File
advertisement

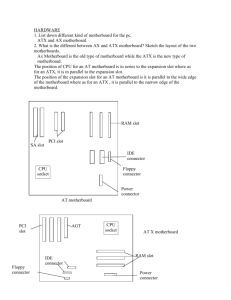
Second Assignment for Semester 1 Hardware 1) List down different kind of motherboard for the pc. Full AT Baby AT Full ATX Mini ATX E-ATX WTX NLX LPX BTX EBX 2) What is the different between AT and ATX motherboard? Sketch the layout of the two motherboard. An ATX motherboard is positioned at a 90 degree angle from the positioning of AT motherboards. As a result, AT case can never be use with an ATX motherboard because it will not fit. AT motherboards use 12-pin plugs to power the motherboard. An ATX motherboard uses one 20-pin plug for the power supply. The AT form factor motherboard is limited to one outside connecter, a five-pin DIN connector for the keyboard. An ATX-style motherboard is built to incorporate many other connectors, including connections for network cards, video cards, sound cards and modems. The power switch for an AT motherboard clicks on and clicks off. The power for an ATX motherboard is a momentary push button that is always open unless pressed. AN AT motherboard uses a two piece single row connector. An ATX motherboard connector is one piece with two rows of ten connections. AT motherboard diagram; Primary and Fl Secondary IDE Controllers ROM/BIOS Chip ISA Slot CPU PGA on a CPU Socket 7 PCI Slot C CMOS Battery Floppy Drive Controller PRN for Parallel Port COM for Serial Ports Heat Sink Chip Set ATX Power Socket L2 Cache Chip Set AT Power Socket 72 SIMM Socket AT DIN/5 Keyboard Connector 168 DIMM Socket ATX motherboard diagram; PS/2 Connector USB Ports Parallel/ Serial Port ATX Power Socket CPU Slot 1 DIMM Slots Floppy Drive Controller IDE Controllers (Primary and Secondary IDE Controller) AGP Slot CMOS Battery Holder Southbridge Chipset ROM/ BIOS Chipset Northbridge Chipset PCI Slot CPU ISA Slot 3) List the pins number of various kind of connector on the motherboard and at the back of the PC. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. PC main power =20pins or 24pins. ATX12V=24pins. IDE= 40pins or 80pins. Parallel=25pin. PS/2=6pins. AT keyboard=5pins. USB=4pins. Firewire=6pins. Floppy=33pins. VGA=15pins. Serial=15pins. DVI=29pins. 4)What are the DC voltages we can find from the DC power supply. I. II. III. 3.3V DV 5V DC 12V DC 5) List down the electrical problem we are facing when operating our PC =The electrical problems might be faced on when PC was operated were the failure to power on, hardware failures, system instability, memory errors, data errors, brownouts or reboots and the problems come from outside the PC entirely e.g. a frayed power cable, bad socket, a dying UPS battery, failing system of power supply and a faulty of soft switch. 6) What are ESD, EMI and RFI? ESD (Electrostatic discharge) is the sudden and momentary electric current that flows between two objects at different electrical potentials caused by direct contact or induced by an electrostatic field. EMI (Electromagnetic interference) is a disturbance that affects an electrical circuit due to either electromagnetic conduction or electromagnetic radiation emitted from an external source. RFI (Radio Frequency Interference) is the process blocking radiofrequency electromagnetic radiation from one circuit to another by separating them with a barrier made of conductive material. This is achieved by separating the circuits with a barrier made of conductive material. 7) List different kind of PC storage. I. II. III. IV. V. VI. VII. Hard disk drive Compact disk(CD) Digital Versatile Disk (DVD) USB drive(Pen drive) Blu-Ray Disk Floppy disk Memory stick 8) List various kinds of RAM and their pin numbers. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. SDRAM (synchronous DRAM)- 168pins. DDR (Double Data Rate SDRAM)-184pins. Rambus DRAM (RDRAM)-184pins. SIMM(Single in-line memory modules)-72pins DIMM (Dual in-line memory modules)-168pins. RIMM (Rambus in-line memory module)-184pins/232pins SODIMM(MircoDIMMs)-144pins.