Russia 7 - lucyrussianrev
advertisement

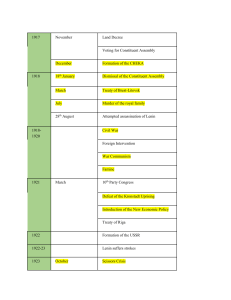
Power-point 9: 1917: Area of Study 2 – Creating a new society Chapter 12: Consolidating st Power – 1 six months Lenin’s Urgent things-to-do list! 1. Form a new government 2 Dismiss the democratic Constituent Assembly 3. Follow through on promises of ‘Land, Peace & Bread 4. Transform society into communism 1.1 Victory in Moscow - With their takeover of Petrograd, Lenin needed to extend his control to the rest of Russia, starting with Moscow - Moscow was a lot harder to take, with 7000 casualties after a week-long battle 1.2 Gain legitimacy from the Congress of Soviets - - - Unlike the Provisional Government, the Soviets were seen to be legitimate as they had been voted by the people. Therefore Lenin wanted the legitimate Soviets to approve his new regime so it wouldn’t be seen as mere Bolshevik coup. He marketed the Oct rev. as a rising by the entire Petrograd Soviet, in which many parties were represented 1.3 One party rule & new titles - - Govt now called ‘Govt of People’s Commissars’ with ministers called Commissars Cabinet filled with Bolsheviks only & called Sovnarkom. This angers other rev. Parties Politburo = policy making arm of Bolsheviks Orgburo = organising arm Secretariat = bureaucrats to implement laws 1.4 Cheka: New political secret police - - - Stands for ‘All Russian Extraordinary Commission to Fight Counter-Revolution, Sabotage and Speculation’ Any enemies of the Bolsheviks, counterrevolutionary agitators, spies etc were rounded up and executed. Headed by Felix Dzerzhinsky 2. Dismiss Democracy Lenin allowed the democratic elections for the Constituent Assembly to go ahead for fear of not looking democratic Results gave the peasant supported SRs 42% of the vote, with worker supported Bolsheviks 23.6% of the vote The Assembly meet once on 18 January 1918 & closed by Bolshevik troops when Bolshevik power was diluted by the other parties Why did the assembly fail? 1. 2. 3. 4. Lack of parliamentary tradition and a mouthpiece of the Bolsheviks Lenin was scared of being undermined Lenin saw the assembly as unnecessary The Bolsheviks weren’t able to make the transition from revolutionaries to politicians 3.1 The Promise of Land - Organised peasants simply seized the land they wanted Bolsheviks simply legitimised this, issuing a decree from the All Russian Congress of Soviets stating private ownership of land was banned, now owned and worked on equally by the people 3.2 The Promise of Bread - - Same problem, different government! The food crisis remained, compounded by the poor harvest of 1917 and the economic impact of the Civil War 3.3 Peace: the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk - WW1 had already toppled the Tsar & Prov. Govt. Lenin didn’t want a repeat! Humiliating and severe demands caused rifts in the Bolshevik Central Committee Lenin had to demand that the committee accept the treaty or he would quit Was signed on 3 March 1918. Germany lost the war in November, making the treaty void Losses in Treaty of Brest-Litovsk 1. 2. 3. 4. Germans wanted 1third of European Russia that included 45 million people & 1 million square km’s 3 Billion in gold Control of Ukraine’s grain farms Demobilise the armed forces 4. Transform Society Private ownership to large houses banned Marriage & divorce equality Universal Suffrage for men & women Education became the right of the state Banks and gold nationalised Julian calendar adopted on 31 Jan 1918 Free religious choice, church separated from the state and education Activities Analysis Activity 1 pg. 125 Focus Questions 1-4 pg. 129 Analysis Activity 4 pg. 130 Do an essay plan for 1 of the 2 essay questions on page 131. Then write a full paragraph or two of your essay. Remember your last SAC is an essay. Remember TEEL