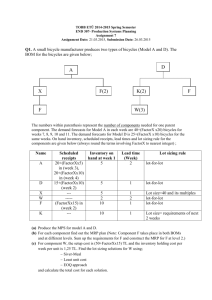
Which of the following is an input to the master production schedule
advertisement

Which of the following is an input to the master production schedule (MPS)? The bill of materials Inventory records file The aggregate plan Planned order schedules The exception report The three main inputs to an MRP system are the bill of materials, the master schedule and the inventory records file. True False A master production schedule is an essential input to a material requirements planning (MRP) system. True False A BOM file is called which of the following? Stocking plan Time bucket schedule Product structure tree Production parts plan Inventory usage record Which of the following is the net requirement using an MRP program if the gross requirement is 1,250 and the inventory on hand is 50? 1,200 1,300 1,150 2,450 None of the above MRP systems seek to achieve which of the following? Improve on JIT methods Provide a yardstick for future improvements Relieve capacity bottlenecks Determine the number of dependent demand items needed Minimize lot sizes The economic order quantity (EOQ) lot sizing technique produces or acquires exactly the amount of product that is needed each time period with none carried over into future periods. True False The lot-for-lot (L4L) lot sizing technique minimizes carrying cost by taking into account setup costs and capacity limitations. True False Computing the quantity of each component that goes into a finished product requires expanding (or exploding) each item in a product structure file and summing at all levels. True False The master production schedule a master production schedule, which states the number of items to be produced during specific time periods. True False Which of the following is considered a primary report in an MRP system? Exception reports Performance reports Planning reports Cycle counting reports Planned order schedules A lot-for-lot (L4L) lot sizing technique does not take into account setup costs or capacity limitations. True False When implemented correctly, MRP links all areas of the business. True False Which of the following is an input file necessary to run an MRP system? Bill of materials (BOM) file Planned-order schedules Purchasing contracts Exception reports Quality management report Which of the following is the planned-order release using an MRP program if the gross requirement is 670 and the inventory on hand is 600? 670 600 530 70 None of the above An output of MRP is a bill of materials (BOM) file. True False Generally, determining lot sizes in MRP systems is simple. True False Enterprise resource planning (ERP) is a computer system that integrates application programs in accounting, sales, manufacturing, and the other functions in a firm. True False The economic order quantity (EOQ) lot sizing technique uses the "square root formula" to balance set-up cost, carrying cost and cost of stock-outs. True False A necessary input to the material requirements planning (MRP) system is an inventory records file. True False Which of the following is the planned-order release using an MRP program if the gross requirement is 5,000 and the inventory on hand is 1,200? 5,000 4,500 3,800 1,200 None of the above A BOM file is often called a product structure file or product tree because it enumerates all of the component parts of the end item product. True False The economic order quantity (EOQ) lot sizing technique uses the "square root formula" to balance set-up cost and carrying cost. True False MRP stands for Material Requirements Planning. True False MRP provides the schedule specifying when each part and component of an end item should be ordered or produced. True False Under the lot-for-lot (L4L) lot sizing technique as used in MRP, we would expect which of the following? Minimized quality problems A just in time management philosophy Minimized set-up costs Minimized carrying costs A consistent lag of supply behind demand MRP stands for Manufacturing Requirements Planning. True False Which of the following is one of the main purposes of a MRP system? To determine the amount of materials needed to produce each end item. Increase inventory accuracy. Stimulate the work force. Decrease labor requirements. Educate personnel in basic work rules. Which of the following is a dynamic lot-sizing technique that adds ordering and inventory carrying cost for each trial lot size and divides by the number of units in each lot size, picking the lot size with the lowest unit cost? Lot-for-lot Inventory item averaging Least total cost Least unit cost Economic order quantity Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) evolved from Materials Requirements Planning (MRP). True False Which of the following is the net requirement using an MRP program if the gross requirement is 1,000 and the inventory on hand is 500? 1,000 400 950 350 500 MRP is most valuable in industries where a number of products are made in batches using the same productive equipment. True False If annual demand is 6,125 units, annual holding cost is $5 per unit, and setup cost per order is $50, which of the following is the EOQ lot size? 350 230 247 185 78 Lot-for-lot (L4L) is the most common lot sizing technique. True False Which of the following is not a lot sizing technique used in MRP systems? Least total cost (LTC) Lot-for-lot (L4L) Warehouse loading factor (WLF) Economic order quantity (EOQ) Least unit cost (LUC) A necessary input to the material requirements planning (MRP) system is an inventory records file. True False