GOODS AND SERVICE TAX IN INDIA
All rights reserved | Preliminary & Tentative
OVERVIEW | IMPLEMENTATION CHALLENGES
Rajeev Dimri | Partner
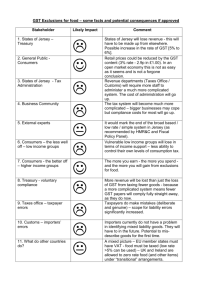
GST – Why so much noise…
• Most significant indirect tax reform in Indian history
• Stakeholders - Government, business community as well as
common man
• Tax administration system will undergo significant functional
change
• Will make indirect tax environment more simple, stable and
predictable (hopefully!)
3 |
GST: IMPLEMENTATION CHALLENGES
All rights reserved | Preliminary & Tentative
• Will impact each commercial / business activity
Taxes to be subsumed under GST
Central Levies
State Levies
Excise Duties including the
additional excise duties
VAT/ Sales tax
Cesses in the nature of
excise duty /customs duty
CST to be abolished
Entertainment tax (unless
levied by the local bodies)
Subsumation
of taxes
Taxes on lottery, betting and
gambling
Service tax
Cesses and surcharges
levied by Union ie education
cess etc
Luxury tax
Purchase tax to
be subsumed
Cesses and surcharges
levied by States, related to
supply of goods and services
• Municipal levies - likely to be out
Central GST
3 |
GST: IMPLEMENTATION CHALLENGES
• Stamp duty - likely to be out
State GST
All rights reserved | Preliminary & Tentative
Additional duties of customs
(ie CVD and ACD)
Entry tax not in lieu of octroi
Overview of the new landscape
KEY GST CONCEPTS
Taxable event to
be ‘supply’
Place of supply
Exemptions
Destination based tax
Valuation
Rules for services?
States to levy tax
on services
Multiplicity of
taxes
GST to subsume most current
indirect taxes
Credit
To be replaced by CGST and
SGST, IGST and additional
tax on inter-state supply
Possible expansion of
credit base
Credit pool to be
maintained for each state
6 |
Likely to be
consistent for all
goods and
services – MRP
valuation may go
GST: IMPLEMENTATION CHALLENGES
Classification
Likely to either be
withdrawn or be
converted into refund
mechanism
Rates
Tax rates to change
for inputs and outputs
Initially 1% additional
tax on inter-state sales
All rights reserved | Preliminary & Tentative
Taxable event
All rights reserved | Preliminary & Tentative
GST – KEY IMPLEMENATION
CHALLENGES
Paradigm shift
Determining
consumption
state
Determining
origin state (to
levy additional
tax)
Taxability of
inter-unit
transfers
6 |
GST: IMPLEMENTATION CHALLENGES
Supply based
taxation
Taxation of
imports
All rights reserved | Preliminary & Tentative
Taxing
jurisdiction in
case of chain
transactions
Job-work /
tolling
arrangements
Crafting a workable design
Need for a pragmatic and business friendly approach
Place of supply rules – special focus needed for service sector
GST rates – difference in SGST rates likely to pose immense challenge (refer
next slide)
Defining valuation principles – need to ensure non repeating FIAT like experience
Defining flexibility norms for states regarding tax rates, exemptions,
compliances etc
7 |
GST: IMPLEMENTATION CHALLENGES
All rights reserved | Preliminary & Tentative
Determining taxable threshold – 10 lac v 25 lac (significant impact on tax paying
base!)
Crafting a workable design
Need for a pragmatic and business friendly approach
Characterization of borderline transactions (eg works contracts, intangibles,
lease, software)
Synchronization with foreign trade benefits
Need for simplified taxation structures for very small & large tax payers
Taxation of key strategic / evolving sectors – eg real estate, ecommerce,
telecom
8 |
GST: IMPLEMENTATION CHALLENGES
All rights reserved | Preliminary & Tentative
Special regimes – SEZ, EOU’s, Area based exemptions
Difference in SGST rates – likely challenges
Jurisdiction
disputes
Distortion of
trade
SGST rate
Tax driven
supply chain
planning to
continue
Multitude of
audits,
investigation
s
May impact
port of
import
decisions
9 |
GST: IMPLEMENTATION CHALLENGES
All rights reserved | Preliminary & Tentative
Customer
state wise
SGST rates
for billing
purposes
Transitional challenges
Phased transition
• Some products / sectors (petroleum, liquor) may be kept outside to begin with
Fate of investment linked incentives
Transition of opening credits
• Tax credits pertaining to the present indirect tax regime will require seamless
transition
Additional tax
• Credit eligibility
• Applicability on imports
10 | GST: IMPLEMENTATION CHALLENGES
All rights reserved | Preliminary & Tentative
• Whether the investment linked indirect tax benefits presently extended by several
states would be continued under the proposed GST regime?
Admin and infrastructural preparedness
• Training
needs
• Defining
procedures
and
processes
11 | GST: IMPLEMENTATION CHALLENGES
Systems
• Alignment
with the new
levy
• Proper
upkeep and
maintenance
Network
• Real time
coordination
between
various
stakeholders
All rights reserved | Preliminary & Tentative
Personnel
Likely challenges to enforcement agencies
Managing risk
of GST fraud
Role of
customs
authorities
Key
challenges
Taxation of
services by
States
Robust GSTN
and online
compliances
Coordination
between state
& central
departments
12 |
GST: IMPLEMENTATION CHALLENGES
All rights reserved | Preliminary & Tentative
Training
needs
Likely challenges for tax payers
A new tax law – a whole lot of tax controversies
Transaction restructuring
Procurement pattern and
trading models to be analysed
– No significant difference
between local and interstate
under GST?
Billing patterns, local vis-à-vis
inter state to be reviewed
Costing / Pricing of goods
Transition of credits
New registrations
Overall pricing of goods –
factoring of GST credits
Change in contract clauses
Change in rate of taxes
Review of procurement
costs
Taxability of transactions
spread across regimes
Treatment of tax paid
inventory
Records/ Accounting
State-wise sales records
Credit availment and utilization
records
13 | GST: IMPLEMENTATION CHALLENGES
Re-designing of the entire
ERP
Current ERP is aligned as
per the current taxes
Compliance
Tax computations
New formats for invoices /
records/ returns/
declarations
Validity of statutory form
(Form F/Form C)
Change in accounting
Manner of payment of
taxes
Re-defining the logics
New compliance dates
Updating masters
Documentation for
movement of goods
All rights reserved | Preliminary & Tentative
Transaction structuring to be
reviewed
Transition
BMR’s take
With current level of preparedness April’16 timeline looks a
daunting task
A well planned and coordinated approach between policy makers,
enforcement agencies and industry critical to achieve the timeline
Urgent need to roll out high-level design of the new law for
deliberations by stakeholders
GST the need of the hour to combat the globally so perceived ‘tax
terrorism’ in India!
13 | GST: IMPLEMENTATION CHALLENGES
All rights reserved | Preliminary & Tentative
However, with increasing global focus on India as investment base
market, no room for postponing this critical indirect tax reform
Disclaimer
Purpose of this presentation is to give a highlights of the proposed GST regime in India and not
render any definitive opinion on any of the activities of stakeholders under the GST regime
Prior professional advise is advised before implementation of aspects covered under this
presentation
Some of the features highlighted including the IGST model for interstate supplies are understood
to be under reconsideration
It is likely that the final model would differ from our understanding and the implications
discussed herein would accordingly vary and the contents of this presentation would
need to be updated basis the revised GST frame-work in the offing
BMR is under no obligation to update this presentation for future changes
15 | OVERVIEW & IMPLEMENTATION OF GST
All rights reserved | Preliminary & Tentative
Our comments in the preceding slides are based on the GST framework outlined in the First
Discussion Paper on GST (2009) and the Constitution Amendment Bill, 2014