Thermal Stress

Thermal Stress at workplace
Ass. Prof. Dr. Laith A. Alrudainy
Thermal Stress
•
Thermal stress is defined as the physical and physiological reactions of the human body to temperatures that fall outside of the human normal comfort zone.
Temperature Regulation
The hypothalamus is a small organelle within the brain which adjusts bodily functions through hormones which:
-Increase heart rate
-Begin the sweating mechanism
-Increase blood flow to the skin surface
How does the body rid itself of excess heat?
There are 4 means of heat removal from the body.
Convection
Radiation
Evaporation
Conduction
What are the health effects of heat stress/strain?
Heat Rash
Sunburn
Heat Fatigue
Heat Cramps
Heat Exhaustion
Heat Stroke
Heat Exhaustion
Cause: Depressed condition of the circulatory system due to a lack of adequate fluid replacement (dehydration). Blood vessels dilate and blood flow is seriously reduced (clinical condition of shock has occurred).
Symptoms: Nausea, dizziness, weakness, headache, blurred vision, profuse sweating, cold/wet (clammy) grayish skin, unconsciousness, coma and death.
Heat Exhaustion (continued) :
First Aid: Place victim in a face down position in a cool location, administer fluids if the victim is conscious. If unconscious, seek medical care or transport to a medical emergency room.
Seriousness: Shock is a serious medical condition regardless of the cause of its onset.
Victims may require several days or even weeks to recover.
Heat Stroke
Cause: The body’s temperature regulation mechanism, located in the hypothalamus, fails and sweating stops. Core body temperature rises dramatically and the victim’s condition becomes a serious medical emergency.
Symptoms: Chills, restlessness, irritability, euphoria, red face and skin, disorientation, hot/dry skin (not always), collapse, unconsciousness, convulsions and death.
Heat Stroke (continued) :
First Aid: Immediate, aggressive cooling of the victim’s body using wet cloths, immersion into cool water or using alcohol wipes. Transport to emergency medical facility.
Seriousness: Heat Stroke is a MEDICAL
EMERGENCY . Without outside intervention, the victim will die.. Recovery times from heat stroke are generally the longest of any heat-related disorder.
Heat effects and people
Heat affects people in different ways. People come in all different sizes, shapes, and tolerances for heat.
Some people can work comfortably in high temperatures, while others will develop sickness from heat stress/strain
Heat effects
Predisposing Factors:
very small body size
poor nutrition overweight over 40 years old (the older the more sensitive)
previous heat illness heart disease high blood pressure diabetes skin disease liver, kidney, and lung problems
Heat effects
Predisposing Factors, cont’d:
poor physical condition
fatigue
excessive clothing dehydration
being female being pregnant alcohol, caffeine, nicotine intake
Sunbathing
Heat effects, cont’d - Drugs
Drugs that interfere with body’s thermo-regulation:
Heat production: thyroid hormone amphetamines
Decrease sweating: antihistamines anticholinergics phenothiazines
Benztropine
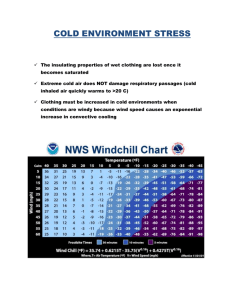
Cold Stress
Hypothermia
“a decrease in the core body temperature to a level at which normal muscular and neurological functions are impaired”
Hypothermia is possible at any temperature under 98.6 F degrees.
Hypothermia - signs
Shows decreased physical and mental capacity.
Hypothermia - mild
Mild Hypothermia:
- core temperature 98.6 – 96 F
- non-voluntary shivering
-complex motor functions impossible
-vasoconstriction to periphery
Hypothermia - moderate
Moderate Hypothermia:
- core temperature 95 – 93 F
- loss of fine motor coordination
- slurred speech
- violent shivering
- apathetic attitude
Hypothermia - severe
•
Severe Hypothermia:
- core temperature 92 – 86 F or below
- shivering in waves
- person curled in fetal position to conserve heat
- muscle rigidity develops
- pale skin/dilated pupils
- reduced pulse
Severe Hypothermia is LIFE THREATENING!
Cold Injuries
Although hypothermia is well known, there are other cold injuries.
-Frostbite
-Immersion foot (trench foot)
Frostbite
Frostbite is a freezing of the surface and deep layers of tissue.
Characterized by:
- white, and feels “woody”
- numbness, possible anesthesia
- deep frostbite can affect bone and muscle
- purple/black color is from ruptured blood vessels
Frostbite - treatment
Immerse affected area in 105 – 110 degree F water until thawing is complete.
- part will be extremely painful
Wrap affected part in sterile gauze
Affected part should not be used for anything
- keep part from refreezing
Immersion Foot – trench foot
Immersion foot is caused by prolonged exposure of the feet to wet, cool conditions.
Characterized by:
- yellowish, smelly feet
- possibly numb
- sloughing of skin tissue/itching
*Immersion foot may cause permanent damage to foot tissues, leaving person susceptible to cold injuries in future.
Immersion Foot - treatment
Careful cleaning and drying of feet.
Keep feet dry as much as possible.
Keep off feet as much as possible until healed.
Thank you