justices (judges) that make up the court and are responsible for interpreting and enforcing the Charter. • To determine whether a rights case should be heard in the Supreme Court of Canada, the following questions are considered… 1. Was the right infringed or violated by government or its agencies? 2. Is the right in question covered under the Charter? 3. Is the violation or infringement within a reasonable limit? Limiting Our Civil Rights • There are reasonable limits set on our rights in Canada. It means the court will not strike down legislation that limits our rights. • The criteria for “reasonable limits” are… 1. The reason for limiting the right must be important enough to justify overriding a constitutionally protected right 2. The measure carried out to limit the right must be reasonable and logically 3. The right must be limited as little as possible 4. The more severe the rights limitation, the more important the objective must be Fundamental Freedoms • Freedom of conscience and religion. • Freedom of thought, belief, opinion and expression. • Freedom of peaceful assembly • Freedom of association. Freedom of Conscience and Religion • People in Canada have the freedom to worship or not worship as they choose. • The religious beliefs of the majority cannot be imposed on the minority. Freedom of Thought, Belief, Opinion and Expression • A person in Canada has the right to express their opinion however there are certain limits to which this can occur. • For example a person yelling “fire” in a public movie theatre could cause panic and injury to those around them and therefore could be charged. Freedom of Assembly • In Canada we have the right to assemble and protest things we disagree with under the condition that it remains peaceful. Freedom of Association • In Canada we are allowed to join different groups such as political parties, unions, church groups etc. • These groups however cannot undertake illegal activity. Limitation on Rights • Section 1 • The Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms guarantees the rights and freedoms set out in it subject only to such reasonable limits prescribed by law as can be demonstrably justified in a free and democratic society. • Translation: Your rights are guaranteed but sometimes there are limits placed on our rights for the benefit of society. • Section 15 ▫ Every individual is equal before and under the law and has the right to equal protection and equal benefit of the law without discrimination and, in particular without discrimination based on race, national or ethnic origin, colour, religion, sex, age or mental or physical disability. Democratic Rights • Right to vote • Right to run in an election • Right to elect a new government every five years. Mobility Rights • Right to enter, remain in, or leave Canada. • Right to live and work wherever you wish. Legal Rights • Right to enjoy life, liberty and security. • Right to be protected against unreasonable search, arrest, detention or imprisonment. • Right to be informed if you have been charged with an offence. • Right to be advised and represented by a lawyer if you have been charged. • Right to a fair trial. Equality Rights • Right to live and work and be protected by the law without discrimination based on race, national or ethnic origin, colour, religion, sex, age, or mental or physical ability. Language Rights • Right to communicate with and receive services from, any federal government office in either English or French. • Right to use either English or French in any federal court. • Right to have your children educated in either English or French where numbers warrant.