2.4 The Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms
advertisement

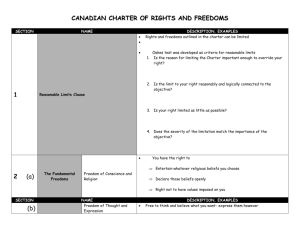
2.4 The Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms Section 1 of the Charter, the reasonable limits clause, allows your rights and freedoms to be limited if there is justifiable reason to do so. Section 2: Fundamental Freedoms Section 2 contains the “fundamental freedoms” Divided into 4 areas: Freedom of Conscience and Religion Freedom of Thought, Belief, Opinion and Expression Freedom of Peaceful Assembly Freedom of Association Freedom of Conscience and Religion People are free to choose to practice (or not practice) religion without fear. This has caused many disputes such as working on holidays, praying publically, and religion in schools Government can impose limits, as long as it doesn’t infringe on the fundamental beliefs of the religion Freedom of Thought, Belief, Opinion, and Expression Deals with communication and expression, such as mass media, writing, painting, sculpture and film. Governments can again limit this if it targets hatred towards groups and individuals. Also limits are not announcing some names of accused and victims Censorship laws, are also used to limit availability of material from citizens (ex: movies and music ratings) This is done to protect vulnerable people who may be harmed and/or influenced Freedom of Peaceful Assembly and Freedom of Association Includes peaceful demonstrations and striking Does not permit unlawful assembly If a riot breaks out police read the Riot Act Section 3, 4 and 5: Democratic Rights Before 1982, the franchise (right to vote) was not guaranteed Voting rights are limited. Restricted by age, residency and citizenship Section 6: Mobility Rights Allows you to move in and out of Canada and throughout the country freely Provinces can restrict mobility into the province to protect the economy (ex: no collecting welfare until they have resided in the province for a certain time; also not looking for work if unemployment is already down in the province) Section 7-14: Legal Rights This will be covered in detail in Unit 2 Section 15 and 28: Equality Rights Section 15 most controversial! Difficult to define “equality” “every individual” has the right to equal treatment by the law Entitled to be treated “in particular, without discrimination based on race, national or ethnic origin, color, religion, sex, age, mental or physical disability” Section 15 (2) allows for affirmative action programs (ex: assist minority groups) Section 15 came into effect 3 years after the Charter, to give more time to define “equality” Section 28 deals with equality of the sexes Section 16-22: Official Languages of Canada States the 2 official languages are French and English They are equal under federal dealings (laws in both languages, debates, offered in federal buildings) Section 23: Minority Language Educational Rights Only dealing with French and English Each province decides whether to offer another language in school Section 25: Aboriginal Rights and Freedoms Charter rights cannot interfere with treaty rights Guarantees the “existing rights” of Aboriginal peoples These rights are not actually laid out because the Canadian politicians and aboriginals could not agree Section 27: Multicultural and Heritage Rights Guides the government to consider ethnic backgrounds when creating and interpreting laws