Phylum Mollusca Chapter 12
advertisement

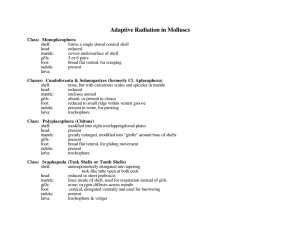
THREE MAIN CLASSES 1. Class Gastropoda (snails, slugs, limpets) 2. Class Bivalvia (muscles, clams, oysters) 3. Class Cephalopoda (octopus, squid, nautilus, cuttlefish) Limpets Bilateral Symmetry Invertebrate - no backbone Hydrostatic Skeleton (fluid under pressure) Triploblastic Coelomate › 1st animals to posses a coelom Yes, even before annelids… › Small cavity; surrounds heart, nephridia, gonads Protostomate › Blastopore become mouth – ‘primitive’ Provides room for organ development Surface diffusion of › Gases › Nutrients › Wastes Storage Elimination of reproductive products Hydrostatic support Size: <1cm – 18m › Garden slug – Giant squid 3 Body Regions › Mantle – tissue that covers the body May secret a shell Fxn: excretion, gas exchange, elimination of wastes, reproductive products › Visceral mass – contains organs › Head foot – elongate foot w/ anterior head Open circulatory system in all except cephalopods Radula – rasping/scraping structure › Covers tonguelike structure Snails, limpets, slugs Over 35,000 species <Largest class> Habitat: Marine, freshwater, terrestrial Operculum ‘lid’ › Dorsal posterior end › Used for protection from predators & desiccation Undergo Torsion during larval stage› 180° Twist of visceral mass & mantle Allows head to enter shell first for protection Allows for clean water in front of the snail to enter mantle cavity Makes snail more sensitive to stimuli coming from the direction in which it moves Locomotion › Flattened foot Sometimes ciliated Muscular contractions › Cilia over mucous trail Nervous Communication › Ospharidia Chemoreceptors Detect sediment & chemicals in inhalant H20 Helps detect prey › Ganglia linked by nerves › Eyes @ base or end of tentacles Photo receptors Lens & Cornea › Statocysts in the foot (balance) Cardiovascular: › Open Circulatory System Blood “hemolymph” leaves blood vessels Blood bathes tissue directly in hemocoel ‘sinus’ › Function of blood: transport nutrients, wastes, & gasses Respiration › Gills › Diffusion of O2 across mantle Digestion › Food trapped in mucus strings Gets incorporated into protostyle › Protostyle – rotating ‘mucoid mass’ in gut of gastropod › Radula › Ciliated digestive tract Excretory Waste Removal › Wastes excreted through coelom from blood › Aquatic – produce ammonia › Terrestrial – produce uric acid (less toxic) – conserves water › Nepheridium – excretory organ Reproduction › Marine snails – external fertilization Dioecious Gametes discharged into sea › Freshwater & Terrestrial snails – internal fertilization Monecious Copulation - Exchange sperm – or One snail may act as the male, the other as the female Mussels, clams, oysters, scallops Habitat: Marine, freshwater Help remove bacteria from polluted water 2 convex halvesvalves Proteinaceous hinge Tongue & grooves in shell to prevent twisting Umbo – swollen area – looks like a notch › Oldest part of shell Sheet like mantle Muscular movement: Adductor muscles to close shell › Defense against predation Sea stars can break this muscle Steaming bivalves… Sessile (immobile) Nervous Communication 3 pairs of interconnected ganglia Margin of the mantle is main sense organ › has sensory cells › Tentacles › Photo receptors or Lens & Cornea Statocysts – balance/gravity Osphraidium – chemoreceptors in mantle Cardiovascular System › Open circulatory system › Blood flow: › heart tissue sinuses nepheridia gills heart Respiration › Gills covered in cillia › diffusion Digestive System Filter feeders Gills trap food particles Move down food grooves (ciliated tracts) Labial palps sort food particles Excretory System › 2 Nepheridia › Duct system › Nephridiopores in anterior region for excretion of wastes Reproduction Most dioecious – male/female Few monoecous – hermaphroditic Most external fertilization › Spew out gametes and fertilize in sea Some internal fertilization (fresh water only) › Female sucks in sperm from inhalent water › Young clams shed from gills Most complex mollusc All except nautilus have a reduced shell › Cuttlefish & squid have internal shell › Nautilus has a coiled shell for support Modified foot for food capture, attachment, locomotion, & reproduction Visceral mass located in head segment Muscular movement Jet propulsion Foot modified into tentacles Nervous Communication Highly developed nervous system Brains are large Fusion of ganglia Statocysts (gravity) Eyes Cardiovascular 1st to have Closed circulatory system Heart consists of 2 auricles and 1 ventricle Have contractile arteries and branchial hearts Respiration Gills & diffusion Digestive System Jaws & Radula Tentacles w/ adhesive cups or foot to capture prey Feed on small invertebrates Efficient predators