Software: Systems and Application Software
advertisement

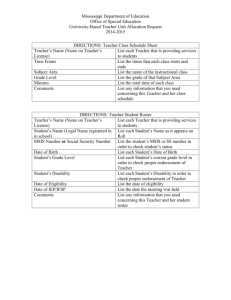
Software: Systems and Application Software Chapter 4 MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 1 Principles and Learning Objectives • When selecting an operating system, you must consider the current and future needs for application software to meet the needs of the organization. In addition, your choice of a particular operating system must be consistent with your choice of hardware. – Identify & describe the functions of the 2 basic kinds of software. – Outline the role of the operating system & identify the features of several popular operating systems. MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 2 Principles and Learning Objectives • Do not develop proprietary application software unless doing so will meet a compelling business need that can provide a competitive advantage. – Discuss how applications software can support personal, workgroup, and enterprise business objectives. – Identify 3 basic approaches to developing applications software and discuss the pros and cons of each. MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 3 Principles and Learning Objectives • Choose a programming language whose functional characteristics are appropriate to the task at hand, taking into consideration the skills and experience of the programming staff. – Outline the evolution of programming languages. • The software industry continues to undergo constant change; users need to be aware of recent trends and issues to be effective in their business and personal life. – Differentiate among the five generations of programming languages. MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 4 An Overview of Software • Computer program - sequences of instructions for the computer • Documentation - describes program functions • Systems software - coordinates the activities of hardware & programs • Applications software - helps users solve particular problems MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 5 The Importance of Software in Business MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 6 Supporting Individual, Group, and Organizational Goals MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 7 Operating Systems MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 8 Operating Systems • • • • • • • Perform common hardware functions Provide a user interface Provide hardware independence Manage system memory Manage processing Control access to system resources Manage files MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 9 The Role of the Operating System MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 10 Common Hardware Functions • Accept keyboard input • Store data on disks • Send data to output devices MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 11 User Interface • Command-based interfaces • Graphical User Interfaces (GUIs) MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 12 Hardware Independence MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 13 Memory Management MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 14 Processing Tasks • Multitasking - more than one program can run at a time using a single processor • Time-sharing - multiple users can simultaneously use the resources of a single processor • Scalability - easy adaptation to more users or tasks MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 15 Access to System Resources • Protection against unauthorized access • Logins and passwords MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 16 Personal Computer Operating Systems MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 17 Personal Computer Operating Systems MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 18 Workgroup Operating Systems • • • • • • Netware Windows NT Server 4.0 Windows 2000 Server Unix Red Hat Linux Mac OS X Server MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 19 Enterprise Operating Systems • IBM’s OS/390 • HP’s MPE/iX (Multiprogramming Executive with integrated POSIX) • IBM’s z/OS • Linux MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 20 Consumer Appliance Operating Systems • • • • • • Windows CE.NET Mobil Linux Windows XP Embedded Handheld PC Pocket PC Palm OS MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 21 Nokia 7650 MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 22 Utility Programs MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 23 Types and Functions of Applications Software MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 24 Sources of Software MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 25 Comparison of Proprietary and Off-the-Shelf Software MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 26 Personal Application Software MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 27 Personal and Application Software MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 28 Personal and Application Software MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 29 TurboTax MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 30 Quicken MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 31 Word Processing MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 32 Spreadsheet Analysis MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 33 Database Applications MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 34 Graphics Programs MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 35 On-Line Information Systems MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 36 Software Suite MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 37 Major Components of Leading Software Suites MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 38 Workgroup Application Software • Groupware • Collaborative computing software MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 39 Group Scheduling MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 40 Examples of Enterprise Application Software MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 41 Enterprise Application Software MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 42 Selected Enterprise Resource Vendors MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 43 Programming Languages • Commands and statements combined according to a particular syntax • Different languages have different characteristics MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 44 Programming Languages MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 45 First-Generation Languages • Machine language • ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange) MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 46 Second-Generation Languages • Assembly languages • Assemblers • Symbolic language MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 47 Third-Generation Languages MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 48 Fourth-Generation Languages • 4GLs • Programs tell the CPU the desired results, not how to get them • Examples: SQL, SAS MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 49 Fifth-Generation Languages • 5GLs • Uses a visual or graphical development interface to create source language • Examples: Visual Basic, PC COBOL, and Visual C++ MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 50 Object-Oriented Programming Languages • Objects - data and actions that can be performed on the data • Encapsulation - group items into an object • Polymorphism - one procedure can work with multiple objects • Inheritance - an object in a particular class gets attributes of that class MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 51 Object-Oriented Programming Languages MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 52 Software Issues & Trends • • • • • • Software bugs Open source software Software licensing Software upgrades Global software support Antitrust issues for software MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 53 How to Deal with Software Bugs MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 54 Summary • Software - consists of programs that control the workings of the computer hardware • Operating system - set of computer programs that controls the computer hardware • Application - software that applies the power of the computer to solve problems and perform specific tasks • Programming languages - provide instructions to a computer to perform some processing activity MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 55