Chapter 3 - Geekysol.in
advertisement

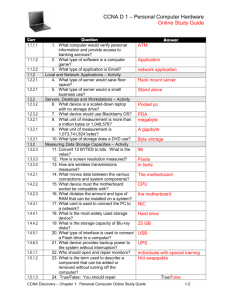
Motherboards Chapter 3 Release 22/10/2010 powered by dj Objectives List the types of motherboards Identify the motherboard form factor Identify the components of the motherboard Explain the use of chipsets List the types of chipsets Configure the motherboard Install the motherboard Troubleshoot the motherboard Chapter 3 Release 22/10/2010 Slide 2 of 60 powered by dj Types of Motherboards - I Integrated motherboards – Have all peripheral device slots, input output ports, serial and parallel ports mounted on the board. Saves space and cheaper as compared to non-integrated motherboards. Non-Integrated motherboards – Have RAM slots integrated on the board. All the I/O ports such as serial and parallel port connectors, other controllers such as hard drive and floppy disk drives controllers are attached to the system using expansion boards Chapter 3 Release 22/10/2010 Slide 3 of 60 powered by dj Types of Motherboards - II Desktop Motherboards – Used in personal computers and desktops Server Motherboards– Designed to offer high-end services and supports various redundancy technologies Laptop Motherboards– Have very advanced features, as compared to the desktop motherboards Chapter 3 Release 22/10/2010 Slide 4 of 60 powered by dj Question for GD Time Limit – 2 Mins What are the different types of motherboard? Sl. Types of Motherboard 1 2 3 Chapter 3 Release 22/10/2010 Slide 5 of 60 powered by dj Form Factors of Motherboard Refers to motherboards physical shape, layout and positioning of components on it Determines the type of system case it will fit into Chapter 3 Release 22/10/2010 Slide 6 of 60 powered by dj Modern Form Factor - I Types of modern form factors: • ATX – Popular and has best features of LPX and AT form factors • Micro ATX – Limited expandability and capacity • NLX – New addition to motherboard form factors, easier assembly, reduced cost, space efficiency and flexibility Chapter 3 Release 22/10/2010 Slide 7 of 60 powered by dj Modern Form Factor - II BTX - BTX form factor was introduced as a replacement for the ATX form factor in the year 2003. Supports better thermal management. This form factor was introduced to support the new emerging technologies such as SATA and USB 2.0. Chapter 3 Release 22/10/2010 Slide 8 of 60 powered by dj Question for GD Time Limit – 2 Mins What is form factor? List the types of form factor. Sl. Types of Form factor 1 2 3 4 5 Chapter 3 Release 22/10/2010 Slide 9 of 60 powered by dj Components of a Motherboard Motherboard contains slots, sockets and connectors for connecting various devices Contains super I/O chip, slots for connecting various peripheral devices Chapter 3 Release 22/10/2010 Slide 10 of 60 powered by dj Connectors – I and show from CBT System panel connector USB headers Digital audio connector MDC connector – connects to modem card module Internal audio connectors – conents to CD ROM or voice modem card GAME/MIDI connector System Management Bus (SMBus) connector Chapter 3 Release 22/10/2010 Slide 11 of 60 powered by dj Connectors - II ATX 12V connector ATX Power Connector CPU and chassis fan connectors Serial Advanced Technology Attachment (SATA) connectors IDE connectors Serial port connector Chapter 3 Release 22/10/2010 Slide 12 of 60 powered by dj On Board Disk Drive Connectors Hard drive and DVD-ROM drive is connected to motherboard using on-board disk drive connectors Primary connector used to connect storage devices is the Integrated Drive Electronics (IDE) port Serial Advanced Technology Attachment (SATA) technology is used to connect the newer versions of hard drive Chapter 3 Release 22/10/2010 Slide 13 of 60 powered by dj Keyboard and Mouse Connector Keyboard and mouse device are connected to (Personal System) PS/2 or USB port of computer Ports are located at the back side of the system PS/2 port contains 6 holes and a notch in the middle Chapter 3 Release 22/10/2010 Slide 14 of 60 powered by dj Other Connectors Power Supply Connector – Types of power connectors used by various power supplies are ATX power supply connector, ATX auxiliary power connector and ATX 12V connector Serial and Parallel Port Connector – 9 pin serial port connector and 25 pin parallel port connector are used to connect various I/O devices Universal Serial Bus (USB) - Offers Plug-andPlay support and also supplies power to the device Chapter 3 Release 22/10/2010 Slide 15 of 60 powered by dj Question for GD Time Limit – 4 Mins List the different connectors available on the motherboard and it’s use. Sl. Connectors Chapter 3 Release 22/10/2010 Slide 16 of 60 powered by dj Expansion Slots Motherboard has PCI slots where you can connect PCI cards. Different PCI cards include LAN card, SCSI card and USB card Extend the capacity of the existing motherboard AGP slot is used to attach a graphic card PCI express or PCI-E is the latest Peripheral Component Interconnect Special Interest Group’s specification for the I/O bus. Chapter 3 Release 22/10/2010 Slide 17 of 60 powered by dj CNR Expansion Slot Communication and Network Riser is a slot found on certain PC motherboards. Intel developed this slot to replace AMR design. Used for specialized networking, audio and telephony equipments Chapter 3 Release 22/10/2010 Slide 18 of 60 powered by dj Peripheral Component Interconnect (PCI) Slot Bus standard developed by Intel Corporation Used for attaching peripheral devices to motherboard Slots work at 33 MHz newer variants are available that have a 64-bit wide bus and work at 33 MHz or 66 MHz Data Transmission Rate of PCI is 133 MBps Chapter 3 Release 22/10/2010 Slide 19 of 60 powered by dj PCI Extended (PCI-X) PCI Extended (PCI-X) is a standard designed jointly by HP, IBM, and Compaq Increase the performance of high-bandwidth devices, such as Gigabit Ethernet and Fibre Channel Fully backward compatible with PCI and data transmission rate is 1GBps Comes in two variants: PCI-X 1.0 and PCI-X 2.0 Chapter 3 Release 22/10/2010 Slide 20 of 60 powered by dj PCI Express (PCI-E) - I PCIe 2.0 doubles bandwidth from 0.25 GByte/s to 0.5 GByte/s, meaning a x32 connector can transfer data at up to 16 GByte/s for both video cards PCIe 2.0 have two 32 bits channels for each GPU (2x16), while first version only 1x16 and operating at 2 GHz. PCIe 2.0 is backward compatible with PCIe v1.x. Having point-to-point, hot-pluggable and hotswappable system bus Chapter 3 Release 22/10/2010 Slide 21 of 60 powered by dj PCI-E - II PCIe 3.0 include a number of optimizations for enhanced signaling and data integrity, including transmitter and receiver equalization and clock data recovery. PCIe 3.0's 8 GT/s bit rate effectively delivers double PCIe 2.0 (5GT/s) bandwidth. Chapter 3 Release 22/10/2010 Slide 22 of 60 powered by dj AGP Slot Accelerated Graphics Port (AGP) is used to display graphics and 3D images in efficient manner Offers high data transfer speed between the video chipset and the CPU AGP cards are available at different speeds, AGP 1x, 2x, 4x, 8x Operate in a voltage of 1.5 to 3.3 volts Chapter 3 Release 22/10/2010 Slide 23 of 60 powered by dj Question for GD Time Limit – 3 Mins List the different expansion slots available on a motherboard. Sl. Types of slots Chapter 3 Release 22/10/2010 Slide 24 of 60 powered by dj Jumpers Small pins that enable you to configure motherboard settings Performs different functions when it is shorted and when it is left open, without the shunt Motherboard manual is a necessity when you deal with jumpers Motherboards may have jumpers to set processor type, system recovery option, over clocking and to discharge the CMOS RAM battery Most of the motherboards currently available in the market have auto jumper setup option Chapter 3 Release 22/10/2010 Slide 25 of 60 powered by dj Practical Perform the activity mentioned in Lab no. 1 in the text book: • To identify various connectors, expansion slots, and jumpers on the motherboard. Chapter 3 Release 22/10/2010 Slide 26 of 60 powered by dj Onboard Components – I and show from CBT CPU socket Northbridge Southbridge DDR DIMM sockets Super I/O controller Flash ROM Standby Power LED Audio CODEC LAN controller Chapter 3 Release 22/10/2010 Slide 27 of 60 powered by dj Onboard Components – II Mouse port Parallel port LAN port Line In jack Line Out jack Microphone jack USB ports Video port Serial port Keyboard port Chapter 3 Release 22/10/2010 Slide 28 of 60 powered by dj Memory Slots Provide an interface for attaching RAM on the board. RAM module is inserted in these slots. Most of the motherboards come equipped with at least 2 memory slots. Maximum number of slots available depends on the motherboard. Most Memory slots are Double Inline Memory Module (DIMM) type. Chapter 3 Release 22/10/2010 Slide 29 of 60 powered by dj CPU Socket Interface that connects CPU with motherboard Consists of holes in which the pins of the processor are installed Sockets are used with particular type of processor Sockets already installed on board Most of the sockets used are built on the Land Grid Array (LGA) architecture where pins are available on sockets. Chapter 3 Release 22/10/2010 Slide 30 of 60 powered by dj CMOS Battery Complementary Metal Oxide Semiconductor (CMOS) batteries power CMOS chip of motherboard Saves settings and time when computer is switched off Last for around 5 years Mostly made up of Lithium Chapter 3 Release 22/10/2010 Slide 31 of 60 powered by dj BIOS Chip Contains necessary code required to operate basic system utilities such as the display device, keyboard or disk drives POST is the test conducted by BIOS BIOS chip Chapter 3 Release 22/10/2010 Slide 32 of 60 powered by dj Onboard Disk Drive Connectors IDE Connector - The hard drive, floppy drive and the CD-ROM drive is connected to the motherboard using the on-board disk connectors i.e. Integrated Development Environment (IDE) port on the motherboard . The connector is a normal 40 pin connector. SATA Connector - Serial Advanced Technology Attachment (SATA) technology is used to connect the newer versions of hard drive. Chapter 3 Release 22/10/2010 Slide 33 of 60 powered by dj Super I/O Chip Controls the serial ports, PS/2 mouse, some keyboard functions and parallel ports. The smaller, slower speed devices are controlled by this chip. E.g. IT8705F, W83757 IC Chapter 3 Release 22/10/2010 Slide 34 of 60 powered by dj CPU Voltage Regulator A Voltage Regulator Module (VRM) is installed on the motherboard and regulates the correct voltage that is needed by the CPU. Facilitates the mounting of different processors with different operating voltages to be mounted on a motherboard. VRM’s senses the voltage needed by the processors from the processor itself. The voltage required by the processor is supplied to VRM by the processor during startup of the computer. Chapter 3 Release 22/10/2010 Slide 35 of 60 powered by dj Practical Perform the activity mentioned in Lab no. 2 in the text book: • To identify various onboard components, disk drive connectors, CPU voltage regulator and Super I/O chip on the motherboard. Chapter 3 Release 22/10/2010 Slide 36 of 60 powered by dj Chipsets and show from CBT Group of integrated circuits (IC) Provide interface for various devices such as the I/O devices, CPU, memory, etc Control all functionalities of the computer Defines the limitations of the system such as the maximum amount of memory that can be added to the system, the processor to be used, etc Chapter 3 Release 22/10/2010 Slide 37 of 60 powered by dj Chipsets Leading manufacturers are • nVidia, Intel, AMD, VIA, and SiS The Intel G41, P45, H55 and the Q43 chipsets are the most common chipsets available today. 64 bit computing technology chipsets are also available today Modern chipset consists of IOH and ICH only The chipset controls the data transfers between every component of the system So the chipset that you choose must support the interface required by your CPU Chapter 3 Release 22/10/2010 Slide 38 of 60 powered by dj Intel-Bridge Architecture - I When Intel started using this architecture it started calling the bridges as “hubs”, the north bridge became MCH (Memory Controller Hub) and the south bridge became ICH (I/O Controller Hub). When the CPU reads data from a hard drive, the data is transferred from the hard drive to the south bridge, then to the north bridge using the dedicated bus and then to the CPU. Also, the manufacturers call this bus as DMI (Direct Media Interface) or Intel Hub Architecture. Chapter 3 Release 22/10/2010 Slide 39 of 60 powered by dj Intel-Bridge Architecture - II The speed of this dedicated bus depends on the chipset model. For example, on Intel 925X chipset this bus has a maximum transfer speed of 2 GB/s. The IOH provides support for the two PCIe graphics slots and connects to the CPU via the Quick Path Interconnect (QPI) bus. The ICH provides the support for the SATA, USB and other system interfaces and is connected to the IOH via the DMI bus. Chapter 3 Release 22/10/2010 Slide 40 of 60 powered by dj Question for GD Time Limit – 3 Mins Define DMI and mention current speed for the same. Chapter 3 Release 22/10/2010 Slide 41 of 60 powered by dj DX58SO Motherboard Platform Chapter 3 Release 22/10/2010 Slide 42 of 60 powered by dj Question for GD Time Limit – 3 Mins What is the difference between IOH and ICH and MCH and ICH? IOH ICH MCH Chapter 3 Release 22/10/2010 ICH Slide 43 of 60 powered by dj Manufacturers of Motherboard - I Manufacturers of motherboards are: • Asus - Asus manufactures motherboards that support different types of processors such as Intel and AMD. The motherboards manufactured by Asus support 64 bit computing technology • Intel - Intel motherboards are available in various configurations and different form factors. Chapter 3 Release 22/10/2010 Slide 44 of 60 powered by dj Manufacturers of Motherboard - II MSI - MSI is well known in for its high performance designs and cutting edge products. MSI's latest motherboard in the Big Bang line is a good example. Gigabyte - Gigabyte manufactures motherboards that are available for different types of processors such as Intel and AMD. The newer versions of the board support the latest processors such as the dual core processors and the 64 bit processors. Chapter 3 Release 22/10/2010 Slide 45 of 60 powered by dj Practical Perform the activity mentioned in Lab no. 3 in the text book: • To identify make, model and chipset of a motherboard. Chapter 3 Release 22/10/2010 Slide 46 of 60 powered by dj Compatible Processors and Motherboards http://processormatch.intel.com/CompDB for Intel products http://products.amd.com/enus/RecommendedMBFilter.aspx for AMD products. Chapter 3 Release 22/10/2010 Slide 47 of 60 powered by dj Factors for selecting a Motherboard – I Form Factor – Defines size and shape of board. Choose a case that is large enough to fit the motherboard of the correct form factor CPU Support – Should support different types of microprocessor and sockets. In the future, if you need to upgrade your processor, you may not have to change the whole motherboard Memory slots – Should have more number of slots. To support new technology software user can upgrade the system in the future Chapter 3 Release 22/10/2010 Slide 48 of 60 powered by dj Factors for selecting a Motherboard – II Expansion Slots –a motherboard with more number of expansion slots can easily be expanded for supporting the various devices SATA support – Allows higher transfer rates of data between hard disk and motherboard and should have SATA controller on it. Number of Ports – Should have more number of USB and other ports to connect different devices to the system. Depending on the type of device to be attached to the system and the port that is required, the board should be purchased. Chapter 3 Release 22/10/2010 Slide 49 of 60 powered by dj Factors for selecting a Motherboard – III Hard Drive transfer speed and RAID support – Should support SATA-II 300 MBps and RAID Bus Speed – Should have higher speed of FSB and BSB which allows faster transfer rate of data in and out of the processor QPI and DMI Speed – Should have higher speed e.g. 2.5GT/s Chapter 3 Release 22/10/2010 Slide 50 of 60 powered by dj Configuring the Motherboard Configure motherboard before it is installed in the system Configuration done with the help of jumpers Set clock frequency, CPU voltage and other settings Chapter 3 Release 22/10/2010 Slide 51 of 60 powered by dj Practical Perform the activity mentioned in Lab no. 4 in the text book: • • To install the motherboard inside a PC. Click on the image to run the video. Chapter 3 Release 22/10/2010 Slide 52 of 60 powered by dj Replace/Upgrade a Motherboard Involves replacing the motherboard and also some components of the system Factors that need to be considered before upgrading the motherboard • • • • • Power Connector Memory Support Hard Disk Support System Case Keyboard – may have to use a converter Chapter 3 Release 22/10/2010 Slide 53 of 60 powered by dj Practical Perform the activity mentioned in Lab no. 5 in the text book: • To uninstall the motherboard from a PC. Chapter 3 Release 22/10/2010 Slide 54 of 60 powered by dj Troubleshooting Motherboards and discuss from CBT Various problems with the motherboard: • Instability in a New System • Motherboard has a Crack • System does not work properly after recent repair • System does not start though fans are working • When switched on, the system only beeps or shows POST error Chapter 3 Release 22/10/2010 Slide 55 of 60 powered by dj Summary – I Motherboard is a printed circuit board that is the most important part of a system Every component of the system connects to the motherboard directly or indirectly There are different types of motherboard There are different motherboard form factors There are different components on the motherboard Jumpers on motherboard enable you to configure the motherboard Chapter 3 Release 22/10/2010 Slide 56 of 60 powered by dj Summary – II You can connect different parts of the system to the motherboard using the connectors and expansion slots The final solution came when the chipset manufacturers started using a new approach: using a dedicated high-speed bus between north and south bridges called DMI and connecting the PCI bus devices to the south bridge. Chipset on a motherboard is a group of integrated circuits and microprocessors Chapter 3 Release 22/10/2010 Slide 57 of 60 powered by dj Summary – III You must configure motherboard using the jumpers, before you perform motherboard installation in the system case You must install CPU, fan and heat sink on motherboard before you install motherboard Follow instructions in motherboard manual when performing configuration or installation You must follow the instructions in the motherboard manual when performing configuration, installation or troubleshooting of the motherboard Chapter 3 Release 22/10/2010 Slide 58 of 60 powered by dj Explorative Work Refer to Internet, reference books or magazine to get the information. Do not copy the information provided in this text book. Consult your faculty for further guidance. Motherboard Sl. Make CPU Socket Chipset Memory Support Available Ports (DVI, HDMI, PCIe, SATA & USB) Approx. Cost 1 2 3 4 5 Chapter 3 Release 22/10/2010 Slide 59 of 60 powered by dj Mind Map Draw a mind map to summarize this chapter Chapter 3 Release 22/10/2010 Slide 60 of 60 powered by dj