Lecture 2 - SusanPannell
advertisement
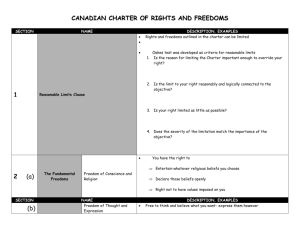
CLU3M - Law Unit 2 Dev. of Rights and Freedoms continued . PP #2 Ms Pannell Source: Gibson, Murphy, Jarman and Grant, . ALL ABOUT THE LAW Exploring the Canadian Legal System. 5th. Toronto: Nelson, 2003. Print. Pp3-6 The Abolition of Slavery 19th Century For over 300 years, approximately 15 million people were captured in Africa and traded as slaves in Europe and North America Even after the revolutions of the 18th century slaves continued to be legally defined as “property” During the 19th century most western countries began to see the injustice in this system and abolished slavery The Abolition of Slavery U.S.A. 19th Century American Civil War (1861-1865) 600 000 people were killed Northern / Union forces wanted to abolish slavery Southern / Confederate forces wanted to keep it 1865, The Northern forces won, and the 13th amendment to the U.S. Constitution abolished slavery forever! The Holocaust (1933-1945) Nazi government targeted specific groups of people Jews, the Roma (gypsies), Gays and lesbians, people with mental disabilities, members of certain religious faiths and political parties Initially stripped of their civil rights Striped of their human rights Imprisoned Executed Totaling nearly 10 million men, women and children killed The United Nations, 1945 Established in the aftermath of WWII and the Holocaust Purpose: “to save succeeding generations from the scourge of war.” 1st step – to try to guarantee all people certain rights and freedom - Human Rights More specific than natural rights Established the UN Human Rights Commission To produce a list of human rights and freedoms fro all people throughout the world Eleanor Roosevelt holding the Universal Declaration of Human Rights Universal Declaration of Human Rights - 1948 1st time nations around the world signed a formal agreement of specific rights and freedoms It is however, only a vision! Palestine Limitations of International Law? China Universal Declaration of Human Rights - 1948 Student Activity Read Page 42-43. Answer for Discussion Questions 3-6 For Discussion 3. Justify the importance of documents like the Universal Declaration of Human Rights to the international community. 4. Which countries do you know of that do not live up to the human rights listed in this document? Give specific examples 5. What action can be taken by the international community to enforce human rights in countries where they are ignored? 6. Explain why the Universal Declaration of Human Rights has been called the “Magna Carta of humanity” Human Rights in Canada after WW2 Much Canadian law is based in British Common Law (unwritten and based on custom and earlier court decisions) Therefore, Canadians had many rights that were not written down but simply understood to exist After the rights abuses of WW2 many Canadians believed these rights needed to be written down Human Rights in Canada after WW2 Canadian Bill of Rights PM Diefenbaker and his government passed the Canadian Bill of Rights – 1960 Set down in legislation the civil rights and freedoms that Canadians had already enjoyed under common law CBC Archives – Clip – Bill of Rights Canadian Bill of Rights continued Criticized: 1. 2. 3. As federal (statute) it applied to only federal matters It was a Parliamentary statute meaning it could be changed by parliament at any time Did little to protect equality rights Student Task: TEXT: Read pg 45, “The Law” Answer questions 1-3 For Discussion Canadian Politics 1960s Pierre Elliott Trudeau Video clip “Just society “Just Society” 1968 “State has no place in the bedrooms of the nation” Promised greater social justice and stronger guarantees of individual rights Prime Minister (15 yrs) April 20, 1968 – June 4,1979 March 3, 1980 – June 30, 1984 Bilingualism – Official Languages Act, 1969 Law reforms: divorce, abortion, homosexuality, and birth control Equality rights for Aboriginal Canadians October Crisis, 1970 Introduction - Revisited What does Canada have that many countries don’t? Civil Rights (and freedoms) - limit the power that a government has over its citizens Human Rights – protect people from being unfairly discriminated against by other individuals Canadians can feel secure in almost all areas of their lives Canadians are free because laws are passed and enforced to protect their rights and freedoms Wealth, gender, race, age, belief, family status … are not supposed to determine how you are treated in Canada – equal under the law “Just Watch Me” clip Contradictions? Explain? Justify? Trudeau – The Constitution Act, 1982 Constitution Act, 1982, including the Canadian Charter of Rights and Freedoms Constitutional Law, not Statute law Changes must be in accordance to the amendment formula Lists civil rights and freedoms for all Canadians at all levels of government Section 24 of the Charter details the “enforcement of guaranteed rights and freedoms” Section 24: “Enforcement of guaranteed rights and freedoms” Anyone whose Charter rights have been infringed (violated), may “apply to a court… to obtain such remedy as the court considers appropriate and just” Any evidence presented to a court must be gathered in a manner that respects Charter rights and freedoms. Otherwise it will be excluded Section 1 : Reasonable limits clause Laws can set limits on your rights and freedoms as long as these “can be demonstrably justified in a free and democratic society Example You have freedom of speech yet you do not have the right to spread lies or make malicious statements that might injure another person Violation of libel laws Section 52 “Constitution of Canada is the supreme law of Canada, and any law that is inconsistent with the provisions of the Constitution is, to the extent of the inconsistency, of no force or effect” Gives Canadian courts much greater power Purpose of the Charter: to limit the power of government By defining the protection of rights and freedoms only in general terms This allows the courts to determine how these ‘protections’ are to be adapted and used Therefore, the Supreme Court of Canada (highest court) plays an important role in interpreting Canadian values and beliefs Supreme Court Judges must balance individual rights with the needs of the community Judges appointed, not elected Section 32: Must determine which matters are ultra vire (outside the authority of the government to legislate) and which matters are intra vire (within the authority…) Charter does protect individual rights from being trespassed upon by the federal, provincial, and territorial governments Which matters are governed by the Charter Is a law in violation of an individuals rights? Charter does not cover private legal matters Would be addressed by human rights legislation How to Analyze a Charter Case: 1. Does the Charter apply? 2. Has a Charter right or freedom been infringed? 3. Does the reasonable limits clause justify the infringement? 4. If not, is there a remedy provided under section 24 Section 33: Notwithstanding Clause Last minute addition – to ease provincial government apprehensions The notwithstanding clause allows Parliament or a provincial legislature to pass a law violating any of these rights (section 2, 7-15) Rarely used Example: Ford v. Quebec (Attorney General) (1988) Supreme Court of Canada ruled that Quebec’s Bill 101 (stating that all signs in Quebec must be in French only) violated the CCRF (Can. Charter of Rights and Freedoms). Quebec government argued that Bill 101 was needed to ensure the survival of the French Language Using the Notwithstanding clause, Quebec passed Bill C-178 allowing Quebec’s Frenchonly signs to stay in effect Legislation that used the Notwithstanding Clause can stay in effect for up to 5 years after which it must be reinacted Notwithstanding clause cannot overrule: Right to vote Minority language education rights Mobility rights Homework Read pages 50-56 Complete the graphic organizer – “Getting to know the Charter” Answer questions 1-7 page 56 Complete Charter Scavenger Hunt