Development of the Nervous System
advertisement

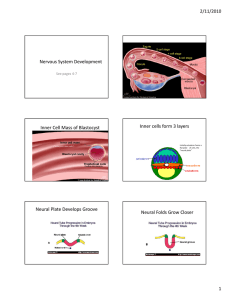
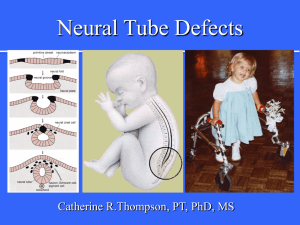
Development of the Nervous System Lesson 4 Development of the Brain Adult brain structure product of… Genetic instructions Cell-to-cell signals Interaction b/n child and external world Early development Before synaptogenesis Activity-independent Critical periods ~ Gastrulation & Neuralation Gastrulation Invagination of embryo single sheet of cells 3 cell layers Formation of notocord Neuralation Induction signals from notocord… To neuroectoderm Growth of neural precursor cells~ Neural Induction Induction signals From embryonic tissue Modulate gene expression Retinoic acid Steroid hormone Peptide hormones Fibroblast growth factor (FGF) Transforming growth factor (TGF) Sonic hedge hog (shh) ~ Retinoic Acid – Jekyl & Hyde? Vitamin A derivative Too little abnormal development Too much abnormal development Inductive signal Critical period Localization ~ Sonic Hedge Hog (SHH) Induction of motor neurons Mutations diseases Holoprosencephaly (1/16 k births) Prevents bilateral development Division of hemispheres facial features (cyclopean eye) Medulloblastoma Most common childhood tumor Basal cell carcinomas of skin 750 k/yr ~ Embryological Origin Embryo has 3 layers endoderm internal organs mesoderm muscles & skeleton ectoderm nervous system & skin ~ Embryological Origin At 18 days Neural plate forms sheet of cells At 20 days Neural groove folds rostral to caudal will form tube ~ Development of N.S. At 22 days Neural tube CNS develops from walls spina bifida - caudal tube fails to close as tube develops dorsal portion pinches off & forms...~ Development of N.S. At 24 days Neural crest develops into all neurons of PNS Mesoderm somites vertebrae & muscles ~ Differentiation Specialization of structures 3 primary vesicles rostral end of tube develops into brain Prosencephalon forebrain Mesencephalon midbrain Rhombencephalon hindbrain ~ Prosencephalon Secondary vesicles form & separate optic retinas retina & optic nerve CNS not PNS telencephalic telencephalon remainder diencephalon ~ Other Primary Vesicles Mesencephalic mesencephalon dorsal - tectum ventral - tegmentum tube - cerebral aqueduct Rhombencephalic rostral - metencephalon caudal - myelencephalon tube - 4th ventricle ~ Neural Tube Defects: Rostral Neural tube fails to close anencephaly skull & brain partially or totally absent perinatal mortality Encephalocele parts of brain protrude outside skull mental disability depends on extent ~ Neural Tube Defects: Caudal Spina Bifida Cleft spine Spina bifida occulta 40% of Americans Spina Bifida Manifesta 1 in a 1000 births 0.1% ~ Occulta Spina Bifida Manifesta Meningocele (*4%) SC/nerves not in sac less severe, repaired Myelomeningocele (*96%) SC/ nerves in protruding paralysis, incontinence, learning disabilities hydrocephalus can cause severe brain damage ~ Neural Tube Defects: Prevention Possible genetic component reoccurrence in families ethnic/racial relationship Folic Acid (Folate) Deficiency 50-70% of cases preventable CDC guidelines not planning pregnancy: 400 mg/day planned pregnancy: 4000 mg/day under direction of health care provider ~