Jawless fishes
advertisement

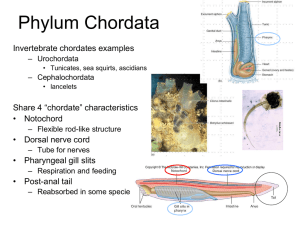
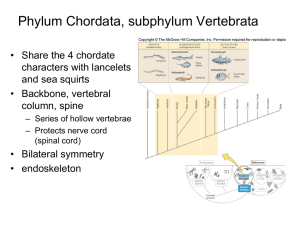
THE FIRST VERTEBRATES Oldest and simplest vertebrates Most abundant vertebrates Three groups of fishes ◦ Jawless fishes ◦ Cartilaginous fishes (Chondrichthyes) ◦ Bony fishes (Osteichthyes) ◦ Yes, it is FISHES- the rule is fish is for a single individual or more than one individual of the same species ◦ FISHES- refers to more than one species Class Agnatha Around 30 known species Includes hagfish & lampreys Feed by suction with aid from teeth No fins, & lack true vertebrae; no scales Body is elongated and cylindrical Most primitive fishes Class Chondrichthyes Skeleton made of cartilage Movable jaws ◦ Mouth ventral Underneath the head Paired lateral fins Sandpaper-like skin because of Placoid Scales Includes sharks, rays, skates, and ratfishes ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ~350 living species Caudal Fin is Heterocercal Powerful jaws with rows of teeth that are Continuously replaced Upper lobe longer than lower lobe Fusiform, or spindle-shaped bodies Five to seven gill slits Carnivores & Filter Feeders Found most often in warm coastal water Most only live in marine env. Some travel upstream ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ ~450-500 known species Dorsoventrally flattened Demersal: fish that live on the bottom Five ventral gill slits Stingrays Electric Rays ◦ Whip-like tail with stinging spines Electric organs on each side of head Skates lack the stinging tail ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Ratfish: AKA Chimaeras ~30 known species Only one pair of gill slits covered by a flap of skin Long, rat-like tail www.itsallaboutfish.co.uk/ratfish.htm Class Osteichthyes ~23,000 known species Skeleton made of bone Cycloid or Ctenoid Scales Operculum: Gill Cover Upper & lower tail fin same size: Homocercal Homocercal tail Cycloid scales Fin Rays: thin membranes supported by bony spine Anterior, terminal mouth More flexible jaws with teeth attached to jawbone Swim Bladder: gas-filled sac above stomach & intestines that helps in buoyancy ICHTHYOLOGY- study of fish Body shape varies with habitat and lifestyle ◦ Fast swimmers are streamlined- like tuna, marlins, mackerels, sharks Dorsoventrally flat- skates, rays and sea moths- demersal fish (live near bottom) Dragon sea moth Image from Liveaquaria.com Laterally flattened bottom dweller fish such as flounder, halibut and sole Born with eyes on both sides of body but as they mature, one eye migrates to the dominant side Elongated bodies such as eels- live in narrow places amongst rock and coral reef Laterally compressed bodies live around coral reefs, kelp beds etc. Butterfly fish snappers CHROMATOPHORES-skin cells that contain pigments; irregular in shape with branches radiating out from the center of the cell STRUCTURAL COLORS-Colors that result when light is reflected by a particular surface ◦ Many times caused by IRIDOPHORESchromatophores with light-reflecting crystals Colors reflect mood ◦ warning coloration- coloration that allows organisms to escape from predators by advertising something harmful or distasteful video ◦ cryptic coloration-color pattern that allows an organism to blend in its surroundings- video ◦ Disruptive coloration- a color pattern that helps break the outline of an organism Ornate cowfish Disruptive coloration COUNTERSHADING- a color pattern that results in a dark back and a light belly- most common in epipelagic fishes (surface to 200 m)