Chordates/ Fish
FISH
Phylum Chordata
Vertebrates
Internal skeletons
Animals which have a spinal cord protected by a backbone
Fish, amphibians, reptiles, birds & mammals
The fish
Live in water
Gills for gas exchange
Fins for locomotion
Skeleton made of cartilage or bone
Most are covered by scales
Cold-blooded – body temp. depends environment on
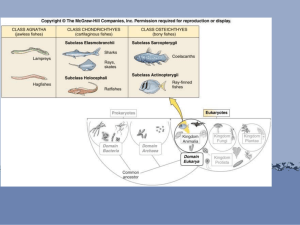
3 classes of fish
1. Jawless fish - agnatha
Oldest group – very primitive
Scale-less skin
Some Parasitic / some filter feed
Circular mouth with fleshy teeth
Cartilaginous skeleton
Hagfish & lamprey
Circular mouth
Gill slits
3 classes of fish
2. cartilaginous fish condrichthyes
Skeleton made of cartilage
Sharks, rays, skates
All are predatory except 4 species!
The 4 exceptions are filter feeders
Whale sharks
– warm shallow water
THE LARGEST FISH IN THE SEA!!!
The 4 exceptions are filter feeders
Basking sharks – cold shallow water
THE SECOND LARGEST FISH IN THE SEA!!!
The 4 exceptions are filter feeders megamouth shark – cold deep water
The 4 exceptions are filter feeders manta ray– shallow warm water
3 classes of fish
3. bony fish - osteichthyes
Skeleton of bone
Most numerous of fish species
Greatest diversity in shape and feeding habits
Sharks, tuna, bluefish
Body forms of fishes
1. fusiform
Streamlined, torpedo shaped
Fast long distance swimmers
Open water predators
Body forms of fishes
2. compressed
Perch, butterfly fish, angelfish
Flattened laterally
Quick bursts of speed - short distance
Easily move in tight spaces
3. depressed
Body forms of fishes
Flounder, fluke, stingray
Dorso-ventrally flattened
Live on the bottom
Eyes on top of body
Body forms of fishes
4. attenuated
Eels, lamprey, pipefish
Elongated, tubular shape
Many Live in holes / burrows
Many secrete heavy mucus
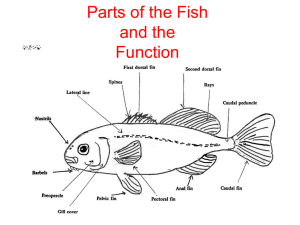
Body parts of fish
Get ready to draw a fish!!!
1. Caudal fin - tail fin
Used for forward motion and acceleration
2. Dorsal fin &
3. Anal fin
Singular fins
Used to prevent rolling/tipping
4. pectoral fin &
5. pelvic fin paired fins ( left & right)
Used to balance, stop & turn
6. Spines Used for protection
Some contain poison sacs
7. operculum Covers & protects gills
Not found in sharks
8. Lateral line
Sensory canals used to detect changes in water pressure around the fish (similar to human ear)
COMPARISON OF
CARTILAGINOUS & BONY FISHES
TRAIT CARTILAGINOUS BONY_____
TUNA, COD, SALMON,
EXAMPLES
SHARKS, RAYS, SKATES
SKELETON
CARTILAGE BONE
SWIM BLADDER
ABSENT – OILY LIVER
PROVIDES BUOYANCY
PRESENT – AIR FILLED
FOR BUOYANCY
COMPARISON OF
CARTILAGINOUS & BONY FISHES
TRAIT CARTILAGINOUS BONY_____
FERTILIZATION
INTERNAL – HAVE FEW LARGE
YOUNG IN LIFE TIME
EXTERNAL – LAY
MILLIONS OF SMALL EGGS
SCALES PLACOID – SPINY EMBEDDED IN
SKIN
GANOID – PLATELIKE
CTENOID & CYCLOID ARE FLAT,
FLEXIBLE, OVERLAP
COMPARISON OF
CARTILAGINOUS & BONY FISHES
TRAIT CARTILAGINOUS BONY_____
GILLS NO OPERCULUM HAVE
GILLS SLITS
HAVE OPERCULUM COVER &
PROTECT GILLS
FEEDING
BEHAVIOR
FINS
TEETH
ALL PREDATORS FOUR
EXCEPTIONS
RIGID AND
UNSEGMENTED
NOT FUSED TO JAW -
REPLACEABLE
GREAT VARIATION IN FOOD
SOURCES
FLEXIBLE AND
SEGMENTED
FUSED TO JAW -
IRREPLACEABLE