17-Cognitive_Complexity_Observation_Tool_SR_11.04.11
advertisement
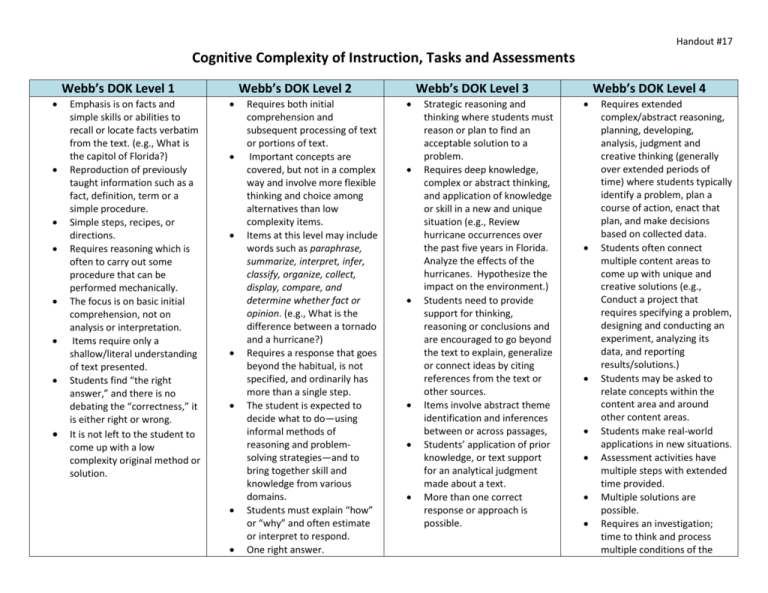
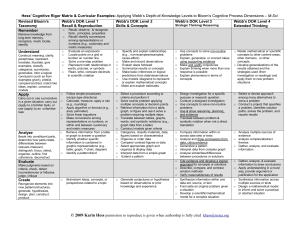
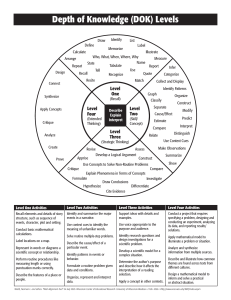
Handout #17 Cognitive Complexity of Instruction, Tasks and Assessments Webb’s DOK Level 1 Emphasis is on facts and simple skills or abilities to recall or locate facts verbatim from the text. (e.g., What is the capitol of Florida?) Reproduction of previously taught information such as a fact, definition, term or a simple procedure. Simple steps, recipes, or directions. Requires reasoning which is often to carry out some procedure that can be performed mechanically. The focus is on basic initial comprehension, not on analysis or interpretation. Items require only a shallow/literal understanding of text presented. Students find “the right answer,” and there is no debating the “correctness,” it is either right or wrong. It is not left to the student to come up with a low complexity original method or solution. Webb’s DOK Level 2 Requires both initial comprehension and subsequent processing of text or portions of text. Important concepts are covered, but not in a complex way and involve more flexible thinking and choice among alternatives than low complexity items. Items at this level may include words such as paraphrase, summarize, interpret, infer, classify, organize, collect, display, compare, and determine whether fact or opinion. (e.g., What is the difference between a tornado and a hurricane?) Requires a response that goes beyond the habitual, is not specified, and ordinarily has more than a single step. The student is expected to decide what to do—using informal methods of reasoning and problemsolving strategies—and to bring together skill and knowledge from various domains. Students must explain “how” or “why” and often estimate or interpret to respond. One right answer. Webb’s DOK Level 3 Strategic reasoning and thinking where students must reason or plan to find an acceptable solution to a problem. Requires deep knowledge, complex or abstract thinking, and application of knowledge or skill in a new and unique situation (e.g., Review hurricane occurrences over the past five years in Florida. Analyze the effects of the hurricanes. Hypothesize the impact on the environment.) Students need to provide support for thinking, reasoning or conclusions and are encouraged to go beyond the text to explain, generalize or connect ideas by citing references from the text or other sources. Items involve abstract theme identification and inferences between or across passages, Students’ application of prior knowledge, or text support for an analytical judgment made about a text. More than one correct response or approach is possible. Webb’s DOK Level 4 Requires extended complex/abstract reasoning, planning, developing, analysis, judgment and creative thinking (generally over extended periods of time) where students typically identify a problem, plan a course of action, enact that plan, and make decisions based on collected data. Students often connect multiple content areas to come up with unique and creative solutions (e.g., Conduct a project that requires specifying a problem, designing and conducting an experiment, analyzing its data, and reporting results/solutions.) Students may be asked to relate concepts within the content area and around other content areas. Students make real-world applications in new situations. Assessment activities have multiple steps with extended time provided. Multiple solutions are possible. Requires an investigation; time to think and process multiple conditions of the Handout #17 problem or task. Instruction and Questioning Tasks and Assessments Indicate the Level of Complexity of: (E) Examples (Q) Questions (M) Models (R) Responses Indicate the Level of Complexity of: (T) Tasks (A) Assessments Class 1 Class 1 Class 2 Class 2 Class 3 Class 3 Class 4 Class 4 Class 5 Class 5