PowerPoint 2
advertisement

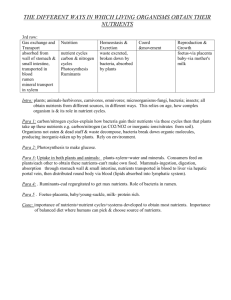
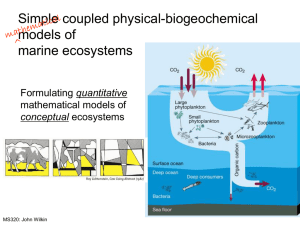
Simulation labs for Biology 4263 • I gave an introductory lab talk on Keystone Predators and Barnacles and Tides on Thursday , April 16th. These labs are due to me by May 4, 2009. • Tonight, I will discuss Limiting Nutrients and Competition, Go Fish, and Oil spills. These labs are due by May 20th. • Background material covered tonight – Limiting Nutrients and Competition – Go Fish – Oil spills Limiting Nutrients and Competition • Algal growth is dependent on the availability of sunlight and essential nutrients including nitrogen, phosphorous, and iron • This lab considers the availability of sunlight to the growth rate of hypothetical green algae and the three nutrients to green, blue, and red algae by themselves and in combinations • The objective of the laboratory exercise is to explore how nutrient availability can influence competition between species of algae Background Information Are phytoplankton adapted to light intensity? • Pmax is the intensity of light at which photosynthesis is maximal – optimum light intensity • Pmax - light intensity relationship for different types of phytoplankton suggests adaptation – diatoms versus dinoflagellates Diatoms reach Pmax at low light levels Dinoflagellate photosynthesis maximal under high light intensities Nutrients: • Various nutrients can be limiting and the kinetics of nutrient uptake is important • Limiting nutrients include N, P, Fe, Si • Nutrients enter phytoplankton cells by active transport – surface area/volume is important to phyto body size Nitrogen • Required for amino acids • Soils on land are 0.5% N • Seawater averages 0.00005% N – Surface water may have no dissolved N • Nitrogen frequently limits phytoplankton in coastal oceans More on nitrogen • Massive amounts of N from fertilizers reach coastal oceans today and is the most important cause of eutrophication • Ammonium (NH4), nitrate (NO3) and nitrite (NO2) are possible forms More on nitrogen • Most phytos prefer ammonium but can use nitrate • N fixation (from N2) important in some locations like estuaries • Inputs from many sources and nitrogen cycle is complex with many bacterial transformations Other nutrients: • Phosphorus (PO4) – Animal excretion is a source of P • Iron (Fe) – In vast areas of the open ocean (Pacific), Fe is limiting – Why iron? – The Geritol Hypothesis • Silicon (Si02) – silicate limiting only in diatoms Nutrient kinetics Rate of uptake depends on nutrient concentration (to a point) • V (uptake rate) = Vmax * S / (ks + S) where S = concentration of a limiting nutrient, Vmax = maximum uptake rate and ks = half saturation constant (the nutrient concentration at Vmax/2) Vmax Go Fish: Fisheries Management Techniques • Collapse of fisheries stocks : • • NMFS – 45% of the fish stocks whose status is known are being overfished Why do fisheries collapse ? – – – Overfishing Environmental factors – climate change, change in salinity, pollution Ecological factors – changes in predators or prey – fishing down the food web (Essay to accompany this report) • • • • Sustainable strategies – – – • Pauly Worms et al. de Musert et al. 2008 Maximal sustainable yield (MSY) – popular but often unsuccessful Constant effort Adaptive methods Squonkfishery Oil Spills : Population Growth • Oil eating bacteria –PWS, Dr. Ralph Portier • Logistic equation – simulations of population growth – Bacterial division rates – Oil (food) availability Incomplete Applications • Must be completed by tomorrow at 4:30 PM or can’t be registered • Two people – notarized participant agreement – Millie Dave – Sumit Patel