How the Internet works
advertisement

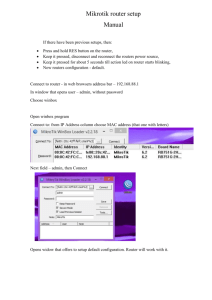
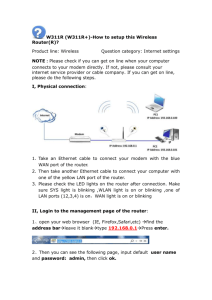
Understanding the Internet I can describe different parts of the Internet. (yr 5) I can tell you the Internet services I need for different purposes. (yr 6) I can describe how information is transported on the Internet. (yr 6) Based on: ‘What is the Internet? How does it work ?’, Helen Greer http://community.computingatschool.org.uk/resources/2114 Modelling the Internet, Barefoot Computing http://barefootcas.org.uk What is the internet? The internet is a vast network of computers and other devices connected together across the planet. The internet is the hardware. http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=WwyJGzZmBe8 There and Back Again: A Packet's Tale - How does the Internet work? Is that all that happens? 1. Web Page Client www.school.org.uk Web Server 1. • Type in a web address on client • Client goes to web server • Sends back web page Is that all that happens? No! 2. Web Page www.school.org.uk Web Server Client LAN /Home Router 2. • Type in a web address on client • Client goes to Home router • Home router goes to web server • Sends back web page Is that all that happens? No! Internet Service Provider (e.g. Talk Talk, BT, Sky) 3. Web Page ISP Router www.school.org.uk Web Server Client LAN/Home Router 3. • Type in a web address on client • Client goes to Home router • Home router goes to ISP • ISP goes to web server • Brings back web page Is that all that happens? No! 4. Internet Service Provider (e.g. Talk Talk, BT, Sky) ISP Router Domain Name Server Web Page 79.110.49.10 www.school.org.uk Web Server Client LAN/Home Router 4. • • • • Type in a web address on client Client goes to Home router Home router goes to ISP ISP takes address to Domain name server • DNS turns web address into IP address to go to correct web server • Sends back web page Is that all that happens? No! 5. Internet Service Provider Domain Name Server Web Page 79.110.49.10 WAN Router ISP Router WAN Router Web Server WAN Router WAN Router www.school.org.uk WAN Router WAN Router WAN Router Client WAN Router WAN Router LAN/Home Router WAN Router 5. • • • • • Type in a web address on client Client goes to Home router Home router goes to ISP ISP takes address to Domain name server DNS turns web address into IP address to go to correct web server • Sends back web page from WAN router to WAN router to WAN router Is that all that happens? No! Internet Service Provider Packets Domain Name Server 79.110.49.10 WAN Router ISP Router WAN Router Web Server WAN Router WAN Router www.school.org.uk WAN Router WAN Router Web Page WAN Router Client WAN Router WAN Router LAN/Home Router WAN Router 6. • • • • • Type in a web address Client goes to Home router Home router goes to ISP ISP takes address to Domain name server DNS turns web address into IP address to go to correct web server • Splits web page into packets • Brings back packets from WAN router to WAN router to WAN router • Puts packets together Is that all that happens? No! 7. Internet Service Provider Domain Name Server Web Page 79.110.49.10 WAN Router ISP Router WAN Router Web Server WAN Router WAN Router www.school.org.uk WAN Router WAN Router WAN Router Client WAN Router WAN Router LAN/Home Router WAN Router 7. • • • • • • • • • Type in a web address on client Client goes to Home router Home router goes to ISP ISP takes address to Domain name server DNS turns web address into IP address to go to correct web server Splits web page into packets Sends back packets from WAN router to WAN router to WAN router finding quickest route if one router isn’t working Puts packets together Is that all that happens? No! But we are getting close! What are clients? Clients are computers setup to access services through the internet. For example, we use a client to view web pages, videos or read emails. Examples of clients include PCs, laptops, mobile phones, some TVs, games consoles and tablet devices. Client Client What are routers? Routers are devices which help information get to where it needs to be across the internet. They route it. To help routers send the information to the correct location, all devices on the internet have an internet protocol (IP) address. Router What are servers? Servers are computers setup to provide internet services, such as the world wide web, e-mail or online games. Some of these computers are web servers - they store information in web pages which is called the WWW. There are also domain name servers (DNS), which we’ll learn more about next. Serve r What are DNS? Domain name servers (DNS) are a type of server which provide the IP address of the web server holding the website you want to view. For example, a DNS could provide the IP address for the server holding the www.barefootcas.org.uk webpage, which is 109.109.131.16. DNS Match the description. A. A computer setup to provide services on the internet. B. A computer used to access services on the internet. Client Server Client C. A computer setup to provide the IP address of web servers holding web pages. Router D. A device used to route information to the correct place on the internet. DNS How can we create a model of the Internet? http://www.bbc.co.uk/guides/z3tbgk7#z9yk87h How will you represent a model of the Internet for your family to understand what happens? Understanding the Internet I can describe different parts of the Internet. (yr 5) I can tell you the Internet services I need for different purposes. (yr 6) I can describe how information is transported on the Internet. (yr 6) Find an IP address http://en.dnstools.ch/visual-traceroute.html Client Server Client http://www.yougetsignal.com/tools/visual-tracert/ Router DNS Who controls the Internet? Fourteen Crypto officers or keyholders have a traditional metal key to a safety deposit box, which in turn contains a smartcard, which in turn activates a machine that creates a new master key. Four times a year a ceremony is held to ‘change the password to the Internet’ - the key which maintains the DNS address book. Seven back-up keyholders with smartcards that contain a fragment of code needed to build a replacement key-generating machine. Once a year, these shadow holders send the organisation that runs the system – the Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers (Icann) – a photograph of themselves with that day's newspaper and their key, to verify that all is well. Who controls your device? MIT Technology review