TEL 355: Communication and Information Systems in Organizations
advertisement

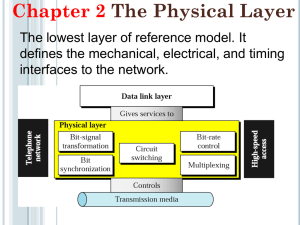
TEL 355: Communication and Information Systems in Organizations Digital Loop Carrier (DLC) Professor John F. Clark Definition of DLC • The local loop is the physical connection between the home or business user and the telco service provider • DLC uses digital technology to offer a wide range of services via copper 2X wires • The development of DLC technology is vital to the future of new online consumer services History of Subscriber Carriers • Loop carrier development originally focused on providing higher quality over longer distances • Was originally deployed in suburban and rural areas. • Relatively few lines and subscribers • Little attention paid to connection methods and signal strength (pair-gain capabilities) Analog Carrier Systems • Designed to provide phone service at distances greater than CO capabilities. • POTS and carrier multiplexer were analog – – – – The advent of electronics in the 60s Multiplexer connected to local exchange switch Subscriber box served 1-8 customers Limited technology, limited deployment • Was difficult to maintain and performance was inconsistent Digital Loop Technology • Early 70s – digital performance benefits – Improved voice quality and higher gain (12 to 1) – Added features: both analog and digital services – Reliable, easy to install and maintain • Architecture was digital on the network end and analog on the subscriber end • 96 line Remote Subscriber Terminal (RST) – Connected to a Local Exchange Terminal – T1 carrier between the terminals Early Next Generation DLCs • In the 80s – based on computer-driven Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI) technology • Primary purpose: deliver services such as – basic and primary rate ISDN – 56k and 64k data rates (DDS) – T1 and other analog services • Designed for fiber from the CO to the RST – Service to 2000 customers per RST • Widespread service was its downfall NGDLC: Rural/Suburban Uses • In the 90s – advanced computing and chip technology makes it possible & economical • Relies on software control and intelligence • Works over any infrastructure – digital T1 or T3, analog, fiber or coax • Based on a mixed network architecture and mesh topology that reflects actual suburban development patterns – its key to success NGDLC Applications • First and foremost – DLC emulation for many remaining analog carriers • Can be implemented a number of ways: – Universal DLC Emulation – old analog carriers – Drop and Insert Configuration – programmable RSTs in any network medium – Star Configuration – radiates T1, fiber, HDSL, or coax facilities – Tree/Mesh Configuration – a mixture of dropand-insert and star topologies Special NGDLC Applications • Integrating voice and video: – Integrated Video/Telephony Point-to-Point – Integrated Video/Telephony Point-to-Multipoint • Hybrid systems that use RF technology to multiplex voice and video over coax and break out voice over 2X for the subscriber • Network flexibility allows any of these configurations to be used with any other for very cost-effective solutions Advantages of NGDLC • Very economical for suburban/rural areas – Cost effective for low line sizes – Low amount of common control overhead – Uses the existing infrastructure • Customers want more service & bandwidth – Means deploying more fiber – Implement the system and upgrade as needed – Pay for upgrades only when implemented Future Directions • Competition between HFC companies and telcos and between different telcos is driving development – especially in xDSL • Increasing use of the Internet and even higher bandwidth services is having an affect on development and on economics • Must supply increasing bandwidth while supporting narrowband economically – migration must be simple and cheap Economics • Equipment must be interchangeable and modular; common control low • Must have minimum frame-relay capability – But not paid for until required • Will move to a three-stage architecture: – – – – Traditional TDM bus for regular traffic SONET bus: 4 or 5 Gbps drop and insert traffic Cell relay bus (ATM) for high bandwidth Common control will handle all three types The Multiservice DLC • Will become a network cloud that includes multiple topologies and protocols • Incorporation of frame relay and ATM figures prominently: OC-12 and OC-48 • Because the high bandwidth infrastructure for this does not exist in many places and may never will, wireless local loop services will be required