5th Edition
PPT 2-1
Chapter 2
Types of Retailers
McGraw-Hill/Irwin
Levy/Weitz:
Retailing Management, 5/e
PPT
2-2
Copyright © 2004 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved.
The World of Retailing
Introduction
to Retailing
Multi-Channel
Retailing
PPT 2-3
Types of Retailers
Customer Buying
Behavior
Trends in Retailing
Increasing Industry
Concentration
Globalization
PPT 2-4
Growing Diversity
of Formats
New Types of Retailers
• Category Specialists
-PetsMart
-Bed, Bath and Beyond
- Michaels
• CarMax and Auto Nation
• Wal-Mart Supercenters
-Supermarket + Discount Store
• Ebay, Priceline, Travelocity
PPT 2-5
Increasing Concentration
53% of sales
85% of sales
Drug Stores
Walgreens, CVS, Rite-Aid and Eckerds
PPT 2-6
Discount Stores
Wal-Mart, Target and Kmart
Globalization of Wal-Mart
PPT 2-7
Types of Retailers
• Retailers Use Different Retail Mixes
-merchandise: variety (breadth) / assortment
(depth)
-services
-store design, visual merchandising
-location
-pricing
• Infinite Variations
• Survival of the Fitness – Some combination of retail
mixes satisfy the needs of significant segments and
persist over time.
PPT 2-8
Classification by Type of Merchandise
PPT 2-9
Sales by Merchandise Category
PPT 2-10
Merchandise Offering
• Variety (breadth of merchandise)
- The number of merchandise categories
Assortment (depth of merchandise)
-the number of items in a category (SKUs)
PPT 2-11
Variety and Assortment of Bicycles
PPT 2-12
Types of Retailers
Food Retailers
General Merchandise Retailers
Mom and Pop Stores
Department Stores
Convenience Stores
Specialty Stores
Supermarkets
Discount Stores
Supercenters
Category Specialists
Off-Price Retailers
Warehouse Clubs
PPT 2-13
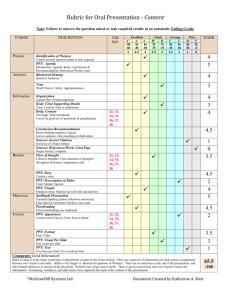
Shopping Patterns by Types of Retail Outlets
Outlet
% Shopping
Number of
Weekly
Weekly Trips
Spending
Supermarkets
100
2.4
$ 72.82
General merchandise
discount stores
68
1.3
32.53
Fast-food restaurants
65
1.9
16.32
Drug stores
39
1.2
18.70
Convenience stores
37
2.4
19.72
Wholesale clubs
27
1.7
75.12
Specialty food stores
9
1.0
23.70
Source: “Consumers Are Skeptical Again,” “63rd Annual Report of the Grocery Industry,” Progressive Grocer, April 1996, p.42.
PPT 2-14
Food Retailers
Mom and Pops – Supermarkets
-Cars, highways and TV to build brands
-Knowledgeable customers – self service
-Perishable vs. packaged goods
Big Box Retailers
-Warehouse Clubs
-Supercenters
-Hypermarkets
Convenience Stores
PPT 2-15
Types of Food Retailers
PPT 2-16
Issues in Food Retailing
Competition from Discount Stores
Efficient
Distribution
Lower Costs
Lower Prices
Changing Consumption Patterns
Time Pressure
PPT 2-17
Eating Out More
Meal Solutions
Types of General Merchandise Retailers
• Discount Stores
• Specialty Stores
• Category Specialists
• Home Improvement Centers
• Department Stores
• Drugstores
• Off-Price retailers
• Value Retailers
PPT 2-18
Characteristics of General Merchandise Retailers
PPT 2-19
Issues in Discount Store Retailing
• Only Big Three Left – Wal-Mart, Kmart,
Target
• Wal-Mart’s Dominance
• Differentiate Strategy
-Wal-Mart = Low Price and Good value
-Target = More Fashionable Apparel
• Competition from Category Specialists
-Toys-R-Us, Circuit City, Sports Authority
PPT 2-20
Issues in Specialty Store Retailing
Mall-Based Apparel Retailers:
Decline in Mall Shopping and Apparel Sales
-Lack of New Fashions
-Less Interest in Fashion
-Increase Price Consciousness
Lifestyle Formats – Banana Republic and Hot Topics
PPT 2-21
Category Specialists
Deep and Narrow Assortments – Destination Stores
Low Price and Service
Wholesaling to Business Customers and Retailing to
Consumers
Incredible Growth
Increased Competition with National Expansion and
Consolidation
PPT 2-22
Issues in Department Store Retailing
• Competition
-Discount Stores on Price
-Specialty Stores on Service, Depth of Assortment
• Lower Cost by Reducing Services (?)
-Centralized Cash Wraps
• More Sales (?)
-Customers Wait for Sale
• Focus on Apparel and Soft Home
• Develop Private Labels and Exclusive Brands
PPT 2-23
Issues in Drug Store Retailing
Consolidation – Walgreens, CVS, Rite-Aid,
Eckerds
Competition from Supermarkets and Discount
Stores – Pharmaceuticals
Evolution to a New Format
-Stand Alone Sites with Drive Thru Windows
-Convenient Store Front End
PPT 2-24
Issues in Off-Price Retailing
• Opportunistic Buying
• Hurt By Sales in Department Stores
• Buying First Line Merchandise
PPT 2-25
Issues in Value Retailing
Target Lower Income Families
Low Cost
Low Prices
-Low Cost Location
-Limited Services
One of the Fastest Growing Retail Segments
PPT 2-26
Summary
Many
New
Types
retailers,
Increased
Many
New
Types
ofof
retailers,
Increased
Diversity to Meet Diverse Needs
Diversity to Meet Diverse Needs
Most People Shop at All Types Depending
on Situations – Growth in Cross-Shopping
PPT 2-27
Non-store Retail Formats
Electronic Retailing
Catalog and Direct Mail
Direct Selling
Television Home Shopping
Vending Machines
PPT 2-28
Types of Nonstore Retailers
PPT 2-29
Sales by Non-store Format
2005
PPT 2-30
Issues in Catalog Retailing
• Low Start Up Cost
• Evolution of Multi-Channel Offering
-Electronic Channel, Stores
• Increasing Mail Costs
• Clutter from other Catalogs
PPT 2-31
Services vs. Merchandise Retailers
Intangibility
-Problems in Evaluating Service Quality
-Performance of Service Provider
Simultaneous Production and Delivery
-Importance of Service Provider
Perishability
-No Inventory, Must Fill Capacity
Inconsistency of the Offering
-Importance of HR Management
PPT 2-32
Examples of Service Retailers
Type of Service
Service Retail Firms
Airlines
American, Delta, British Airways, Singapore Airways
Automobile maint/repair
Jiffy Lube, Midas, AAMCO
Automobile rental
Hertz, Avis, Budget, Alamo
Banks
Citibank, NCNB, Bank of America
Child care centers
Kindercare, Gymboree
Credit cards
American Express, VISA, Mastercard
Education
University of Florida, Babson College
Entertainment parks
Disney, Universal Studios, Six Flags
Express package delivery Federal Express, UPS, US Postal Service
PPT 2-33
Financial services
Merrill Lynch, Dean Witter
Fitness
Jazzercise, Bally’s, Gold’s Gym
Health Care
Humana, HCA
Home maintenance
Chemlawn, MiniMaid, Roto-Rooter
Examples of Service Retailers
PPT 2-34
Type of Service
Service Retail Firms
Hotels and motels
Hyatt, Sheraton, Marriott, Days Inn
Income tax preparation
H & R Block
Insurance
Allstate, State Farm
Internet access/Elec info.
American On-Line, CompuServe
Long-distance telephone
AT&T, MCI, Sprint
Movie theaters
AMC, Loews/Sony, Universal
Real estate
Century 21, Coldwell Banker
Restaurants
TGI Friday’s, Wendy’s, Pizza Hut
Truck rentals
U-Haul, Ryder
Weight loss
Weight Watchers, Jenny Craig
Video rental
Blockbuster
Vision centers
Lenscrafter, Pearle
Merchandise/Service Continuum
PPT 2-35
Types of Retail Ownership
• Independent, Single Store Establishments
Consumer Owned Cooperatives
Wholesaler Owned Cooperatives
• Corporate Chains
• Franchises
PPT 2-36
Trends in Ownership
Concentration on One Format
Growth in Services Franchising
PPT 2-37
Franchising
30 – 40% of US Retail Sales
Franchisee Pays Fixed Fee
Plus % of Sales
Franchisee Implements
Program
Why is This Ownership Format
Efficient?
PPT 2-38
Reasons for Franchising Growth
Technological advances
Profitable utilization of capital resources
Attainment of the “American Dream”
Demographic expansion
Product/service consistency
PPT 2-39
Types of Franchise Systems
Territorial
Operating
Mobile
Distributorship
Co-ownership
Co-management
Leasing/Licensing
Manufacturing
Service
PPT 2-40
Reasons for Franchising Failure
Inept management
Fraudulent activities
Market saturation
PPT 2-41
Franchisor Positions in the Marketing Channel
Manufacturer - retailer
Manufacturer - wholesaler
Wholesaler - retailer
Service sponsor - retailer
PPT 2-42
Franchisor Benefits
Continuous market
Market information
Money
Royalty fees
Sales of products
Rental and lease fees
License fees
Management fees
PPT 2-43
Franchisee Benefits
Initial Services
Market survey and site selection, facility design
and layout, lease negotiation advice, financing
advice, operating manuals, management training
programs, and employee training.
Continuous Services
Field supervision, merchandising and promotional
materials, management and employee retraining,
quality inspection, national advertising, centralized
purchasing, market data and guidance, auditing
and record keeping, management reports, and
group insurance plans.
PPT 2-44
Franchisor Advantages/Disadvantages
Advantages
Rapid expansion, highly motivated franchisees
do a good job, additional profits by selling
franchisees products and services.
Disadvantages
Company-owned units may be more profitable,
less control then independent retailers over
advertising, pricing, personnel practices, etc.
PPT 2-45
Franchisee Advantages/Disadvantages
Advantages
Established/proven product/service, business
and technical assistance, and reduction in risk.
Disadvantages
Loss of control since only semi-independent,
franchisee outlets may compete with corporateowned outlets, and high royalties, fees, costs on
equipment, supplies, merchandise, rental/lease
rates and mandatory participation in promotional
and support services.
PPT 2-46
Franchising Trends for the New Millennium
Sustained growth
Enduring plus un-imagined applications
International expansion
Increasing tensions
Greater emphasis on financial returns
PPT 2-47
Theories of Retail Institution Change
CYCLICAL THEORIES
Wheel of retailing (price/service)
Accordion Theory (assortment)
EVOLUTIONARY THEORIES
Dialectic process (retailer)
Natural selection (customer)
PPT 2-48
Wheel of Retailing
PPT 2-49
The Dialectic Process
THESIS
Department store
High margin
Low turnover
High price
Full service
Downtown location
Plush facilities
ANTITHESIS
Discount store
Low margin
High turnover
Low price
Self-service
Low rent location
Spartan facilities
PPT 2-50
SYNTHESIS
Discount department
store
Average margins
Average turnover
Moderate prices
Limited services
Suburban locations
Modest facilities
Source: Reprinted with the permission of
Macmillan College Publishing Company from
Retailing, 4th Edition, by Dale M. Lewison.
Copyright © 1991 by Macmillan
College Publishing Company, Inc.