Motherboard Form Factors
advertisement

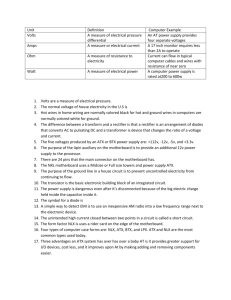
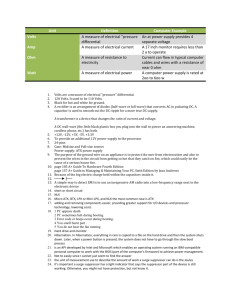
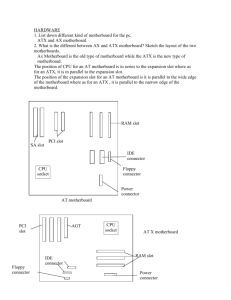
HANDOUT – Motherboard Form Factors Objective 101.02 What are the different types of motherboards? Introduction to Motherboards A motherboard (MB), also known as a Mainboard, system board or logic board, is the central or primary circuit board in a Personal Computer (PC). It is an extremely complex electronic system that every device in a computer system connects to in order to send and receive data. A typical motherboard is made up of a main microprocessor, called the CPU, two or more DIMM slots to hold memory modules, support chips called the Chipset, controller ports for connecting storage drives, expansion slots for adding connections, and integrated input and output ports for connecting external devices. Motherboard Form Factors The size, shape and configuration of integrated devices of the motherboard is called the form factor. Through the history of PC’s, motherboards have been available in many forms, sizes, shapes, names, brands and purposes. The original PC motherboard created by IBM is called the PC/XT. This MB became the defacto standard that many companies cloned. The open architecture allowed others to copy the design, electronics, layout and concept legally. This greatly increased the knowledge, technology and sharing of ideas within the PC industry. The XT MB fit into a case built specifically for the ports and expansion bus integrated into the MB. Page | 1 HANDOUT – Motherboard Form Factors Objective 101.02 The next form factor released was the AT (Advanced Technology) in 1984. This IBM styled MB helped the PC to boom. It is easy to recognize this MB for it has a large keyboard connector (standard or DIN, 5-pin) and power from the power supply connects with a P8 and P9 connector. This MB also became known as the IBM-Clone. In 1995, the next generation of MB was developed. The ATX (Advanced Technology Extended) form factor was released by Intel. It was a completely different MB style. The CPU is placed on one end with the DIMM slots to the right and the back panel connectors to the left. The expansion slots are on the opposite side of the board. The power connector and hard drive controllers are on the right side of the board. This form factor required a different case style and power supply connection. Both the case and the power supply style followed the ATX form factor name. The advantage of the ATX MB is that it made the MB more user-friendly for the system builder. The micro ATX, is smaller in size than the original ATX but it still maintains the same basic layout of ports and components. Micro ATX boards still use ATX power supplies and ATX cases. Page | 2 HANDOUT – Motherboard Form Factors Objective 101.02 Variations on the ATX Form Factor In 2006, Intel introduced the BTX (Balanced Technology Extended) which was a low-profile board with improved thermal or heat regulation. To allow for better air flow, the backside connectors and the expansion slots were switched. These boards are also available in microBTX and picoBTX and have been used by Gateway and HP. NLX is another motherboard form factor developed by Intel. NLX mobos were developed for the big PC companies like Dell, IBM and HP to allow for smaller, slimmer cases. The most notable feature of the NLX board is the use of the riser card, also known as a daughterboard. This is a smaller board that plugs into the motherboard in a perpendicular fashion. The riser card is used to install expansion cards while maintaining the slim system case size. Proprietary Form Factors Large computer manufacturers like Dell, HP, IBM often make changes to motherboard form factors. These boards tend to have small changes to connector types and component location. The reason for this is so that if a technician needs to service one of these MBs or needs parts, they have to purchase these items from the manufacturer. What does Form Factor mean to you? A PC technician must be aware of motherboard form factors when looking to buy or replace a motherboard. The case and power supply form factors must match the motherboard form factor. Therefore, if you are using an ATX motherboard, then you would want an ATX system case and an ATX power supply. Page | 3