Fishies-Slideshow - Chaparral Star Academy
advertisement

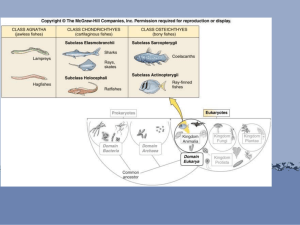
The 4 basic characteristics of chordates…. › › › › Have a single, dorsal, hollow nerve chord Gill or pharyngeal slits a notochord a post anal tail Agnatha ("no jaws") is a superclass of jawless fish in the phylum Chordata, subphylum Vertebrata. gnathostomes- all vertebrates with jaws Has no paired fins or scales Lampreys (30 species) Temperate regions, primarily freshwater breed in rivers/lakes attach to other fish and suck their blood, or feed on bottom invertebrates Hagfish/slime eels (20 Species) Feed on dead and dying things Bore into pray and eat them from the inside out Live in burrows, in muddy bottoms Skin is used to make leather http://video.nationalgeographic.com/video/news /animals-news/new-zealand-hagfish-slime-vin/ Cartilaginous fishes Includes: Sharks, rays and skates and ratfishes Skeleton made of cartilage Moveable jaws Have paired lateral fins Placoid scales Sharks › fast swimming + predatory feeding › living fossils (similar to the sharks that swam 100 mil yr ago) Well developed caudal fin › Heterocercal- upper lobe is longer than the lower lobe › › › › First dorsal fin longer and almost triangular Paired pectoral fins, large and pointy 5-7 gill slits behind head Lots of rows of teeth › http://animal.discovery.com/tv-shows/other/videos/spy-on- the-wild-basking-shark.htm › http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EukudEBC_hY Hammerhead sharks (sphyrna) Sawsharks (Pristiophorus) Size varies Pygmy shark Whale shark found in tropical waters, are filter feeders Basking shark Great White Bull shark may live in rivers Several sharks are only found in deep water Shark meat is eaten round the world and overfishing is common Sharks still fished for oil and skin and fins used for soup in the Orient 450-550 species Dorsoventrally flattened bodies demersal - fishes that live on the bottom Have gills on their underside (located ventrally) Stingrays: Many species have a whiplike tail Feed on clams, crabs, small fishes and small animals in sediment http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ufxGw8EqY5 Q Electric Rays have special organs, that produce that produce electricity on both sides of their head › Romans and Greeks used them to help headaches and other ailments Skates lay egg cases The larger species are hunted by humans for food Similar to rays in appearance and feeding but lack whip like tail and spines Ratfishes deep water fish, cartilaginous Feed on bottom dwelling crustations and mollusks http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=yCsa-YLTQVQ Have cycloid or ctenoid scales - are flexible, thin, and overlap cycloid scales- smooth ctenoid scales- have many spikes on the exposed borders The scales are made of bone, covered by a thin layer of skin and a protective layer of mucus They have an operculum- a gill cover which is a flap of bony plates and tissue that protects the gills The upper and lower lobes of the caudal fin are generally the same size (homocercal ) Mouth is terminal (located at the anterior end ) Jaws are protrusible, b/c they can be projected outward from the mouth Have a swim bladder- gas filled sack, just above the stomach and intestines allows fish to adjust its buoyancy to keep it stable, compensates for bone skeleton Ichthyology- study of fishes Body shape is directly related to it's lifestyle › fast swimmers have a streamlined shape › Laterally compressed seen on many inshore fish › Many demersal fishes are dorsoventrally flattened some are laterally flattened › eels-like fishes - distinctly elongated › slow fish- elongated vertically, triangular and truncate or round › And random shapes › Body shapes can be used for camouflage Chromatophores - cells where pigments are found structural colors- result when a special surface reflects a certain type of light › Mostly because of crystals that act like little mirrors Some change colors with mood, or reproductive condition › used to advertise that they're dangerous, taste bad, poisonous know as warning coloration, Disruptive coloring- the presence of color stripes, bars or spots used to break up the outline of the fish › common in coral reef fish Open water and shallow water fish are rarely as colorful Deep water fish tend to be either black or red, both are extremely hard to see in the deep ocean Swimming, its needed to... feed, reproduce, escape, to get water through their gills Swimming types…. Swim with side to side motion of either the body or the tail S-shaped contractions produced by bands of muscle called myomeres, which run along the sides the body, attached to the back bone for support Sharks tend to sink, to fix this they have large stiff pectorals that provide lift Oil rich liver Skates and Rays use the pectoral fins to provide the lift Bony fishes have more maneuverability because of swim bladder Dorsal and anal fins are used as rudders and provide stability Some fish like tuna just use sheer speed most sharks are carnivores Nurse shark Cookie cutter shark Lots of cartilaginous fish are filter feeders filter water with gill rakers- slender projections on the inner surface of the gill arches Digestion food passes through the pharynx through the esophagus and into the stomach stomach is typically J-shaped or elongated Food then passes into the intestines Other enzymes are secreted in the walls of the inner walls of the digestive track and in the pancreas Liver secretes bile needed to down fat Carnivorous fish have short straight intestines Fish that eat seaweed have coiled intestines The intestines of cartilaginous fishes contain spiral valve which increases the internal surface area of the intestine the intestine is responsible for absorbing nutrients Undigested material passes through the anus or the cloaca All fishes have a 2 chambered heart that is located below the gills › Sharks have to swim constantly to keep their heart working Nurse shark doesn't have to do this (uses mouth opening and closing to force water through their gills) › In cartilaginous fish every gill lies in its own chamber and each chamber opens to the outside through a separate gill slit The 1st pair of gill slits is modified into spiracles- a pair of round openings just behind each eye, located on the dorsal surface of skates and rays Bony fishes: gills on each side share a common gill chamber that opens to the outside, each opening is covered by an operculum, when the mouth opens the opercula close and the pharynx expands, sucking water in. when the mouth this process is in reverse Gill arches support the gills and each arch has 2 rows of fleshy projections called gill filaments, › Have a red ish color › Each gill filaments have many rows of thin plates called lamellae (they contain capillaries) Surface area Diffusion will only happen if oxygen is more concentrated in the water than in the blood countercurrent system of flow- the blood in the gills flows the opposite way as the water once the oxygen has entered the blood it is carried through the body by hemoglobin, which is a red protein. It is contained in erythrocytes › Muscles also have myoglobin which is similar to hemoglobin. Blood of bony fishes less salty than › Lose water by osmosis, “drink” a lot of water. Salt is extracted by kidneys and chloride cells in the gills. Small concentrated amounts of urine. Cartilaginous fishes making their blood concentration closer to the concentration of seawater. › Retain a chemical called urea, amount in blood is controlled by the kidneys. › “drink” water › Salts are excreted by kidneys, intestines and special gland near anus called rectal gland. Vertebrates have most complicated and advanced nervous systems › Central nervous system, brain and spinal chord coordinates body activities and stores information. › Olfactory sacs, on both sides of the head, used to smell, Each sac opens to the outside through 1 or 2 openings (nares) Have LOTS of taste buds- located in their mouth, lips, fins, and skin. › Found on barbels in many bottom feeders. Eyes- focuses by moving closer or further away from the subject › bony fish depend more on eyesight than cartilaginous fish. Bony fish have colored vision, cartilaginous fish have none or vary little Some sharks have a nictating membrain Lateral line- detect vibrations in the water, system of small canals that runs along head and body, filled with sensory cells (neuromasts) that are sensitive to vibrations. Cartilaginous fishes have ampullae of Lorenzini that can detect weak magnetic electrical fields. Fish also have inner ears- paired hearing organs located to the sides of the brain, just besides the eyes. Set of fluid filled canals that contain sensory The swim bladder can amplify sound. Gives equilibrium and balance. Detect changes in body position from movement of calcareous ear stones or otoliths that rest on sensory hairs