Mo Enzymes.1 - Bryn Mawr College
advertisement

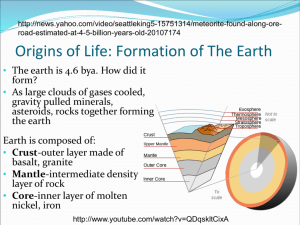
What is the answer to Life, the Universe and Everything? Nov. 9 2005 in the beginning… 4 bya Hadean 3 bya Archean 2 bya 1 bya Proterozoic today Hadean 4.5 -3.8 bya Archean 3.8 -2.5 bya Oldest rocks? 4.5 bya! BANG! 3.5 bya! 0.5 bya Oldest fossils: stromatolites = Calcium carbonate deposits from blue-green algae or cyanobacteria. Most famous characteristic? Nitrogen “fixing” bacteria: N2 + 3 H2 --> 2 NH3 What do we find deep within cyanobacteria’s amazing N2-fixing machinery? # 42 Mo Molybdenum (Greek ‘molybdos’ ) lead-like “Moly” The Answer to Life, the Universe, and Everything (?) Paleozoic 540 - 250 mya Mesozoic 2.5 -0.6 mya “age of dinosaurs” Plants!! Cenozoic 65 mya - today! Animals!! Another extinction!! 540 mya 250 mya 65 mya “age of mammals” quagga Has evolution moved on without #42 - Mo? Grown with Mo Grown without Mo Tobacco plants (Arabidopsis thaliana) Healthy (wild type) Sick (mutant) Nitrate Nitrite Proteins All plants require the molybdoenzyme Nitrate Reductase nitrate nitrite Cyanobacteria Need Mo Plants Need Mo in the Beginning of Life… 4 bya 3 bya 2 bya 1 bya What about the animals? Got Mo? enzyme in mammalian milk xanthine oxidase two enzymes in livers of mammals and avians aldehyde oxidase sulfite oxidase Why the correct oxidation state matters MRI of brain of deceased baby with Sulfite Oxidase Deficiency MRI of healthy brain The baby died because this reaction didn’t happen: SO32- + Sulfite S4+ H 2O ---> SO42- + 2H+ + 2eSulfate S6+ The baby has a genetic defect in the enzyme that catalyzes this reaction. Babies with this genetic disease die within hours. The enzyme is Sulfite Oxidase. You have it in your liver. Review the terms: Oxidation SO32- + H2O ---> half reaction S4+ in Sulfite Reduction Mo6+ + half reaction Net redox reaction SO32- + H2O + 2e- ---> Mo6+ ---> SO42- + 2H+ + 2eS6+ in Sulfate Mo4+ SO42- + 2H+ + Mo4+ Human Molybdenum Cofactor Disorder: Combined Oxidase Deficiency xanthine dehydrogenase xanthine uric acid •xanthinuria •(gout) sulfite oxidase aldehyde oxidase hypoxanthine xanthine •No detoxification of heterocycles sulfite sulfate •Mental/motor retardation •Epileptic seizures •Brain atrophy •Dislocated ocular lens •death Human Molybdoenzyme Deficiencies: Cured with more Mo? defective molybdoenzymes Not repaired by adding Mo alone + Mo Non-functional enzyme Bioinorganic Chemistry 1. Not having the structure or organization of living bodies 2. Not characterized by vital processes 3. Not fundamental or related; extraneous 4. Pertaining to compounds that are not hydrocarbons 5. Mineral 1. (Gr. “bios” ‘life, course or way of living’). In compounds formed in Greek itself, as biography; and in modern scientific words in which bio- is extended to mean ‘organic life.’ 2. A prefix meaning “life” Websters, OED Bioinorganic Chemistry Molybdenum Enzymes Vitamin B12 (Co) Tungsten Enzymes Cis-platin (Pt) cancer Hemoglobin (Fe) Iron enzymes V, Ti, Cr Therapeutics Zinc Enzymes (Zn) Copper Enzymes (Cu) Manganese Enzymes Auranofin (Au) arthritis Bioinorganic Chemistry Molybdenum Enzymes Vitamin B12 (Co) Tungsten Enzymes Cis-platin (Pt) cancer Hemoglobin (Fe) Iron enzymes V, Ti, Cr Zinc Enzymes (Zn) Copper Enzymes (Cu) Manganese Enzymes 3 Therapeutic s 4 Aurial (Au) arthritis Questions asked of molybdoenzymes and their model compounds: -What is the redox potential ( energy of) Mo redox reactions? - What are the structural details? What is bond order? (angles, bond distances) -How well do models mimic reactions of Mo in enzymes? in structure in reactivity Mo Chemistry 1.Oxidation states Mo occurs in oxidation states from 0 +6 Project 1 will generate complexes in states +4 – 6, same as enzymes Mo Chemistry 2. Geometries: Mo complexes have Coordination Numbers from CN 4 8 Project 1 uses reagents or makes products with CN 4 7 Mo Chemistry 3. Reaction ChemistryMo S; dtc ligand Mo O; Mo=O ligands Molybdenum, atomic # 42: is it the answer to Life, the Universe and Everything? Sure looks like it! What’s the Ultimate Question? Adams speculates in “The Restaurant at the End of the Universe”: What do you get if you multiply nine by six? A proposed catalytic cycle for how Mo oxidizes SO32coupled oxygen electron proton transfer atom + SO3 2- O transfer S Mo+6 S O O S O - H+, - e- O S O O Mo+5 OH O - H+, - e- SO42- S S O O S S a S Mo S S O S Mo+4 O H H S + H2O Mo+4 O O Mo+4 S O O dithiolene Mo pterin molybdopterin O O P O P O O O NH2 O Mo S Mo O S HN HO O N N O OH NH N O HN NH2 Ball and stick diagram Chemical structure diagram O O O P O P O O O S Mo O S & HN O NH N HN & O HO N S Mo NH2 N O HN OH NH2 O N N O HO O S O & O O O P O P O O O OH NH N HN Mo compound released (isolated) NH2 NH2 rapid decomposition Protein structure destroyed O HN Mo H2N N HS H N N HO H SH O O O N HN H2N S N N S CHOHCH2OH P O O