Heroin
advertisement

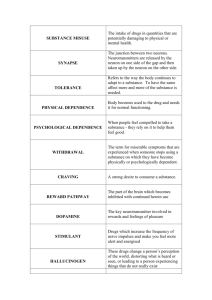
Heroin What’s the Real Dope? Overview • • • • • • • What is heroin and where does it come from? What are heroin’s effects? Who uses heroin? What are signs of heroin use? What are the treatment options? What can be done to prevent heroin use? Where can we get more information? What is heroin and where does it come from? What is heroin? • • • • A highly addictive opiate Processed from morphine An illegal drug Has no medical use Where does heroin come from? Heroin Smack Horse Skag Big H Brown Sugar Mud Junk Black Tar Dope Although heroin has been around for many years, it has found new popularity. What are heroins effects? Immediate effects • Rapid physical changes • Feeling of euphoria (being “fixed”) • Slow, drowsy, “in the nod” state Heroin’s downside • Impairs coordination and self-control • Causes physical abnormalities • Can cause overdose – Convulsions – Coma – Death Heroin can be deadly • Varying potency increases the chance of an overdose • Using heroin with cocaine or alcohol is especially dangerous Long-term effects • Addiction • Poor hygiene • Loss of life-focus Long-term effects • Blood-borne diseases such as AIDS and hepatitis B and C • Collapsed veins • Severe skin infections • Infection of the heart lining and valves Withdrawal • • • • Starts in 6 to 12 hours Peaks in 48 to 72 hours Lasts about a week Has many symptoms Effects on newborns • • • • • Spontaneous abortions Low birth-weight Sudden infant death syndrome HIV/AIDS Heroin withdrawal Who uses heroin? Who uses heroin? • About 1.4 percent of people 12 and older have used heroin. (1999 National Household Survey on Drug Abuse) • The average age of new users is dropping. (1999 National Household Survey on Drug Abuse) Anyone can become a heroin user College students Lawyers Blue-collar workers Celebrities Office managers High school students Nurses White-collar professionals Heroin is used by both genders and by people of all economic classes, ethnicities, and cultures. What are signs of heroin use? Clues that someone is using What are the treatment options? Available treatments • • • • Detoxification Therapeutic community Outpatient drug-free programs Drug therapies – – – – – Methadone maintenance LAAM Rezia Naloxone Naltrexone What can be done to prevent heroin use? Caregivers can help prevent heroin use • Establish and maintain good communication with youth • Be involved in young people’s lives • Be a positive role model • Make clear rules and enforce them • Teach youth to choose friends wisely • Monitor youth activities Adults should be role models Prevention requires community involvement A community working together includes: • Parents, youth, and families • Faith communities • Media • Schools • Professional and civic groups • Health and social services • Courts/law enforcement • Businesses • Treatment agencies and health organizations Establish a no-use community norm Where can we get more information? Resources • SAMHSA’s National Clearinghouse for Alcohol and Drug Information at 1-800-729-6686; www.SAMHSA.gov. Click on the “Drug Facts” icon • Informational Web sites – – – – www.preventiondss.org www.whitehousedrugpolicy.gov www.nida.nih.gov www.cadca.org Heroin: What’s the Real Dope? To view slide presentation, 30-minute video, and 90-minute teleconference go to: www.SAMHSA.gov Click on the Drug Facts icon To order the VHS video, call: 1-800-729-6686 Heroin: What’s the Real Dope? Teleconference produced by Office of National Drug Control Policy Substance Abuse and Mental Health Services Administration’s Center for Substance Abuse Prevention Community Anti-Drug Coalitions of America National Guard Bureau’s Counterdrug Office National Institutes of Health’s National Institute on Drug Abuse as part of the teleconference series Myths, Facts, and Illicit Drugs: What You Should Know Heroin Losing Everything 40 Min