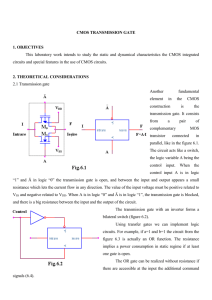
DE_UNIT _I - WordPress.com
advertisement

UNIT I: DIGITAL LOGIC FAMILIES Q.1) In a positive logic system, logic state 1 corresponds to A. positive voltage B. higher voltage level C. zero voltage level D. lower voltage level Answer: Option B Q.2) …….. are used to perform digital operations such as AND ,OR, NOT, etc. A. Switches B. Amplifiers C. Rectifiers D. Waveform generators Answer: Option A Q.3) A logic gate is an electric circuit which A. Makes logic decisions B. Allows electron flow only inone direction C. Works on binary algebra D. Alternates between 0 & 1 valves. Answer: Option A Q. 4) A NOR gate is ON only when all its inputs are A. ON B. Positive C. High D. OFF Answer: Option D Q.5) For getting an output from an XNOR gate, its both inputs must be A. High B. Low C. At the same logic level D. At the opposite level Answer: Option C Q.6) In a certain 2 input logic gate, when A=0, B=0 then C=1 . It must be …….. gate A. XOR B. AND C. NAND D. NOR Answer: Option C Q.7) Boolean algebra is essentially based on A. Symbols B. Logic C. Truth D. Numbers Answer: Option B Q.8) Saturaed logic circuit have inherently A. Short saturation delay time B. Low switching speed C. Higher power dissipation D. Lower noise immunity Answer: Option A Q.9) Schottky transistors are preferred over normal transistors in digital circuits because of their….. A. Lower propagation Delay B. Higher Propagation Delay C. Lower power dissipation D. Higher power dissipation Answer: Option A Q.10) The number of inputs the gate is designed to handle is called A. fan-out B. fan-in C. noise margin D. none of these Answer: Option B Q.11) The time needed for an output to change from the result of an input change is known as: A. noise immunity B. fan-out C. propagation delay D. rise time Answer: Option C Q.12) The rise time (tr) is the time it takes for a pulse to rise from its ________ point up to its ________ point. The fall time (tf) is the length of time it takes to fall from the ________ to the ________ point. A. 10%, 90%, 90%, 10% B. 90%, 10%, 10%, 90% C. 20%, 80%, 80%, 20% D. 10%, 70.7%, 70.7%, 10% Answer: Option A Q.13) Ten TTL loads per TTL driver is known as: A. noise immunity B. fan-out C. power dissipation D. propagation delay Answer: Option B Q.14) How is the speed–power product of a logic family determined? A. The propagation delay in s is multiplied by the power dissipation in mW. B. The propagation delay in ms is multiplied by the power dissipation in C. The propagation delay in ns is multiplied by the power dissipation in mW. D. The propagation delay in ns is multiplied by the power dissipation in Answer: Option C Q.15) How is the noise margin of a logic family defi ned? A. VOH – VOL B. greater of VDD – VOH and VOL – GND C. smaller of VIL – VOL and VOH – VIH D. VIH – VIL. Answer: Option C Q.16) The NAND gate output will be low if the two inputs are A. 00 B. 01 C. 10 D. 11 Ans: D The NAND gate output will be low if the two inputs are 11 (The Truth Table of NAND gate is shown in Table.1.1) X(Input) Y(Input) F(Output) 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 0 Table 1.1: Truth Table for NAND Gate Q.17) A "floating" TTL input may be defined as: A. B. unused input that is tied to Vcc through a 1 k unused input that is tied to used inputs. resistor. W. W. C. unused input that is tied to the ground. D. unused input that is not connected. Answer: Option D Q.18) A TTL circuit acts as a current sink in the A. Low state B. High state C. High impedance state D. None of these Answer: Option A Q.19) A TTL circuit acts as a current source in the A. Low state B. High state C. High impedance state D. None of these Answer: Option B Q.20) What is the standard TTL noise margin? A. 5.0 V B. 0.0 V C. 0.8 V D. 0.4 V Answer: Option D Q.21) Why is the operating frequency for CMOS devices critical for determining power dissipation? A. At low frequencies, power dissipation increases. B. At high frequencies, the gate will only be able to deliver 70.7 % of rated power. C. At high frequencies, charging and discharging the gate capacitance will draw a heavy current from the power supply and thus increase power dissipation. D. At high frequencies, the gate will only be able to deliver 70.7 % of rated power and charging and discharging the gate capacitance will draw a heavy current from the power supply and thus increase power dissipation. Answer: Option C Q.22) An open collector output can ________ current, but it cannot ________. A. sink, source current B. source, sink current C. sink, source voltage D. source, sink voltage Answer: Option A Q.23) Using the schematic diagram of a TTL NAND gate, determine the state of each transistor (ON or OFF) when all inputs are high. A. Q1-ON, Q2-OFF, Q3-ON, Q4-OFF B. Q1-ON, Q2-ON, Q3-OFF, Q4-OFF C. Q1-OFF, Q2-OFF, Q3-ON, Q4-ON D. Q1-OFF, Q2-ON, Q3-OFF, Q4-ON Answer: Option D Q.24) If all inputs to a TTL NAND gate are low, what is the ON, OFF condition of each transistor in the circuit? A. Q1-ON, Q2-OFF, Q3-ON, Q4-OFF B. Q1-ON, Q2-ON, Q3-OFF, Q4-OFF C. Q1-OFF, Q2-OFF, Q3-ON, Q4-ON D. Q1-OFF, Q2-ON, Q3-OFF, Q4-ON Answer: Option A Q.25) A universal logic gate is one, which can be used to generate any logic function. Which of the following is a universal logic gate? A. OR B. AND C. XOR D. NAND Answer: Option D NAND can generate any logic function. Q.26) What should be done to unused inputs on TTL gates? A. They should be left disconnected so as not to produce a load on any of the other circuits and to minimize power loading on the voltage source. B. All unused gates should be connected together and tied to V<sub<cc< sub=""> through a 1 k resistor.</sub<cc<> C. All unused inputs should be connected to an unused output; this will ensure compatible loading on both the unused inputs and unused outputs. D. Unused AND and NAND inputs should be tied to VCC through a 1 k unused OR and NOR inputs should be grounded. resistor; Answer: Option D Q.27) In digital ICs, Schottky transistors are preferred over normal transistors because of their A. Lower Propagation delay. B. Higher Propagation delay. C. Lower Power dissipation. D. Higher Power dissipation. Answer: Option A Lower propagation delay as shottky transistors reduce the storage time delay by preventing the transistor from going deep into saturation. Q.28) Which logic family is characterized by a multiemitter transistor on the input? A. ECL B. CMOS C. TTL D. None of the above Answer: Option C Q.29) What is unique about TTL devices such as the 74S00? A. The gate transistors are silicon (S), and the gates therefore have lower values of leakage current. B. The S denotes the fact that a single gate is present in the IC rather than the usual package of 2–6 gates. C. The S denotes a slow version of the device, which is a consequence of its higher power rating. D. The devices use Schottky transistors and diodes to prevent them from going into saturation; this results in faster turn on and turn off times, which translates into higher frequency operation. Answer: Option D Q.30) Refer to the figure given below. What type of device is shown and what input levels are required to turn the LED off? A. The device is an open-collector AND gate and requires both inputs to be HIGH in order to turn the LED off. B. The device is a Schottky AND gate and requires only one low input to turn the LED off. C. The device is an open-collector AND gate and requires only one low input to turn the LED off. D. The device is a Schottky open-collector AND gate and requires a low on both inputs to turn the LED off. Answer: Option A Q.31) A TTL totem-pole circuit is designed so that the output transistors: A. are always on together B. provide linear phase splitting C. provide voltage regulation D. are never on together Answer: Option D Q.32) Why is a pull-up resistor needed for an open collector gate? A. to provide Vcc for the IC B. to provide ground for the IC C. to provide the HIGH voltage D. to provide the LOW voltage Answer: Option C Q.33) Why is a pull-up resistor needed when connecting TTL logic to CMOS logic? A. to increase the output LOW voltage B. to decrease the output LOW voltage C. to increase the output HIGH voltage D. to decrease the output HIGH voltage Answer: Option C Q.34) An open collector output can ________ current, but it cannot ________. A. sink, source current B. source, sink current C. sink, source voltage D. source, sink voltage Answer: Option A Q.35) What type of circuit is shown below, and how is the output ordinarily connected? A. It is an open-collector gate and is used to drive loads that cannot be connected directly to Vcc due to high noise levels. B. It represents an active-LOW inverter and is used in negative logic systems. C. It is an open-collector gate. An external load must be connected between the output terminal and an appropriate supply voltage. D. Any of the above could be correct, depending on the specific application involved. Answer: Option C Q.36) Refer to the given figure. What type of output arrangement is being used for the output? A. Complementary-symmetry B. Push-pull C. Quasi push-pull D. Totem-pole Answer: Option D Q.37) What type of circuit is represented in the given figure, and which statement best describes its operation? A. It is a tristate inverter. When the ENABLE input is HIGH, the output is effectively an open circuit—it is neither LOW nor HIGH. B. It is a programmable inverter. It can be programmed to function as either an active LOW or an active HIGH inverter. C. It is an active LOW buffer, which can be turned on and off by the ENABLE input. D. None of the above. Answer: Option A Q.38) The word "interfacing" as applied to digital electronics usually means: A. a conditioning circuit connected between a standard TTL NAND gate and a standard TTL OR gate B. a circuit connected between the driver and load to condition a signal so that it is compatible with the load C. any gate that is a TTL operational amplifier designed to condition signals between NMOS transistors D. any TTL circuit that is an input buffer stage Answer: Option B Q.39) What type of logic circuit is shown below and what logic function is being performed? A. It is an NMOS AND gate. B. It is a CMOS AND gate. C. It is a CMOS NOR gate. D. It is a PMOS NAND gate. Answer: Option C Q.40) What type of circuit is shown below and which statement best describes its operation? A. It is a two-input CMOS AND gate with open drain. B. It is a two-input CMOS buffer with tristate output. C. It is a CMOS inverter with tristate output. D. It is a hybrid TTL-CMOS inverter with FET totem-pole output. Answer: Option C Q.41) CMOS circuits consume power A. Equal to TTL B. Less than TTL C. Twice of TTL D. Thrice of TTL Answer: Option B As in CMOS one device is ON & one is Always OFF so power consumption is low. Q.42) The output of a logic gate is 1 when all its inputs are at logic 0. the gate is either A. a NAND or an EX-OR B. an OR or an EX-NOR C. an AND or an EX-OR D. a NOR or an EX-NOR Answer: Option D The output of a logic gate is 1 when all inputs are at logic 0. The gate is either a NOR or an EX-NOR . Q.43) Which family of devices has the characteristic of preventing saturation during operation? A. TTL B. MOS C. ECL D. IIL Answer: Option C Q.44) What must be done to interface TTL to CMOS? A. A dropping resistor must be used on the CMOS 12 V supply to reduce it to 5 V for the TTL. B. As long as the CMOS supply voltage is 5 V, they can be interfaced; however, the fan-out of the TTL is limited to five CMOS gates. C. A 5 V Zener diode must be placed across the inputs of the TTL gates in order to protect them from the higher output voltages of the CMOS gates. D. A pull-up resistor must be used between the TTL output-CMOS input node and Vcc; the value of RP will depend on the number of CMOS gates connected to the node. Answer: Option D Q.45) The problem of different current requirements when CMOS logic circuits are driving TTL logic circuits can usually be overcome by the addition of: A. a CMOS inverting bilateral switch between the stages B. a TTL tristate inverting buffer between the stages C. a CMOS noninverting bilateral switch between the stages D. a CMOS buffer or inverting buffer Answer: Option D Q.46) What is the advantage of using low-power Schottky (LS) over standard TTL logic? A. more power dissipation B. less power dissipation C. cost is less D. cost is more Answer: Option B Q.47) What causes low-power Schottky TTL to use less power than the 74XX series TTL? A. The Schottky-clamped transistor B. Nothing. The 74XX series uses less power. C. A larger value resistor D. Using NAND gates Answer: Option C Q.48)What is the difference between the 74HC00 series and the 74HCT00 series of CMOS logic? A. The HCT series is faster. B. The HCT series is slower. C. The HCT series is input and output voltage compatible with TTL. D. The HCT series is not input and output voltage compatible with TTL. Answer: Option C Q.49) How does the 4000 series of CMOS logic compare in terms of speed and power dissipation to the standard family of TTL logic? A. more power dissipation and slower speed B. more power dissipation and faster speed C. less power dissipation and faster speed D. less power dissipation and slower speed Answer: Option D Q.50) What is unique about TTL devices such as the 74SXX? A. These devices use Schottky transistors and diodes to prevent them from going into saturation; this results in faster turn-on and turn-off times, which translates into higher frequency operation. B. The gate transistors are silicon (S), and the gates therefore have lower values of leakage current. C. The S denotes the fact that a single gate is present in the IC rather than the usual package of 2–6 gates. D. The S denotes a slow version of the device, which is a consequence of its higher power rating. Answer: Option A Q.51) Which of the following logic families has the shortest propagation delay? A. CMOS B. BiCMOS C. ECL D. 74SXX Answer: Option C Q.52) What does ECL stand for? A. It stands for electron-coupled logic; all of the devices used within the gates are Ntype transistors. B. It stands for emitter-coupled logic; all of the inputs are coupled into the device through the emitters of the input transistors. C. It stands for emitter-coupled logic; all of the emitters of the input transistors are connected together and each transistor functions as an emitter follower. D. It stands for energy-coupled logic; the input energy is amplified by the input transistors and allows the device to deliver higher output currents. Answer: Option C Q.53) Which of the following logic families has the highest noise margin? A. TTL B. LS TTL C. CMOS D. HCMOS Answer: Option D Q.54) Why is the fan-out of CMOS gates frequency dependent? A. Each CMOS input gate has a specific propagation time and this limits the number of different gates that can be connected to the output of a CMOS gate. B. When the frequency reaches the critical value, the gate will only be capable of delivering 70% of the normal output voltage and consequently the output power will be one-half of normal; this defines the upper operating frequency. C. The higher the number of gates attached to the output, the more frequently they will have to be serviced, thus reducing the frequency at which each will be serviced with an input signal. D. The input gates of the FETs are predominantly capacitive, and as the signal frequency increases the capacitive loading also increases, thereby limiting the number of loads that may be attached to the output of the driving gate. Answer: Option D Q.55) What is the major advantage of ECL logic? A. very high speed B. wide range of operating voltage C. very low cost D. very high power Answer: Option A Q.56) The digital logic family which has minimum power dissipation is A. TTL B. RTL C. DTL D. CMOS Answer: Option D The digital logic family which has minimum power dissipation is CMOS. (CMOS being an unipolar logic family, occupy a very small fraction of silicon Chip area) Q.57) CMOS circuits are extensively used for ON-chip computers mainly because of their extremely A. low power dissipation. B. high noise immunity. C. large packing density. D. low cost. Answer: Option C Because CMOS circuits have large packing density. Q.58) Which of following consume minimum power A. TTL. B. CMOS. C. DTL. D. RTL. Answer: Option B CMOS consumes minimum power as in CMOS one p-MOS & one n-MOS transistors are connected in complimentary mode, such that one device is ON & one is OFF. Q.59) The logic family which gives complementary output is A. B. C. D. TTL ECL CMOS MOS Answer: Option B Q.60) The logic family preffered in superfast computers is A. B. C. D. TTL ECL IIL MOS Answer: Option B Q.61) The Ics used in watches & calculators are of s A. B. C. D. TTL ECL CMOS MOS Answer: Option C Q.62) Special feature of I2L logic circuit is that it A. uses only high value resistors B. dissipates negligible power C. is a bipolar saturated logic D. uses no biasing & loading resistors Answer: Option C Q.63) A unique advantage of CMOS logic family is its A. Use of NMOS circuits B. Power dissipation is in nanowatt range C. Speed D. dependence on frequency for power dissipation Answer: Option B Q.64) CMOS circuits are extensively used for one chip computers mainly because of their extremely A. low power dissipation B. large packing density C. high noise immunity D. low cost Answer: Option B Q.65) Power is drawn by a CMOS circuit only when A. its output is high B. its output is low C. it switches logic levels D. in static state Answer: Option C Q.66) Noise Margin is expressed in A. decibel B. watt C. volt D. phon Answer: Option C Q.66) DTL family employs A. resistors & transistors B. Diode & resistor C. Diode & transistor D. diode , resistors & transistors Answer: Option D Q.67) The chief advantage of schotty TTL logic family is its least A. power dissipation B. propagation delay C. fan in D. Noise immunity Answer: Option B Q.68) The main advantage claimed for ECL family of logic gates is its A. very large fan in B. use of negative power supply voltage C. extremely low propagation times D. least power dissipation Answer: Option C Q.69) The main advantage of a CMOS logic family over the TTL family is its A. much reduced power B. increased speed of operation C. extremely low cost D. series base resistor Answer: Option A Q.70) CMOS logic family uses only A. MOSFETs & Resistors B. NMOS circuits C. MOSFETs D. bipolar transistors Answer: Option C Q.71) The most obvious identifying feature of a TTL gate is its A. large fan-out B. high power dissipation C. interconnected transistors D. multiemitter input transistor Answer: Option D Q.72) In digital circuits schottky transistors are preffered over normal transistor because of their A. lower propagation delay B. higher propagation delay C. lower power dissipation D. higher power dissipation Answer: Option A Q.73) A unique operating feature of ECL circuit is its A. very high speed B. high power dissipation C. series base resistor D. compatibility with other logic series Answer: Option A Q.74) The fan – in a logic gate refers to the number of A. input devices that can be connected B. input terminals C. output terminals D. circuits output can drive Answer: Option B Q.75) which of the following statements regarding Ics is not correct A. ECL has the least propagation delay B. TTL has the largest fan out C. CMOS has the biggest noise margin D. TTL has the lowest power consumption Answer: Option D Q.76) Which of the following is an inverter? A. Common base amplifier B. Common collector amplifier C. Common emitter amplifier D. All of the above Answer: Option C Q.77) If a NAND latch has a 1 on the SET input & a 0 on the CLEAR input, then the SET input goes to 0, the latch will be: A. High B. Low C. Invalid D. Noneof these Answer: Option A