theorists
advertisement

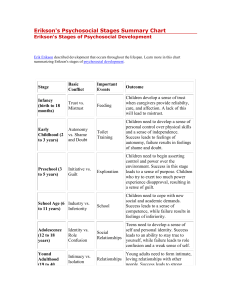
Erik Erickson’s theory of psychosocial development is one of the best-known theories of personality in psychology. Erikson believed that personality develops in a series of stages, and his theory describes the impact of social experience across the whole lifespan. Psychosocial Stage 1 - Trust vs. Mistrust Psychosocial Stage 2 - Autonomy vs. Shame and Doubt Psychosocial Stage 3 - Initiative vs. Guilt Psychosocial Stage 4 - Industry vs. Inferiority Identity vs. Role Diffusion (12—18 years). Intimacy vs. Isolation (young adulthood). Generative vs. Stagnation (adult middle years). Ego Integrity vs. Despair (older years). --1859-1952 • Pragmatism • Traditional and Progressive Education • • • • • • • Humanistic Improving the human condition—societal purposes and individual purposes Teacher-directed Continuity Interaction Learning is active Children should be involved in real-life tasks Progressivism John Dewey John Dewey most famous Protest against Perennialism Instead of books and authoritative teachers, stressed activities, experiences, nature as a classroom Cooperative learning instead of competitive learning developmental psychologist known for his sociocultural perspective Vygotsky posited two types of psychological functioning: "natural," consisting of biological growth, both physical and cognitive development; and "cultural," consisting of learning to use psychological and cultural tools, including signs, symbols, and language He suggested that learning and development are facilitated in a hypothetical region called the zone of proximal development (ZPD). Scaffolding a psychologist and professor at Harvard Graduate School of Education, challenged the view that something called “intelligence” can be objectively measured and reduced to a single number or “IQ” score. definition of intelligence is multifaceted Project Zero, at Harvard intelligence can be learned and improved upon throughout a lifetime. Maria Montessori (1870 - 1952) Student-centered Supports the natural development of children Encourages creativity, problem solving and critical thinking Children develop self-care skills first woman in Italy to qualify as a physician children learn best in a “child-sized” environment stimulating and inviting offers beauty and order child chooses own work activities have meaning and purpose hands-on; self-correcting; sensorial; didactic daily living skills practiced conceptual. Behaviorism BF Skinner BF Skinner, Ivan Pavlov and John Watson – major theorists Free will is an illusion. We are all products of our external environment Operant and Classical Conditioning Positive and Negative Rewards Some would say this is not a true philosophy, but a theory of behavior management Humanistic approach Father of Client-Centered Therapy Realness in the facilitator of learning When an educator is “real” with the student she/he is a more effective teacher. Prizing, acceptance, trust Accepting the students and valuing their opinions and feelings. . Empathic understanding. This creates a climate of self-initiated learning. Cognitive learning Brain based research Differentiation Control theory Constructivism Piaget’s theory of child development Erikson’s 8 stages