Chlorine Dioxide and Chlorine» Compound Disinfectant produced
advertisement

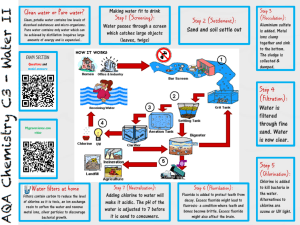
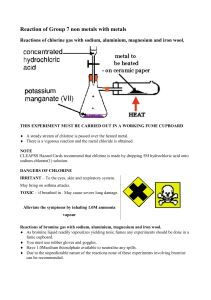
JSC “The Urals Research chemical Institute with an Experimental plant” (JSC “UNICHIM & EP”) Field experience by water treatment facilities of “Chlorine Dioxide & Chlorine” Compound Disinfectant, replacing the traditional chlorine treatment . Infections associated with the factor of water account for 80% of all infectious diseases in the world. Inadequate water treatment causes two billion cases of diarrhea each year, resulting in 4 million deaths. 1.2 billion people in developing countries don’t have access to clean drinking water. Of all the disinfectants Chlorine was and continues, at least for now, being the most common one. Principal hazards associated with transporting, storing and handling the liquefied (“liquid”) chlorine are of the following types: Environmental Production induced Primary alternatives to chlorine Hypochlorites of sodium and calcium Ozone UV irradiation Chlorine Dioxide «Chlorine Dioxide & Chlorine» CD* * «Chlorine Dioxide and Chlorine» Compound Disinfectant produced by the DCh-100 series plants INTERNATIONAL AND DOMESTIC PRACTICE IN USING CHLORINE DIOXIDE FOR DRINKING WATER DISINFECTION Advantages of chlorine dioxide over chlorine or hypochlorites • • • • • • • • 5 to 10 times reduced concentration of chlorine dioxide to achieve the same grade of water disinfection as with chlorine; no toxic trihalomethanes, chlorophenols or other non-removable organic halogens formed in water; strong disinfecting effect along a wide range of water pH ; strong action against spores, viruses, and algae; eliminates odors, improves the water’s taste and removes any color; improves flocculation of suspended impurities during water purification; better iron and manganese removal from water; extended (7-10 days) bactericidal effect preventing the possibility of secondary pollution of water in distributing pipelines. Attractiveness of chlorine dioxide is rooted in the optimal correlation of its biocidal effectiveness, stability and aftereffect, these being the fundamental criteria for assessment of chemical disinfectants. These properties’ combination allows to consider chlorine dioxide to be the same as ozone, just without its drawbacks. Thanks to the prolonged bactericidal action of chlorine dioxide it is currently used at the last stage in the water treatment process at major water distribution facilities (in Dusseldorf, Zurich, Brussels and Paris). It can be concluded that chlorine dioxide is a valid alternative to chlorine and hypochlorite for bactericidal purposes. Use of Chlorine Dioxide in water conditioning • Chlorine dioxide introduced at the pre-oxidation step enhances the coagulation process, reduces the concentration of organic and inorganic deoxidizers, improves the water’s taste and smell, inactivates any bacteria or viruses • At the post-disinfection stage the chlorine dioxide provides for the water in long distributing pipelines to stay in compliance with the sanitary standards, serves to remove any biofilms or microbial fouling and, subsequently, to prevent their reappearance. Chlorine Dioxide cleans and disinfects equipment Field tests in disinfection of water treatment equipment, such as filters and pipelines, demonstrated efficacy of chlorine dioxide solutions at concentrations of 2-10 mg / l. Disinfections of this type have a lasting bacteriostatic effect. Comparison of effectiveness of oxidizing agents in aftertaste and odor removal, mg/dm3 Chlorine 5-10 Chlorine Dioxide 0,25-0,75 Potassium Permanganate 1-10 Ozone 2-4 Chlorine dioxide can be successfully used to treat water containing: - green algae, diatoms, and cyanobacteria - their metabolites Use of ClO2 for water treatment • • • • USA 1944 - Niagara Falls, NY; 1970s - the period of the widespread introduction of ClO2; 1983 - a new US regulation on drinking water, among other things, defined a limit for chloroform in treated water – 0.1 dm3; • Introduction of ClO2 at wastewater treatment facilities in Chesapeake (Virginia) allowed to reduce the dosage of disinfectant from 0.6 dm3 to 0.02 dm3. • 1977 - 103 facilities; • 1986 - 400 facilities and growing. • Canada, Germany, France, Japan, Italy, Belgium, Switzerland Standards for residual chlorine dioxide and chlorite ions in Germany, USA, Italy, Belarus and Ukraine № Country ClO2 ClO2- 1 World Health Organization Not regulated 0,2 2 Russian Federation Not regulated 0,2 3 Germany 0,05-0,2 0,2 4 USA (US EPA) 0,8 1,0 5 Italy Not regulated Not regulated 6 Belarus 0,2 0,2 7 Ukraine 0,4 0,2 Recommended residual chlorine dioxide content in produced drinking water amounts to 0,05 – 0,30 mg/l (using “Chlorine Dioxide & Chlorine” Compound Disinfectant) When implementing the “Chlorine Dioxide & Chlorine” Compound Disinfectant technology for disinfection and purification, it is necessary to undertake a study on the specific water treatment facilities, the way it is done all over the world and as promoted by all international water-related programs and organizations. JSC «UNICHIM & EP» engineered, manufactures and implements DCh-100 local automated plants for production of “Chlorine Dioxide & Chlorine” Compound Disinfectant for water treatment systems. The “Chlorine Dioxide & Chlorine” Compound Disinfectant is a highly effective and efficient alternative to treating water with liquid chlorine or hypochlorites. The two disinfectants’ simultaneous introduction into the water ensures that the chlorine dioxide maintains its useful properties - potent disinfecting action and reduced levels of organochlorines – as well as eliminates its principal disadvantage – formation of chlorite ions as byproducts – in the comparable range of delivered doses. The project has received over fifteen awards at various scientific events, such as the golden figure of St. George – the highest award of the "XXI Century's High-Tech" 10th Anniversary International Forum. Four years of commercial operation have proven the technology’s competitive advantage, in addition to the water quality improvement, entails a significant reduction in operating costs compared to any other disinfection method. Principal advantages of Chlorine Dioxide & Chlorine Compound Disinfectant Compared to chlorine and sodium hypochlorite: • chlorine dioxide’s concentration required to achieve the same antiseptic effect is 6 to 20 times lower than in case of using chlorine or sodium hypochlorite; • practically no toxic organochlorines get formed in the water; • strong disinfecting effect along a wide range of water pH ; • strong effect on spores, viruses, and algae; • elimination of odors, improvement of taste and color of water; • improved flocculation and coagulation of impurities during water purification; • better iron and manganese removal from water; • extended (7-10 days) bactericidal effect preventing the possibility of secondary pollution of water in distributing pipelines; • does not require organizing any sanitary protection zones (as opposed to the case of liquid chlorine) Compared to pure chlorine dioxide (without chlorine): • with comparable doses of chlorine dioxide no violation of limits on content of chlorite ions in treated water takes place; • significantly lower capital and operating costs (no additional treatment to remove chlorites required, raw materials readily available). The reaction that takes place in the plant’s reactor is as follows: NaClO3 + NaCl + H2SO4 = ClO2↑ + 0,5Cl2↑+ Na2SO4 + H2O DCh-100 series Plants These serve to produce a water solution of the chlorine dioxide and chlorine compound (Mass ratio ClO2 : Cl2 = 1 : 0,65) The plants of the series produce from 20 to 2000 grams of chlorine dioxide per hour, which corresponds to 50 -14000 m3 per hour of treated water (depending on the quality of source water and the water preparation procedures) Fully automated Consume no more than 100 W Dimensions: 1000 х 1000 х 320 mm Reduction of chlorine dioxide from chlorites Most chlorites get eliminated due to their interaction with chlorine which comes as a component of the disinfectant compound, here are the corresponding reactions: 2ClO2- + HOCl → 2ClO2 + Cl- + OHClO2- + Cl2 → ClO2 + 2Cl- All necessary approvals for Russia and the Customs Union's member countries authorizing the “Chlorine Dioxide and Chlorine” Compound Disinfectant and the DCh-100 series plant for its production have been obtained. Patents have been taken out in Ukraine and Kazakhstan for the DCh-100 plant. The project has received positive reviews from leading water treatment organizations of Russia. Here are a few extracts from such opinions: 1. "... Given the positive comprehensive laboratory and industrial tests, it is appropriate to consider the "chlorine dioxide and chlorine" compound disinfectant produced through chlorate process on DCh-100 plants as an alternative to the use of liquid chlorine or sodium hypochlorite in the centralized water supply systems, and to recommend continuing work on developing engineering and operational procedures. 2. “Conclusion. Positive results of tests of the DCh-100 plant and its corresponding technology of drinking water disinfection using the “Chlorine dioxide and chlorine" compound disinfectant allow to endorse the technology developed by the “UNICHIM & EP" comprising production of a compound disinfectant and its application for drinking water disinfection. We believe it is possible to recommend the technology for implementation in any relevant government programs. 3. " As a result of the reviewing and analyzing the submitted materials it can be concluded that the “Chlorine dioxide & chlorine" compound disinfectant produced under the process developed by the “UNICHIM & EP" on plants of the DCh-100 series has a high bactericidal, virucidal and antiparasitic effect. The oxidizing processes activated during water treatment improve the water’s color, decrease concentrations of iron, manganese, and other compounds. The Compound Disinfectant has a strong prolonged action to ensure the drinking water is protected against any secondary pollution during its transportation through the distribution network. The completed studies allow us to recommend the developed process of water disinfection and its corresponding equipment for practical implementation in the water supply industry. Reviews based on results of operating the DCh-100 type plants JSC “The Urals Research chemical Institute with an Experimental plant” (JSC “UNICHIM & EP”) Thank you for your attention! Manufacturer Company: JSC “The Urals Research chemical Institute with an Experimental plant” (JSC “UNICHIM & EP”) 5, The 8th of March Street, Yekaterinburg, 620014, Russia Phone: (343) 371-06-51, 323-30-01. Fax: (343) 371-31-01. marketing@unichim.ru, info@unichim.ru Yuri Y. Lasychenkov, General Director (CEO)