BRUSHING UP ON VISUAL AIDS
advertisement

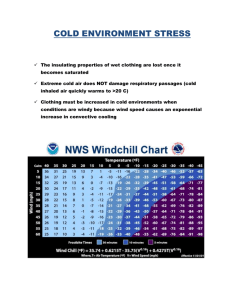
Cold Stress Training Objectives • By the end of the session you will: • • • • • • Know what cold stress is Understand the WorkSafeBC Regulations Understand the risks Know how to control the risk Be able to identify symptoms Know first aid response Agenda • • • • Definitions Regulations Responsibilities Hazard Identification Agenda • • • • Risk Assessment Risk Controls Recognizing Symptoms First Aid Procedures Definitions • • • • • • Accidental Exposure Artificially Cold Workplace Cold-Related Injuries Cold Stress Equivalent Temperature Hypothermia Regulation • The Regulation applies if workers may be exposed to thermal conditions that: • May cause cold stress injury • Could cause core body temp to fall • Are below ACGIH acceptable levels Regulation • • • • Assessment and exposure control Cold stress controls Heated shelters Clothing and PPE Responsibilities • Employer • Conduct risk assessments • Develop and implement exposure control plan • Provide training • Provide heated shelter or vehicle Responsibilities • Employer – continued • Maintain records • Ensure adequate first aid coverage Responsibilities • Managers • Ensure that a cold stress assessment is performed • Provide administrative controls • Ensure protective clothing is available • Ensure workers receive training Responsibilities • Supervisors • Known or reasonably foreseeable cold hazards • Health and safety of all workers • Safe work practices Responsibilities • Workers • Follow safe work procedures • Seek shelter if displaying symptoms of hypothermia • Wear adequate clothing • Avoid getting wet Responsibilities • Workers – continued • Wear eye protection when warranted • Wear PPE Responsibilities • Joint OHS Committee • Advise the Employer on procedures and systems • Help evaluate workplace conditions • Deal with worker complaints • Help with incident investigations and worksite inspections Risk Identification • Environmental Hazards • Job or Task-Related Hazards • Personal Risk Hazards Risk Identification • Environmental Risks • Observe conditions and note hazards • Determine risks of accidental exposure • Look at previous history of exposure to cold • Conduct risk assessment if hazard(s) is present Risk Identification • Job / Task Related Risks • Observe the tasks • Determine hazards that may expose workers to risk • If task-related hazard is present implement controls Risk Identification • Personal Risks • • • • • • • Poor physical fitness Not used to working in the cold Cold or other flu like symptoms Chronic illness or circulatory problems Using certain drugs or medication Exhibiting symptoms of fatigue Vibration white finger disease Risk Assessment • • • • • • Documentation Taking measurements Categorizing the risk Vibration and accidental exposure Accidental exposure Conditions that require a mandatory assessment Risk Assessment • Cold Stress Risk Assessment Form • Section One • Section Two • • • • Measurements Category and control Hand/arm vibration Accidental exposure Risk Assessment • Conditions Requiring Assessment • Conditions that cold cause cold stress or injury • Conditions that could cause worker’s core body temperature to fall below 36C • Conditions below levels classed by ACGIH as “little danger” Risk Controls • Working in hazardous wind chill conditions • Contact with cold surfaces • Bare hands in a cold environment • Administrative controls • Personal Protective Equipment & Clothing Risk Controls • Wind Chill Conditions • Heated shelter or vehicle to be available • Worker instructions • Workers must wear adequate protective clothing Risk Controls • Contacting Cold Surfaces • Protective clothing and equipment • Wear protective gloves, mittens and footwear • Wear insulated gloves when surfaces are colder than -7C • Avoid skin contact with cold surfaces Risk Controls • Hand Protection • Warm air jets, radiant heaters or warm contact plates for hand warming • Controls designed for operation by gloved hands Risk Controls • Administrative Controls • • • • • Adjustment to the cold Reduce activities performed outdoors Remain well hydrated Eat properly according to the cold climate Establish a buddy system Risk Controls • Personal Protective Clothing and Equipment • Wear insulated outer clothing • Use protective clothing in controlled environments • Change out of wet clothing Risk Controls • Personal Protective Clothing and Equipment – continued • Immediately change to dry clothing if immersed in water • Wear PPE if danger of frostbite Prevention • • • • • Understanding the personal risk factors Following safe work practices Proper use of clothing Using shelters Following guidelines for eating and drinking Prevention • Personal Risk Factors • • • • • Poor physical fitness Not used to working in the cold Cold or other flu like symptoms Chronic illness or circulatory problems Using certain drugs or medication that inhibit the body’s response to the cold or impairs judgment • Vibration white finger disease Prevention • Safe Work Practices • Use a “buddy system” • Do a regular “self-check” for symptoms • If you discover a cold-related injury NOTE: this last point isn’t finished. Prevention • Proper use of clothing • Under Layer • Insulating Layer • Outer Layer Prevention • Use of Shelters • Provide shelters at -7C or below • Use shelters at regular intervals • Remove outer clothing and allow ventilation • Assess cold injury or hypothermia victims Prevention • Eating and Drinking Guidelines • High caloric intake is recommended for cold work • Warm sweet drinks available • Drink frequently • Avoid coffee • Avoid alcohol Recognizing Symptoms • • • • Mild Hypothermia Moderate Hypothermia Severe Hypothermia Frostnip & Frostbite Recognizing Symptoms • Mild Hypothermia • • • • • • Feel chilled / cold Goose bumps Limited hand movement Poor judgment Shivering Numb hands Recognizing Symptoms • Moderate Hypothermia • Violent shivering or shivering has stopped • Inability to think / focus • Mild confusion Recognizing Symptoms • Moderate Hypothermia – continued • • • • Slow, shallow breathing Slurred speech Poor co-ordination Slow, weak pulse Recognizing Symptoms • Severe Hypothermia • • • • Shivering has stopped Unconsciousness Little or no breathing Weak, irregular or non-existent pulse Recognizing Symptoms • Severe Hypothermia – continued • Dilated pupils • Exposed skin blue and/or puffy • Similar symptoms to clinical definition of death Recognizing Symptoms • Frostbite / Frostnip • • • • • Top layers of skin tissue freeze Skin appearance: white, waxy Top layer of skin feels hard & rubbery Deep tissue is still soft Numbness Recognizing Symptoms • Superficial Frostbite • • • • Skin appearance: white Wooden feeling throughout affected area All layers of skin affected Numbness, sensation may be absent Recognizing Symptoms • Deep Frostbite • • • • Skin appears white Affected areas feels ‘wooden’ to touch Includes all layers of skin May include freezing of muscle or bone First Aid • • • • General Procedures Frostbite Managing & Re-warming Injuries Accidental Exposure First Aid • General Procedures • • • • • Handle victim gently Remove from cold and assess Give hot fluids only if victim is conscious Do not attempt to exercise victim Prevent further heat loss First Aid • Frostbite • • • • Rewarm the area gently Do not rub the area If area is large, use immersion method Transport to hospital if necessary First Aid • Management and Re-Warming • • • • Minimize exertion Remove wet clothing Get the victim into warm, dry clothes Wrap victim in warm blankets First Aid • Management and Re-Warming - continued • Cover victim’s head • Place something warm and dry under the victim • Move the victim to a warm environment First Aid • Management and Re-Warming - continued • • • • Do not make the victim exercise Do not suppress shivering Do not massage extremities or trunk Do not place in warm bath or shower First Aid • Accidental Exposure • • • • Unplanned event Clothing and equipment Treat appropriately Assessed by OFAA or physician Survival Kit • • • • A change of clothing Emergency supplies Light weight emergency rain poncho Spare gloves, footwear, head covering and face mask Survival Kit • Protective eye wear • Sleeping bag stored in plastic vaporbarrier wrapper • Means of communication i.e. cell phone, 2-way radio Summary • • • • • • WorkSafeBC OHS Regulation Risk identification Risk assessment Risk controls Symptoms First aid Questions?