Power Point for Round 1 of DOK Training
advertisement

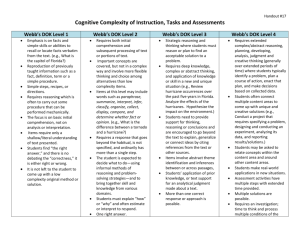
a sudden feeling of cold with shivering accompanied by a rise in temperature, often with copious sweating, especially at the onset or height of a fever. short for rigor mortis. When It Rains Rigor The puddles are deeper! Bringing Clarity to …. Cognitive Rigor and the Depth of Knowledge Your Card Part 1 Cognitive Rigor Overview Objectives: 1. Recognize what DOK level a question or task is. Conceptualizing Cognitive Rigor Dddd Your Questions Dddd Dddd Different Models of Rigor The Cognitive Rigor (CR) Matrix Let’s Play a Game Revisit Your Questions Applying Rigor 2 basic comprehension questions... 2 rigorous comprehension questions… Your Questions Golden Keys A bunch of golden keys is mine To make each day with gladness shine. "Good morning!" that's the golden key That unlocks every door for me. When evening comes, "Good night!" I say, And close the door of each glad day. When at the table "If you please" I take from off my bunch of keys. When friends give anything to me, I'll use the little "Thank you" key. "Excuse me," "Beg your pardon," too, When by mistake some harm I do. Or if unkindly harm I've given, With "Forgive me" key I'll be forgiven. On a golden ring these keys I'll bind, This is its motto: "Be ye kind.“ I'll often use each golden key, And so a happy child I'll be. YOUR QUESTIONS Two basic comprehension questions would be: 1.__________________________________________________________________ 2.__________________________________________________________________ Two more rigorous questions would be: 1._________________________________________________________________ 2._________________________________________________________________ 3 Common Different Models of Rigor There are different models describing cognitive rigor. Each model actually addresses something different. Bloom – What type of thinking (verbs) is needed to complete a task? Webb – How deeply do you have to understand the content to successfully interact with it? How complex is the content? Hess combined Dr. Norman Webb’s Depths of Knowledge and Dr. Benjamin Bloom’s Bloom’s Cognitive Taxonomy to develop the Cognitive Rigor (CR) Matrix. Different Models of Rigor Three Parts of the CR Matrix The DOK Levels DOK Blooms DOK LEVEL 1 Recall and Reproduction DOK 2 Skills and Concepts DOK LEVEL 3 Strategic Thinking and Reasoning DOK 4 Extended Thinking Knowledge Comprehension The Bloom’s Levels Application Cognitive Rigor Tasks Analysis Evaluation Synthesis The Cognitive Rigor (CR) Matrix Hess Cognitive Rigor Matrix Webb’s Depth of Knowledge Blooms DOK LEVEL 1 Recall and Reproduction DOK LEVEL 2 Basic Skills and Concepts DOK LEVEL 3 Strategic Thinking and Reasoning DOK LEVEL 4 Extended Thinking Remember (Knowledge) Retrieve knowledge from longterm memory, recognize, recall, locate, identify. o Ka Recall, recognize, or locate basic facts, details, events, or ideas explicit in texts. o Kb Read words orally in connected text with fluency & accuracy. o Kc-Define terms. Understand (Comprehend) o Cd Identify or describe literary elements (characters, setting, sequence, etc.) o Ce Select appropriate words when intended meaning/definition is clearly evident. o Cf Describe/explain who, what, where, when, or how. o Ch Specify, explain, show relationships; explain why, cause-effect. o Give non-examples -examples.* o Ci Summarize results, concepts, ideas. o Cj Make basic inferences or logical predictions from data or texts. o Ck Identify main ideas or accurate generalizations of texts. o Cl Locate information to support explicitimplicit central ideas. o Cu Explain, generalize, or connect ideas using supporting evidence (quote, example, text reference). o Cv Identify/ make inferences about explicit or implicit themes. o Cw Describe how word choice, point of view, or bias may affect the readers’ interpretation of a text. o CK Explain how concepts or ideas specifically relate to other content domains or concepts. o CL Develop generalizations of the results obtained or strategies used and apply them to new problem situations. Apply Carry out or use a procedure in a given situation; carry out (apply to a familiar task), or use (apply) to an unfamiliar task. o APgUse language structure (pre/suffix) or word relationships(synonyms/antonym) to determine meaning. o APm Use context to identify word meanings o APn Obtain and interpret information using text features. o APx Use concepts to solve nonroutine problems. o Devise an approach among many alternatives to research a novel problem.* o APM Illustrate how multiple themes (historical, geographic, social) may be interrelated. Analyze Break into constituent parts, determine how parts relate, differentiate between relevantirrelevant, distinguish, focus, select, organize, outline, find coherence, deconstruct (e.g., for bias or point of view). o ANo Identify whether specific information is contained in graphic representations (e.g., map, chart, table, graph, T-chart, diagram) or text features (e.g., headings, subheadings, captions). o ANp Categorize/compare literary elements, terms, facts, details, events. o ANq Identify use of literary devices. o ANr Analyze format, organization, & internal text structure (signal words, transitions, semantic cues) of different texts. o ANs Distinguish: relevant-irrelevant information; fact/opinion. o ANt Identify characteristic text features; distinguish between texts, genres. o ANy Analyze information within data sets or texts. o ANz Analyze interrelationships among concepts, issues, and problems. o ANA Analyze or interpret author’s craft (literary devices, viewpoint, or potential bias) to critique a text. o ANB Use reasoning, planning, and evidence to support inferences. o ANN Analyze multiple sources of evidence, or multiple works by the same author, or across genres, time periods, themes. o ANO Analyze complex/abstract themes, perspectives, concepts. o ANP Gather, analyze, and organize multiple information sources. o ANQ Analyze discourse styles. o EVC Cite evidence and develop a logical argument for conjectures. o EVD Describe, compare, and contrast solution methods. o EVE Verify reasonableness of results. o EVF Critique conclusions drawn. o EVR Evaluate relevancy, accuracy, & completeness of information from multiple sources. o EVS Draw & justify conclusions o EVT Apply understanding in a novel way; provide argument or justification for the application. Construct meaning, clarify, paraphrase, represent, translate, illustrate, give examples, classify, categorize, summarize, generalize, infer a logical conclusion), predict, compare/contrast, match like ideas, explain, construct models. Evaluate Make judgments based on criteria, check, detect inconsistencies or fallacies, judge, critique. Create (Synthesize) Reorganize elements into new patterns/structures, generate, hypothesize, design, plan, produce. o SYG Generate conjectures or hypotheses o SYH Synthesize information based on observations or prior within one source or text. knowledge and experience. o SYI Develop a complex model for a given situation. o SYJ Develop an alternative solution. o SYU Synthesize information across multiple sources or texts. o SYV Articulate a new voice, theme, knowledge or perspective. One Step DOK-1 Reporter DOK-2 Interpreter DOK-3 Judge Two Steps Three Steps DOK-1 Key Details, Facts, Words, Terms, Events acts . These can stand alone as sources of information. They require the skills of recalling, locating, reading, defining and recognizing. These questions or tasks require students to go to the source or recall information and are one –step DOK-1 questions. Students do one thing. The answer is either right or wrong. DOK-1 Example: What is an important fact about spiders? DOK-2 Cause and Effect, Results, Relationships, Concepts, Ideas. These are not stand alone concepts. They are broader. They require the skills of specifying, explaining, showing, summarizing, logically inferring, identifying, predicting and showing explicit generalizations using two-steps (1) locating and selecting those stand-alone pieces of information (DOK1 facts, terms, words, etc…) to (2) identify and verify the correct answer. The answer is still either right or wrong. DOK-2 Example: What is the main idea of the story? DOK-3 Evidence, Quotes, Examples, References, Word Choices, Points of View, Bias, Purpose., New Problems, Conclusions, Generalizations, Conjectures. These concepts move students into reasoning. They require the skills of explaining, generalizing, connecting, describing the effects of, solving and interpreting. DOK3, three -step questions are asking students to (1) explain “HOW” the two-step questions are connected [how are the key details helping us identify the main idea? How do the illustrations in the text contribute more to the story?] (2) show how they solved the question using words, pictures, graphic organizers and (3) draw and justify a conclusion. DOK-3 Example: What character traits did Goldilocks have that contributed to the sequence of events? DOK-1 Recall and Reproduce SHOW ME TELL ME a DOK-2 DOK-2 Skills and Concepts Skills and Concepts I can In order to… LOCATE IDENTIFY and and SELECT Information or details… VERIFY a new concept. a b DOK-3 DOK-3 DOK-3 Strategic Thinking and Reasoning Strategic Thinking and Reasoning Strategic Thinking and Reasoning I can ...which I use to show my LOCATE and SELECT REASONING so I can show HOW I SOLVED and CONCLUDED information and details IDENTIFY and VERIFY to a new concept… and then I EXPLAIN my THINKING the question a b c Can you identify the two steps? verify/identify locate/select DOK-2 • How would you summarize the story? unspoken details • Why did Jack fall? Explain your answer. • How do the pigs’ houses reveal their characters? • What facts support that Goldilocks was curious? Explain. • How are the bad wolf and grandma different? unspoken details • What identifies Huck from Tom? unspoken details • What evidence best explains why Jack sold the cow? • According to the book, how does Johnny climb a tree? unspoken details Can you identify the three steps? Locate/select verify/identify Reason How Solve and Conclude Explain (justify) Your Thinking DOK-3 • How does the author’s use of hyperbole lead the reader to believe that she is exaggerating? • Which event most likely contributed to the fire? How do you know? • If Hansel and Gretel had not left a trail of bread crumbs then what may have happened? Explain. • How did Ben’s belief effect the outcome? UNSTATED • How did Mr. Taylor enable Casey to keep the horse? UNSTATED • What factors most influenced the outcome of the civil ward? Explain how you know. • Should the electricity have been turned off at that moment? UNSTATED UNSTATED Determining Depth-of-Knowledge Levels The intended student learning outcome determines the DOK level. What mental processing must occur? While verbs may appear to point to a DOK level, it is what comes after the verb that is the best indicator of the rigor/DOK level. Describe the physical features of a plant. Describe how the two political parties are alike and different. Describe the most significant effect of WWII on the nations of Europe. Rules of Thumb If there is only one correct answer, it is probably level DOK 1 or DOK 2 •DOK 1: you either know it (can recall it, locate it, do it) or you don’t •DOK 2 (conceptual): apply one concept, then make a decision before going on applying a second concept If more than one solution/approach, requiring evidence, it is DOK 3 or 4 Dr. Hess •DOK 3: Must provide supporting evidence and reasoning (not just HOW solved, but WHY – explain reasoning) •DOK 4: all of “3” + use of multiple sources or texts. The Hess Cognitive Rigor Matrix: Applies Webb’s DOK to Bloom’s Cognitive Process Dimensions Note: not a complete matrix – an abbreviated example Depth + thinking Level 1 Recall & Reproduction Level 2 Skills & Concepts Level 3 Strategic Thinking/ Reasoning Level 4 Extended Thinking Remember -Recall, locate basic facts, details, events Understand -Select appropriate words to use when intended meaning is clearly evident -Specify or explain relationships -summarize -identify central idea -Explain, generalize, or connect ideas using supporting evidence (quote, example…) -Explain how concepts or ideas specifically relate to other content domains or concepts -Use context to identify meaning of word -Obtain and interpret information using text features -Use concepts to solve non-routine problems Apply -Use language structure (pre/suffix) or word relationships (synonym/antony m) to determine meaning -Devise an approach among many alternatives to research a novel problem -Identify whether information is contained in a graph, table, etc. -Compare literary elements, terms, facts, events -analyze format, organization, & text structures -Analyze or interpret author’s craft (literary devices, viewpoint, or potential bias) to critique a text -Analyze multiple sources -Analyze complex/abstract themes -Cite evidence and develop a logical argument for conjectures -Evaluate relevancy, accuracy, & completeness of information -Synthesize information within one source or text -Synthesize information across multiple sources or texts Analyze Evaluate Create Not appropriate at this level Not appropriate at this level -Brainstorm ideas about a topic -Generate conjectures based on observations or prior knowledge The CR Matrix Lesson Plan Template Example Back to Your Questions! Depth + thinking Remember Understand Level 1 Recall & Reproduction Level 2 Skills & Concepts Level 3 Strategic ThinkingReasoning Level 4 Extended Thinking -Recall facts -Identify characters, setting, etc. -Retell or summarize… Apply -Comparecontrast -Analyze multiple texts/sources & using text evidence for support Analyze -Justify judgments using details/evidence from text Evaluate Create -Develop a creative summary Revisit Your Questions