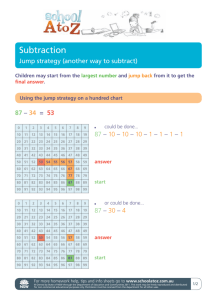
Testing, Measurement and Evaluation for Quality Assurance in
advertisement

Testing, Measurement and Evaluation for Quality Assurance in Teaching Kanchana Prapphal Jump to first page Tests, Measurement and Evaluation Test: 1. Measurement instrument 2. Designed to elicit specific sample of behavior Measurement: 1. Quantification: assigning numbers 2. Characteristics: abilities, traits, attributes, constructs 3. Rules and procedures: must be replicable Jump to first page Tests, Measurement and Evaluation Evaluation: 1. Systematic 2. Gathering of information 3. Making decisions: value judgments Measurement = Testing+ Quantitative Data Evaluation = Testing + Quantitative Data + Qualitative Data + Judgment (Bachman, 1990) Jump to first page Uses of tests in educational programs Individuals a. students b. teachers c. administrators Programs a. effectiveness b. appropriateness c. efficiency d. revision Jump to first page Assumptions necessary for using tests 1. Information regarding educational outcomes is essential to effective formal education. 2. Educational outcomes are measurable. (Bachman, 1990) Jump to first page Learning Outcomes Learning outcomes are statements of what is expected that a student will be able to DO as a result of a learning activity. Quality Assurance: INPUT PROCESS OUTCOMES Descriptors Jump to first page Bloom’s Taxonomy Three domains of educational activities: Cognitive Domain: involves knowledge and the development of intellectual attitudes and skills Affective Domain Psychomotor Domain (Bloom, 1956) Jump to first page Cognitive Objectives Knowledge Comprehension Application Analysis Synthesis Evaluation Simple Complex Jump to first page Knowledge The remembering of previously learned material Examples of learning objectives: -know common terms -know specific facts -know methods and procedures -know basic concepts -know principles Jump to first page Knowledge (Example) Who wrote Brave New World? A. D.H. Lawrence B. Aldous Huxley C. Hemmingway D. Shakespeare Jump to first page Comprehension The ability to grasp the meaning of material Examples of learning objectives: -understand facts and principles -interpret verbal materials -interpret charts and graphs -translate verbal material to mathematical formulae justify methods and procedures Jump to first page Comprehension (Example) What is the main idea of this paragraph? A. Nitrous oxide can cause an environmental problem. B. Nitrous oxide is a potent greenhouse gas. C. Nitrous oxide destroys the earth’s ozone layer. D. Nitrous oxide’s concentration appears to be rising. Jump to first page Application The ability to use learned material in new and concrete situations Examples of learning objectives: -apply concepts and principles to new situations apply laws and theories to practical situations solve mathematical problems construct graphs and charts demonstrate the correct usage of a method or procedure Jump to first page Application (Example) Which one of the following values approximates best to the volume of a sphere with radius 5m? A. 2000 m3 B. 1000 m3 C. 500 m3 D. 250 m3 E. 125 m3 (MCQ) Jump to first page Analysis The ability to break down material into its component parts Examples of learning objectives: - recognize unstated assumptions -recognize logical fallacies in reasoning distinguish between facts and inferences evaluate the relevancy of data analyze the organizational structure of a work Jump to first page Analysis (Example) Here are the five Basic Needs determined by Maslow: 1. Comfort and survival 2. Safety 3. Belongingness and love 4. Self-esteem and the esteem of others 5. Self-actualization Jump to first page Analysis (Example) Determine in what way the Germans meet these needs and to what extent the German pattern differs from the American pattern. Give examples. (Valette) Jump to first page Synthesis The ability to put parts together to form a new whole Examples of learning objectives: -write a well organized theme -give a well organize speech write a creative short story propose a plan for an experiment integrate learning from different areas into a plan for solving a problem Jump to first page Synthesis (Example) Write a paragraph summarizing the text you have read. Your summary should have a topic sentence defining the problem, some of the causes, some of the effects, and a conclusion. Jump to first page Evaluation The ability to judge the value of material for a given purpose based on definite criteria Examples of learning objectives: - judge the logical consistency of written material -judge the adequacy with which conclusions are supported by data judge the value of a work by the use of internal criteria (organization) or external standards of excellence Jump to first page Evaluation (Example) “The United States took part in the Gulf War against Irag BECAUSE of the lack of civil liberties imposed on the Kurds by Saddam Hussein’s regime.” A. The assertion and the reason are both correct and the reason is valid. B. The assertion and the reason are both correct but the reason is invalid. Jump to first page Evaluation (Example) C. The assertion is correct but the reason is incorrect. D. The assertion is incorrect but the reason is correct. E. Both the assertion and the reason are incorrect. (MCQ) Jump to first page Verbs specifying different sorts of outcome (Knowledge) arrange order define recognize duplicate label recall list repeat memorize state relate reproduce Jump to first page Comprehension classify report identify locate describe recognize discuss explain restate express select indicate translate review Jump to first page Application apply operate choose practice demonstrate schedule dramatize sketch employ solve illustrate use interpret write Jump to first page Analysis analyze differentiate appraise discriminate distinguish categorize examine contrast question criticize compare calculate experiment test Jump to first page Synthesis arrange formulate assemble organize compose create propose manage collect plan construct prepare design write Jump to first page Evaluation appraise judge rate attach argue predict assess score choose select compare support estimate evaluate Jump to first page Advantages of specifying learning outcomes Help students learn more effectively. Make it clear what students can hope to gain from a course. Help instructors to design their materials more effectively. Help instructors select the appropriate teaching strategy. Assist in setting examinations based on the materials delivered. Ensure that appropriate assessment strategies are employed. Jump to first page Process Descriptors Behavioral Objectives Product Descriptors Quality Assurance in Teaching Jump to first page References Bachman, L.F. 1990. Fundamental Considerations in Language Testing. Oxford: Oxford University Press. Bloom, B.S. (Ed.) 1956. Taxonomy of Educational Objectives: The Classification of Educational Goals: Handbook I, Cognitive Domain. N.Y.; Toronto: Longmans, Green. Cronbach, L.J. 1989. Essentials of Psychological Testing. Fourth Edition. N.Y.: Harper & Row Jump to first page References (continued) Gronlund, N. and Linn, R.L. 1990. Measurement and Evaluation in Teaching (6th ed.). N.Y.: Macmillan. Thorndike, R. L. and Hagen, E. (1969). Measurement and Evaluation in Psychology and Education (3 rd ed.). N.Y. :Wiley. http://www..coun.uvic.ca http://www. reach.ucf.edu http://www.uct.ac.za Jump to first page Chulalongkorn University -- Academic Testing Center (CU-ATC) Http://www.cuatc.chula.ac.th Jump to first page