Cold Related Emergencies
advertisement
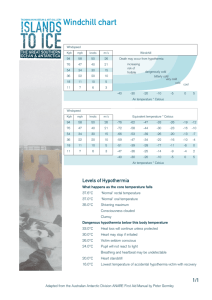
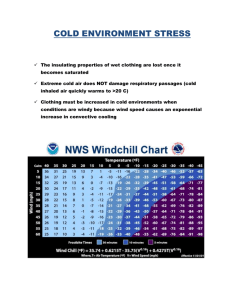
Cold Related Emergencies Factors That Promote Susceptibility To Cold Unfit (conflicting) >50 years and small children Alcohol and caffeine consumption Use of tobacco products Previous cold related emergency Inactivity in cold Cold Factors #2 Dehydration Nutrition Illness Injury Wind Wet clothing (transfers heat from the body) Proper Clothing 3 layers of clothing – Purpose is to insulate by trapping layers of air – A single heavy layer is not recommended Additional Considerations Cap – 50-60% of body’s heat is lost through the head Neck – Site of significant heat loss – Gloves / Boots Cold Related Emergencies Hypothermia Frostbite Hypothermia Core body temperature of 95 or less May be mild or profound (<90 degrees) – Core temperature of 80 degrees usually results in death – Can occur in temps above 32 degrees Medical emergency – Victim may present with no heartbeat, breathing, or response to touch or pain, but may not be dead All victims should be evaluated by a physician Mild Hypothermia Body temperature 90 to 95 degrees – (marathon) Shivering Slurred speech Memory lapses Fumbling hands May stumble or stagger Usually conscious and can talk Cold abdomen and back Profound Hypothermia Body temperature below 90 degrees (AR hunter) Shivering has ceased Muscles stiff and rigid Skin appears blue No response to pain Pulse and respirations slowed Pupils dilate / Victim “appears dead” / 50-80% will die Child in Canada, winter 2001, core body temp. 60 Hypothermia: What To Do Stop heat loss (more on next slide) Call EMS RESCUE EXAMINE INSULATE TRANSPORT Check ABC’s – Take pulse for 30-45 seconds Always try to re-warm in a hospital Hypothermia: Stop Heat Loss Remove from cold environment Use blankets, towels, pillows, newspapers to wrap around victim Cover head Replace wet clothing Hypothermia: Handling The Victim Gentle handling – Roughness could cause cardiac arrest Keep victim horizontal – Elevating legs would shunt cold blood to the core of the body Victim should not walk or exercise do not massage the body – These actions could drive cold blood into the torso resulting in temperature after-drop Hypothermia Controversial: – Body to body contact – Warm drinks Do not consume unmelted snow and ice – Lowers body temperature – Sometimes, that’s your only choice Hypothermia and CPR Do not start CPR if: – Body temperature 60 degrees or below – Frozen chest – Lethal injury – Rescurer is endangered – Always take pulse for 30-45 seconds Frostbite (frozen tissue) Freezes deep into the skin Mainly affects feet, hands, ears, nose Frostbite: How Damage Occurs Freezing of tissue – Ice crystals form between tissue cells Obstruction of blood supply to tissues “Sludged” blood clots form More damaging than ice crystals Frostbite: Signs and Symptoms (pre-thaw) White, waxy or grayish-yellow skin Pain followed by no feeling Affected part is very cold or numb Hard or crusty skin – Post-thaw resembles burn stages First Aid: Re-warming 1. Medical center 2. Rapid (wet) re-warming: – Preferred re-warming method outside of hospital setting in water temperatures around 103 to 105. 3. Slow re-warming: – involves warming body to body, arm pit, etc. Do not re-warm with a heating-pad, stove or over a fire Rapid Re-Warming NEVER Place RUB FROZEN TISSUE body parts in water 102 to 105 (20 to 40 minutes) Do not re-warm if there is a chance of re-freezing