food
advertisement

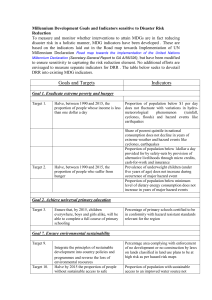
Africa - an investigation into issues of population and food supply Dr Kenny Lynch food security is … “when all people, at all times, have access to sufficient, safe and nutritious food to meet their dietary needs and food preferences for an active and healthy life” food security is … “when all people, at all times, have access to sufficient, safe and nutritious food to meet their dietary needs and food preferences for an active and healthy life” World Food Summit Target: To halve the number of undernourished people by no later than 2015 That means reducing the number of undernourished to 412 million Millennium Development Goal No. 1 Target 1. Between 1990 and 2015 halve the proportion of people whose income is less than $1 a day Target 2. Between 1990 and 2015, halve the proportion of people who suffer from hunger Comparison MDG T2/WFST WFST (1996) • Halve the number of undernourished • by 2015 • = 412 million MDG T2 (2000) • Halve the proportion • by 2015 • = 585 million Activity 2 • What proportion of the world’s population is undernourished now? • What proportion of Africa’s population is undernourished? • All stand … Source: SOFI, 2006 Changes in measures of malnourished in LEDCs Period Change (millions) Change (%) 1970s - 37 9% 1980s - 100 8% Early 90s - 26 Late 90s +23 } 3% Source: SOFI, 2006 Source: SOFI, 2006 http://www.unmillenniumproject.org/ “The region is off track to meet every Millennium Development Goal … Without sustained support, SubSaharan Africa is unlikely to meet any of the Goals. ” Millennium Project Final Report (2005) Earthrise, Apollo 8 photo 22nd December 1968 Source: NASA Malthus on Food & Population 100 deficit 80 60 Food Population 40 20 0 surplus Thomas Robert Malthus (1798) An Essay on the Principle of Population Or a View of Its Past and Present Effects on Human Happiness; with an Inquiry Into Our Prospects Respecting the Future Removal or Mitigation of the Evils which It Occasions • Population increases geometrically • Food production increases arithmetically • Leads to food deficit • Balance is restored by population ‘checks’ such as disease, conflict Esther Boserup (1965) The condition of Agricultural Growth; The Economics of Agrarian Change under Population Pressure • Population increases lead to population pressure • Which leads to … • Increases in productivity through intensification and innovation • Increased population could mean increased labour leading to increased productivity Food insecurity is … • temporary, localised food shortages • protracted and large-scale famine. • Chronic, widespread poverty means millions of people are permanently vulnerable to famine Food Production Headline Trends • Food production has more than doubled since 1960 • Food production per capita has grown • Food prices have fallen Source: Millennium Ecosystem Assessment Subsistence Cultivation > 50% of world population engaged in subsistence agriculture mainly remote areas Self-sufficiency Production for exchange is minimal Extensive - Pastoralism, shifting cultivation Intensive - small scale sedentary agriculture exclusively subsistence nature breaking down Subsistence Cultivation Peasant Production Small-scale Labour-intensive Production for exchange Mostly family labour Wealth flows: child-to-parent Source: FAO, 1996 Case Study 1 • Musa, Tanzanian farmer • Recently gave up cotton farming to grow tomatoes • Delighted with the performance of some new seeds he bought for last season • Optimistic about his future as a tomato farmer • But: we discovered during the discussion that his seeds were ‘suicide seeds’ … Case Study 2 • Lamin, Gambian farmer • Peasant producer in village near River Gambia • Keen to develop his horticultural production business • Concerned that villagers moving away because of the attractions of employment in tourism on the coast • Leading to rural labour shortages: ‘If we had more people in the countryside, we could produce more food.’ Case Study 3 • Mustapha, farmer in Kano, Nigeria • He grows small quantities of maize, tomatoes and peppers for the market • The price he receives varies according to the economy • The strength of the economy depends largely on the global oil price and the performance of the Nigerian economy Conclusions • Nether MDG Target 2 (on food) nor WFS Target on track (esp. not in Africa) • Malthus-Boserup debate continues • Complexity of systems • Africa has potential – access to markets, irrigation, labour, inputs, credit, infrastructure • Key to this is market (domestic and global) • 2008 special year, but highlights problems and solutions But … • Poorest are vulnerable to globalisation • Consumer behaviour in West affects farmers in LEDCs • Impact of current economic crisis “credit crunch” and energy prices To learn more … www.foodfirst.org www.fao.org www.ifpri.org www.millenniumecosystem.org www.dfid.gov.uk/mdg/ IFPRI Report 2008 • biofuel production accounts for about 30% of grain price increases 2000-7 • Existence of food stocks would help reduce volatility “People living on less than US$2 a day have cut out health and education and sold or eaten their livestock. Those living on less than US$1 a day have cut out protein and vegetables from their diet. Those living on less than US$0.50 a day have cut out whole meals, and sometimes go days without meals. Josette Sheeran, WFP Policy Responses • • • • • • Seeds Fertilise Financial Services Infrastructure Subsidies Markets Food price trends 2008 • Appear to have peaked • But still much higher than previous years • High cost of oil leads to increased transport, inputs and so food will remain higher • Predicted increases in food production • Solution in Africa is increased domestic food production