Class Amphibia (frogs, toads, salamanders)

Phylum Chordata
(includes the vertebrates)
• i.e. fish, sharks, amphibians, reptiles, birds, mammals
• Notochord, nerve cord, gill slits, tail
Vertebrates
Kingdom Animalia
Phylum Chordata
6 classes:
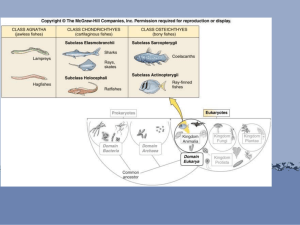
Class Osteichthyes: Bony Fish
Class Chondrichthtyes: Sharks and Rays
Class Amphibia: frogs, toads, salamanders
Class Reptilia: lizards, snakes, turtles, crocadiles
Class Aves: Birds
Class Mammalia: Mammals
Class Osteichtyes: Bony Fish
(salmon, trout, halibut, goldfish!)
•Bony skeleton
•Operculum (gill cover)
•Fish use oxygen in water
•Swim bladder
•Scales
•Aquatic
•Ectotherms
•Ecological roles: mutualism
•Sensitive to pollution: PCBs, pesticides, mercury
•Fish farms
Class Chondrichthyes: Sharks and Rays
•Skeleton made of cartilage
•Oil in liver (no swim bladder)
•Ectotherms
•Placoid scales
•Cloaca
•9 of 250 shark species are man-eaters
•Shark cartilage used for burn victims
•Find prey by electrical fields
•Key predators in the ocean (maintain a balance)
•Relation to cancer, cataracts
Class Amphibia (frogs, toads, salamanders)
•Double life: semi-terrestrial (land and water)
•Young are aquatic, adults mostly on land
•(metamorphosis)
•No scales/Mucus on skin
•Ectotherms
•Frog life cycle
•No amniotic egg
•Difference between frog and toad?
•Declining amphibians?
•Frog calls
•Poison glands
•Warning coloration
Class Reptilia: snakes, lizards, turtles etc
•Scales
•Amniotic egg
•Terrestrial
•No metamorphosis
•Hemi-penis
•Jacobson’s organ (tongue flicking)
•Ectotherms
•Useful predators
•Venemous snakes/pit vipers
•Importance of alligators (keystone species)
Snake Locomotion
1. Lateral Undulation: most common form
Effective in any habitat
Body pressed sideways against substrate
2. Sidewinding: 2-3 points of body in contact with substrate as they pull forward sideways
3. Concertina: loops of the body used
Used in burrow
4. Rectilinear: body in nearly a straight line
Muscles on ribs move scutes
Used by heavy snakes
Class Aves: Birds
•Feathers, scales on legs
•Terrestrial
•Endotherms
•Reptilian ancestors
•No urinary bladder
•Uropigial gland: oil gland at base of tail
•Uric acid
•Archaeopteryx (primitive bird)
•Many ecological roles
•Owl pellets
•illegal pet trade of exotic birds
Archaeopteryx :
An Early Bird
Altricial: helpless and featherless
Sparrow, eagles
Lay less eggs
Precocial: feathered, independent
Ducks
Lay more eggs
Class Mammalia: Mammals
•Terrestrial, although some have returned to the water
•Mammary glands (Milk glands)
•Monotremes: Primitive mammals that lay eggs
(Platypus and echidna)
•Live birth, mouse life cycle
•Endotherms
•Types of mammals:
Placentals (mouse, humans)
Cetaceans (whales and dolphin)
Carnivores (meat eaters such as bears, wolves)
Ungulates (hooved)
A phylogeny showing the relationships among cetacean families.
Reconstruction of Kutchicetus
Reconstruction of Ambulocetus natans
Reconstruction of Pakicetus