Chapter 13
advertisement

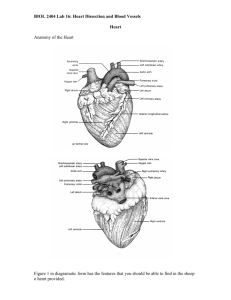
Cardiovascular System Basics of this system Organs Heart Pumps 7k L/day Blood Vessels ArteriesAtriolesCapilariesVenulesVeins Two circuits Pulmonary Systemic Without circulation, what would happen? Structure of Heart Basics- Heart is a muscular pump. Location Between 2nd and 5th intercostal space Pericardium Visceral, Parietal Wall of Heart Epi-,Myo-,Endo Cardium Chambers and Valves Flow of Blood Starting at Right atrium… Tricuspid valve Right Ventricle Pulmonary Valve Pulmonary Artery Lungs Pulmonary Veins Left atrium Bicuspid valve Left Ventricle Aortic valve Aorta The cusps (flaps) of the bicuspid and tricuspid valves are anchored to the ventricle walls by fibrous “cords” called chordae tendineae, which attach to the wall by papillary muscles. This prevents the valves from being pushed up into the atria during ventricular systole. 1. Right Atrium 2. Right Atrioventricular Valve (Tricuspid Valve) 3. Right Ventricle 4. Left Atrium 5. Left Atrioventricular Valve (Mitral Valve) 6. Left Ventricle 7. Papillary Muscle 8. Chordae Tendinae 9. Mitral Valve cusps Cardiac Conduction SA Node Junctional Fibers AV Node AV Bundle Perkinje Fibers Bruce Protocol Heart Actions Heart Actions Can you identify these parts? Heart Actions Heart Actions During one complete heartbeat Systole- contraction of chamber Diastole- relaxation of a chamber Cardiac cycle Difference in pressures Atria Ventricle 70% of blood moved by pressure alone VentriclesArteries Difference in pressure Atria fill as ventricles contract Heart Sounds Two part sound (use stethoscopes if available) Lubb-Dupp Lubb- ventricle contraction Dupp- ventricle relaxation ECG Electrocardiogram Recording of the electrical events during a cardiac cycle P Wave Depolarization of the atria QRS Complex Depolarization of ventricles T Wave Repolarization of the ventricles Interpreting ECGs An ECG is printed on paper covered with a grid of squares. Notice that five small squares on the paper form a larger square. The width of a single small square on ECG paper represents 0.04 seconds. A common length of an ECG printout is 6 seconds; this is known as a "six second strip." Analyze an ECG Each one of the figures represents an ECG pattern displaying three types of abnormal rhythms: Tachycardia, Bradycardia, and Arrhymthmia. Identify each. Regulation of Cardiac Cycle Volume of blood pumped changes Exercise Controlled by Medulla Oblangata Parasympathetic Impulses decrease heart rate Sympathetic Increase heart rate and force of contractions Temperature Baroreceptors Cardiac Output Cardiac Output Stroke Volume LVEDV-LVESV Heart Rate Q=SV x HR Changes in HR, SV, CO SNS PNS Venous Return Exercise Elite Athletes Calcium HR BP Arteries and Veins Tunica Externa Tunica Media Tunica Interna Vasoconstriction Vasodilation Capillaries Blood Pressure Pressure is highest in arteries, why? Systolic Dyastolic Pulse Recoiling of the arterial walls Factors Influencing BP Stroke Volume Blood discharged per contraction of ventricles Cardiac Output SV x HR Blood volume 5 liters in adult Peripheral Resistance Friction between blood and blood vessels Viscosity Fluid content Cardioinhibitor Reflex Cardioaccelerator Reflex