Going Beyond Indicator 13 - Ed O'Leary
advertisement

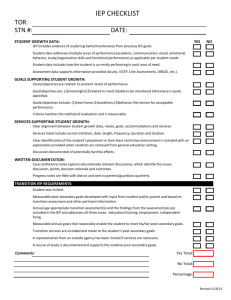
South Dakota Transition Summer Institute Going Beyond Indicator 13 Requirements July 14 – 16, 2014 Dr. Ed O’Leary Introduction to the I-13 Requirements Introduction to ‘Enhanced Practices’ Identification of ‘Predictor Activities’ Incorporate into IEP: Requirements Enhanced Practices Predictor Activities Identify ‘practices’ AND/OR ‘policies’ that need to be put into place or changed to meet I-13 and enhanced practices. Purpose: A free appropriate public education... designed to meet their unique needs and prepare students for further education, employment and independent living. Shift in emphasis to: Results oriented approach. Focus on improved results. Annual report to the public on the performance of each local educational agency according to the targets in the SPP. Annual report to the Secretary on its performance according to the states SPP targets. This report is called the Part B Annual Performance Report (APR). Outlines 20 Indicators that must be reported annually Provides Data Sources and Measurement Delineates Measurable and Rigorous Targets for the Six Years of the Plan Outlines Improvement Activities Four indicators deal directly with transition efforts Percent of youth aged 16 and above with an IEP that includes appropriate measurable postsecondary goals that are annually updated and based upon age appropriate transition assessment; and IEP that includes transition services, including courses of study, that will reasonably enable the student to meet those postsecondary goals; an IEP that includes annual goals related to the student’s transition services; evidence that the student was invited to the IEP Team meeting where transition services will be discussed; and evidence that a representative of any participating agency was invited to the IEP Team meeting with the prior consent of the parent or student who has reached the age of majority. March 2009 Indicator 13 Questions The primary focus of Federal and State monitoring activities shall be on: • Improving educational results and functional outcomes for all children with disabilities; and • Ensuring that States meet the program requirements under Part B/Part C, with a particular emphasis on those requirements that are most closely related to improving educational/early intervention results for children with disabilities. 9 Monitoring must use quantifiable indicators and qualitative indicators needed to measure performance in the following priority areas: Provision of a free appropriate public education in the least restrictive environment/provision of appropriate early intervention services to infants and toddlers with disabilities in natural environments. State exercise of general supervisory authority, including: • child find • effective monitoring • the use of resolution sessions, mediation, and • a system of transition services - secondary transition and early childhood transition Disproportionate representation of racial and ethnic groups in special education and related services, to the extent the representation is the result of inappropriate identification. 10 Indicator 13 Transition Services in Schools Indicator 14 Employment and Postsecondary Outcomes O’Leary, E. 2008 Broad definition: Formal process of cooperative planning that will assist students with disabilities to move from school into the adult world. Present Level of Performance O’Leary, E., 1998 © Copyright Annual Goals Short Term Objectives Step II: Present Levels of Academic Achievement and Functional Performance Step I Measurable Post-secondary Goals Step III: Transition Services Step IV: Measurable Annual Goals Includes: Courses of study Ageappropriate transition assessments •Training •Education •Employment •Independent Living Skills – where appropriate Includes: •Instruction •Related services •Community experiences •Employment and other postschool adult living objectives When appropriate: •Daily living skills •Functional vocational evaluation O’Leary, E., 2005 © Copyright Is there evidence that the student was invited to the IEP team meeting? TOPs - Question 1. There is documented evidence the student was invited to the IEP Team meeting held to consider transition services. The student invitation is signed by the LEA and dated prior to the date of the IEP conference OR When looking at the Parent Notice to determine documentation of student invitation, the student's name is identified as an addressee on the Parent Notice (e.g. "Dear Mr. & Mrs. Smith and Julie") OR A review of student records show a record or copy of a student invitation or telephone log that shows invitation of the student (student invitation or phone log) OR There is documentation of a verbal invitation. The student is prepared before the IEP Team meeting so they know what to expect and how to best participate. The student attends and actively participates in the discussions and decisions at their IEP meeting. The student: Is aware of and discuss their disability and the accommodations they need to be successful. Understands how their disability impacts their daily life in school, at work and in the community. Actively participates in the discussions and decisions. Provides information on their strengths, preferences and interests. Presents and discusses goals. Presents a summary of the transition assessments (strengths, preferences, interest) and how they used that information to help them determine their MPGs Advocates for themselves. Students are instructed on how to participate and take a leadership role in their IEP Team meeting. Students receive self-advocacy and self-determination instruction. 9.1, 9.3, 9.5, 9.6, 9.8, 11.6 Beginning with the first IEP to be in effect when the student turns 16 years of age, or younger if determined appropriate, the student must be invited to their IEP meeting. Parent Notice is NOT an invitation to the student to attend their IEP meeting. Invitation to attend does not mean equal opportunity for participation or decision making. Invite or Inform Invite implies the intent to participate Inform does not Participation requires preparation One of the most critical practices to immediately improve the development and delivery of transition services that will impact post school results is to actively engage the student in all discussions and decision making in their IEP Who Talked The Most – The Least Average Length of Meeting Teacher Directed 29.05 minutes Student Self-Directed 33.57 minutes Student directed meetings are not statistically significantly longer than teacher-directed meetings. http://www.ou.edu/content/education/centers-and-partnerships/zarrow.html 1. 2. Incorporate into IEP: Requirements Enhanced Practices Predictor Activities Identify ‘practices’ AND/OR ‘policies’ that need to be put into place or changed to meet I-13 and enhanced practices. Is there evidence that the measurable postsecondary goals were based on ageappropriate transition assessment? Step II: Present Levels of Academic Achievement and Functional Performance Step I Measurable Post-secondary Goals Step III: Transition Services Step IV: Measurable Annual Goals Includes: Courses of study Ageappropriate transition assessments •Training •Education •Employment •Independent Living Skills – where appropriate Includes: •Instruction •Related services •Community experiences •Employment and other postschool adult living objectives When appropriate: •Daily living skills •Functional vocational evaluation O’Leary, E., 2005 © Copyright Step I Measurable Post-secondary Goals Age-appropriate transition assessments O’Leary, E., 2005 © Copyright •Training /Education •Employment •Independent Living Skills – (where appropriate) The results of the age-appropriate transition assessment(s) can be located in the IEP or file. That at least one age-appropriate transition assessment was used to gather information on the student's needs, strengths, preferences, and interests and that information was used to develop the Measurable Postsecondary Goal(s). The age-appropriate transition assessments provided (student's needs, strengths, preferences and interests) information on which to develop each postsecondary goal. NOTE: The requirement for age-appropriate transition assessment is met whether the MPG is or is not measurable. Transition assessment is an on-going process of collecting and using information on the individual's strengths, needs, preferences, and interests to help define the measurable postsecondary goals. Transition assessment tells a student "story" that leads to the development of measurable postsecondary goals, course of study, transition services, annual goals, agency linkages, and the Summary of Performance (SOP). Transition assessment is the foundation for the discussions and decisions in the entire IEP. Formal or informal transition assessment(s) were selected based on the individual needs of the student. The age-appropriate transition assessment is current and updated annually. Transition assessment data was gathered through a combination of methods. Transition assessment included a variety of sources and instruments. Age-appropriate transition assessments range from formal tests and interest inventories to informal tests, observations of the student, to discussions with the student. Two or more transition assessments were conducted that are appropriate for the age/grade level of the student. All assessments are available for review (either in the record or at the school). The assessment results demonstrate a clear connection to MPG’s, transition services, course of study, and annual goals. 1.4, 1.5, 4.10, 5.4, 5.8, 9.5, 10.1, 10.2, 10.7, 11.7, 12.3, 12.4, 13.8, 14.7, 16.8 Division of Career Development & Transition Transition assessment is "the ongoing process of collecting data on the individual’s strengths, needs, preferences, and interests as they relate to the demands of current and future working, educational, living, and personal, and social environments. Assessment data serve as the common thread in the transition process and form the basis for defining goals and services to be included in the IEP" (Sitlington, 1996). Measurable Postsecondary Goals – Help students define their MPG’s Course of study – Help students determine and plan courses and educational experiences Transition services – coordinated set of activities – what needs to happen by when, and who will be responsible to carry out and oversee each activity Promotes self advocacy and self-awareness 1. Explain the purpose of assessments to students (MPG’s, course selection, develop long range plan and activities). 2. Describe the variety of assessments (career, self determination, life skills, etc.) assessment tools and the different kinds of results. 3. With the student, decide which assessments/assessment tools. 4. Conduct assessments. 5. With the student review results: What the results mean Why the results How the information can be used 6. Have students report on assessments – what – why - the results and how they used the information to define their MPG’s. South Dakota - Technical Assistance Guide For Transition in the IEP http://www.ou.edu/content/education/centers-and-partnerships/zarrow/self-determination-assessment-tools.html Collaboration – Assessment Reviews Reviews on 20 different transition assessments Interactive matrix that lists a sampling of different assessments for use when planning transition services. Includes: name of the assessment area of transition planning (i.e., employment, education/training, independent living/community participation, etc.) appropriate age group or grade level web-based assessment publisher’s contact information http://www.vcu.edu/ttac/transition/pdf/assessment_matrix.pdf http://www.vcu.edu/ttac/transition/pdf/assessment_matrix.pdf http://www.vcu.edu/ttac/transition/pdf/assessment_matrix.pdf Interactive matrix that allows you to choose the transition domain, grade level and disability level. The system shows Transition Assessments that meet the chosen criteria. Includes: Title/name of the assessment Description of the assessment Provides a direct link to the assessment or more information http://www.iidc.indiana.edu/styles/iidc/defiles/CCLC/tran sition_matrix/Transition_Matrix.html 1. 2. Incorporate into IEP: Requirements Enhanced Practices Predictor Activities Identify ‘practices’ AND/OR ‘policies’ that need to be put into place or changed to meet I-13 and enhanced practices. • • • • Are there appropriate measurable postsecondary goals in the areas of education training employment, and where appropriate, independent living skills? The Measurable Postsecondary Goal(s) (MPGs) are written for education, training, employment and, if needed, independent living MPG can be located in the IEP. MPG can be counted or measured (using the word "will" is measurable; words like "intends", "plans", or "wants" are not measurable). MPG occurs after high school words like "after graduation" or "after high school" are acceptable). Education and training may be combined into one measurable postsecondary goal when determined appropriate by the IEP Team. Based upon the information available about the student (Present Level of Academic, Functional Performance, student's strengths, preferences, and interests), the postsecondary goal(s) seem appropriate for this student. The MPGs are well-written and contain all of the required components. The MPGs are the basis for decisions regarding course of study, annual goals and the development of the transition services. The MPGs reflect what the student wants to do following high school and lead to further education or training, employment and independent living. The MPGs are designed to be attainable by the student. 1.4, 16.1 Step I Measurable Post-secondary Goals •Training /Education •Employment •Independent Living Skills – (where appropriate) O’Leary, E., 2005 © Copyright Age-appropriate transition assessments Measurable Annual Goals Educators/Systems Measurable Post secondary Goals Student’s Where will student work or engage in productive activities after graduation? Where and how will student continue to learn and/or develop skills after graduation? Where will student live and how will he or she access adult services, participate in the community, and have fun after graduation? From: Secondary Transition Indicator 13: What Is It and Where Can I Find Resources, Dr. David Test There is no requirement for public agencies to determine whether the postsecondary goals have been met once a child is no longer eligible for FAPE. FAPE must be made available to all children residing in the State in mandatory age ranges. However, the obligation to make FAPE available does not apply to children who have graduated from high school with a regular high school diploma or to children who have exceeded the mandatory age range. When a child's eligibility for FAPE terminates under these circumstances, the LEA must provide a summary of the child's academic achievement and functional performance, including recommendations on how to assist the child in meeting the child's postsecondary goals. Nothing in the IDEA requires the LEA to measure the child’s progress on these postsecondary transition goals, or provide any special education services to the child after the child has graduated from a regular high school or exceeded the mandatory age range for FAPE. If the goal is measurable and occurs after the student has left…I am concerned about liability issues when student’s don’t meet the stated goals after school. NSTTAC Response …IDEA 2004 does not require that LEAs are held accountable for the attainment of postsecondary goals. The stated measurable postsecondary goals are required components of transition planning. There are numerous mediating factors that positively or negatively affect an adult's acquisition of goals, for which a school could not be held accountable. The purpose of the legislation and this indicator is that a student's education program support their goals beyond secondary school. NSTTAC Indicator 13 Checklist Frequently Asked Questions and Responses – Question # 14 www.nsttac.org/pdf/i13checklistqa.pdf For each measurable post-secondary goal identified, BOTH a linked goal AND at least one transition service/activity need to be developed. Technical Assistance Guide For Transition in the IEP South Dakota Transition Services Liaison Project Training or Education Specific vocational or career field, independent living skills training, vocational training program, apprenticeship, OJT, job corps, 4 year college or university, technical college, 2 year college, Vocational Technical School (less than a two year program) etc. Employment Paid (competitive, supported, sheltered); unpaid employment (volunteer, in a training capacity); military; etc. Independent Living, where appropriate Adult living, daily living, independent living, financial, transportation, etc. Initially, broad descriptions of the student’s preferences, interests, or vision of what they might like to do in employment, education, training, and independent living . Each year reassess and refine. Should be specific and measurable one year out by last year/IEP. Use results-oriented terms such as “attend”, “work”, “live independently” Use descriptors such as “full time” and “part time” Begin with “After high school…” A Helpful Formula will (After high school) (After graduation) (Upon completion of high school) (The Student) From: Secondary Transition Indicator 13: What Is It and Where Can I Find Resources, Dr. David Test (Behavior) (Where and how) 16 year old male student with a disability of Autism Employment: I will be employed as a math or science college professor. Education: I will enroll in a public college and major in Math or Science. Training: N/A Independent Living: I will live in a dorm by myself or with one roommate. 16 year old male student with learning disability in reading decoding & comprehension Employment: I will either enlist in the military or work full-time for my dad’s concrete business. Education: N/A Training: I will enroll in a Commercial Driver’s License training through Career Learning Center and obtain a CDL. Independent Living: I will live independently with supports for budgeting & time management. 18 year old female student with significant learning disabilities in math & reading Employment: I will work part part-time producing Native American artwork. Education: N/A Training: I will take a drawing class. I will also take a ‘budgeting class’ through the Independent Living Center . Independent Living: I will live with family until I can afford to live on my own. South Dakota Technical Assistance Guide For Transition in the IEP 19 year old male student with mental retardation Employment: I will work in a school as a janitor, part-time to start with. Education: N/A Training: I will receive on-the-job training through the Division of Rehabilitation Services to learn how to be a janitor. Independent Living: I will continue living with my dad for several years. 17 year old female with emotional disturbance Employment: I will enlist in the Navy when I am 18 and enroll in computer programming. Education: N/A Training: I will complete the basic training and enroll in an advanced computer training program Independent Living: N/A 15 year old female with specific learning disabilities in written expression Employment: I will be a registered nurse and work in a hospital. Education: I will attend a university in SD which has a 4-year nursing program. Training: N/A Independent Living: N/A South Dakota Technical Assistance Guide For Transition in the IEP Training and/or Education Specific vocational or career field, independent living skills training, vocational training program, apprenticeship, OJT, job corps, 4 year college or university, technical college, 2 year college, Vocational Technical School (less than a two year program) etc. Employment Paid (competitive, supported, sheltered); unpaid employment (volunteer, in a training capacity); military; etc. Independent Living, where appropriate Adult living, daily living, independent living, financial, transportation, etc. Where will student work or engage in productive activities after graduation? Where and how will student continue to learn and/or develop skills after graduation? Where will student live and how will he or she access adult services, participate in the community, and have fun after graduation? From: Secondary Transition Indicator 13: What Is It and Where Can I Find Resources, Dr. David Test Postsecondary Goals: Students with Moderate Disabilities Education/Training: After high school, Lissette will participate in weekly instruction on independent living skills at the local Independent Living Center in her community Employment: After high school, Lissette will work on-campus parttime in the food court at the college with supports from Vocational Rehabilitation and the staff at the college. From: Secondary Transition Indicator 13: What Is It and Where Can I Find Resources, Dr. David Test Independent Living: • After high school, Lissette will live semi-independently with a roommate in a assisted living apartment with supports provided through DD Services • Upon completion of high school, Lissette will utilize public transportation, including the public bus and uptown trolley with time limited supports provided through Vocational Rehabilitation. From: Secondary Transition Indicator 13: What Is It and Where Can I Find Resources, Dr. David Test 1. Independent Living • After completion of school, I will live in my own home. 2. Training/Education • After completion of school, I will own my own business. 3. Employment • After completion of school, I will work and run my own business. http://www.poppinjoes.com/about_us www.dol.gov/dol/media/webcast/20110610-odep-ce/ Postsecondary Goals: Students with Severe Disabilities Education/Training: After graduation, Lilly will participate in a centerbased program with an adult curriculum focused on gaining maximum social communication, daily living, and vocational skills. Employment: After graduation, Lilly will participate in a centerbased program with an adult curriculum, receiving services to increase her stamina and mobility to prepare her for work. From: Secondary Transition Indicator 13: What Is It and Where Can I Find Resources, Dr. David Test Independent Living: • After graduation Lilly will use an augmentative communication device at home and the centerbased program to communicate her wants, needs, and desires and to interact with her environment more independently. From: Secondary Transition Indicator 13: What Is It and Where Can I Find Resources, Dr. David Test Bill has significant limitations across all areas of functioning as well as being medically fragile. Training programs will not be appropriate for him. He will require full time nursing care throughout his life and recreational day service programs designed for individuals with such specific needs will probably be most appropriate following high school. 18 years old. Receives specially designed instruction with an alternate curriculum in a self-contained setting all day. Receives related services of OT, PT and nursing Fed via G-tube Has tracheotomy and uses a ventilator with oxygen to breathe Strengths Curious, stays alert and awake throughout the school day, seems to enjoy activity around him. Enjoys getting verbal and tactile attention from his peers and staff. Tolerant of position changes on mat table and allows hand-over-hand assistance to participate in activities. Likes using a switch (with assistance) to activate a variety of devices, including the radio and computer. Present Levels of Academic Achievement and Functional Abilities Benefits from sensory stimulating activities and activities to improve his independence and communication. Uses facial gestures to communicate his pleasure and displeasure with his current state. Offers a smile to show happiness and a blank stare to show his disinterest. Picture/symbol augmentative communication supports have not been successful. Will use simple one-button communication devices with assistance when offered during class activities. Uses a manual wheelchair dependently. Requires a 2-person lift or mechanical device for all transfers. Tolerates positioning on mat table. Limited fine motor skills result in dependency for all care and hand-over-hand assistance for all activities. Education/Training Training programs are not appropriate After graduation, Bill will participate in an in-home or center-based program designed to provide habilitative and vocational training with medical and therapeutic supports. After graduation, Bill will participate in on the job training in using micro switches Employment Recreational day service program. Following graduation Bill will participate in technologically supported self-employment or volunteer work and receive job development services from vocational rehabilitation or a community rehabilitation program within 1 year of graduation. Independent Living After graduation Bill will live at home and participate, to the maximum extent possible, in his daily routines (e.g. feeding, dressing, bathing, activating small appliances/media devices, choice making, etc.) and environment through the use of technology. After graduation Bill will participate in communityintegrated recreational/leisure activities at the YMCA, going to movies, going to church. After graduation Bill will utilize an augmentative communication device at home and in the community that allows individuals to communicate with him regarding needs, wants, and desires. Employment After completion of school Bill will volunteer at the Heritage nursing home. Is (are) the postsecondary goal(s) updated annually? There are Measurable Postsecondary Goals(s) for Education, Training, Employment, and as needed Independent Living in the current IEP. The MPGs are updated annually. 1. 2. Incorporate into IEP: Requirements Enhanced Practices Predictor Activities Identify ‘practices’ AND/OR ‘policies’ that need to be put into place or changed to meet I-13 and enhanced practices. Do the transition services include courses of study that will reasonably enable the student to meet his or her postsecondary goal(s)? Step II: Present Levels of Academic Achievement and Functional Performance Step I Measurable Post-secondary Goals Step III: Transition Step IV: Measurable Services Annual Goals Includes: Courses of study Ageappropriate transition assessments •Training •Education •Employment •Independent Living Skills – where appropriate Includes: •Instruction •Related services •Community experiences •Employment and other postschool adult living objectives When appropriate: •Daily living skills •Functional vocational evaluation O’Leary, E., 2005 © Copyright Step III: Transition Services 1.Courses of study Includes 2.Coordinated set of Activities - Instruction - Employment and other post-school adult living objectives - Related services - Community experiences - Employment and other post-school adult living objectives When appropriate: - Daily living skills - Functional vocational evaluation O’Leary, E., 2005 © Copyright Step III: Transition Services 1.Courses of study Includes 2.Coordinated set of Activities - Instruction - Employment and other post-school adult living objectives - Related services - Community experiences - Employment and other post-school adult living objectives When appropriate: - Daily living skills - Functional vocational evaluation O’Leary, E., 2005 © Copyright The courses of study can be located in the IEP. The courses of study are a multi-year description of coursework from the student's current to anticipated exit year that is designed to help the student achieve their desired postsecondary goals. The courses of study align with the student's postsecondary goals. The course of study list specifies classes the student will take while in school. Classes are identified according to academic school year and at least one year of classes is identified. Students take an active role in all discussions and decisions in developing their course of study and long range education plan. The course of study is reviewed and updated annually. Students meet with the guidance counselor to develop their course of study. Guidance counselors take an active role in helping the student decide what courses to take to achieve their desired postsecondary goals and develop their course of study (long range education plan). Students are scheduled into the courses that are designated in their course of study. Beginning in middle school, students develop their course of study identifying all courses they will be taking each year through completion of their education. Parents take an active role in helping their child develop and plan their course of study. 1.1, 1.2, 1.3, 2.1, 2.2, 2.3, 2.4, 2.5, 2.6, 3.1, 3.2, 3.3, 3.4, 4.1, 4.2, 4.6, 4.7, 5.1, 5.2., 5.6, 5.9, 7.5, 8.1, 8.2, 8.3, 8.4, 8.5, 9.2, 10.3, 10.4, 10.8, 11.1, 11.2, 12.2, 14.2, 16.2, 16.3, 16.4 The ARD/IEP team helps the student identify the courses and educational experiences that will prepare them for post-secondary life. Focus on: — — — Courses of study [all courses and educational experiences] How the educational program can be planned and relate directly to the student’s goals beyond secondary education Show how those courses are linked to the MPG’s Promotes the concept that the high school program focuses on post-school results. Help students and family select courses of study that are meaningful and motivate students to complete their education. If the student and parent are aware of and agree to a change in a course and that change would not have a direct impact on the student achieving his or her desired post-school outcome; or if the student taking the course would not require any accommodations or modifications (which would require goals and objectives); then this change would not be considered a substantive change and would not necessitate another IEP meeting. South Dakota - Technical Assistance Guide For Transition in the IEP 1. 2. Incorporate into IEP: Requirements Enhanced Practices Predictor Activities Identify ‘practices’ AND/OR ‘policies’ that need to be put into place or changed to meet I-13 and enhanced practices. Are there transition services in the IEP that will reasonably enable the student to meet his or her postsecondary goal(s)? Step III: Transition Services 1.Courses of study Includes 2.Coordinated set of Activities - Instruction - Employment and other post-school adult living objectives - Related services - Community experiences - Employment and other post-school adult living objectives When appropriate: - Daily living skills - Functional vocational evaluation O’Leary, E., 2005 © Copyright Transition services/activities can be located in the IEP. There is at least one transition service/activity that will reasonably enable the student to meet each stated postsecondary goal. For each MPG, there is at least one transition service/activity from at least one of the following area is listed in the IEP: Acquisition of daily living skills Community experiences Employment, including supportive employment Functional vocational evaluation Instruction Other post-school adult living objectives Related services Transition services are the 'long range plan' for adult life. When planning for the future consider what transition services the student will need in the areas of postsecondary education, training, employment, and, independent living. Transition services activities are a 'coordinated set of activities'. Coordination implies the active involvement in planning and implementing activities that include school, student, family and adult agencies/providers. Transition services are designed within a 'results-oriented process'. The 'results' are the student attaining their measurable postsecondary goals. Transition services are based upon the student's needs taking into account their strengths, preferences and interests. Transition services specify who is responsible for each activity and a timeline when that activity will be completed. Transition services include specifying who will provide and pay for each activity. The IEP team can include transition activities for the student's participation in non-academic school activities as well as participation in community activities like recreation, leisure, shopping and living. Include social and community support networks. As students transition into adulthood they may need support from a variety of sources. Given the advances in social media technologies, families and professionals can help build support and social networks that can include family, social groups, professionals, faith-based community, or others who could help provide social, recreational, work, living or financial support and assistance. 1.6, 4.3, 4.8, 5.3, 6.1, 10.5, 11.5, 11.6, 12.5, 12.6, 12.8, 13.1, 14.3, 14.4, 14.5, 14.6, 16.6 “Herding Cats” The CSA must show evidence that: 1. Activities are individualized and student specific. 2. Activities lead toward the achievement of the student’s measurable postsecondary goals 3. Activities should show a minimum of 2 years 4. The activities demonstrate coordination between school, family, student and/or outside agency(ies) Multi year - at least a 2 year description of coordinated activities/strategies to help students achieve their measurable post secondary goals while they are still in high school Should complement the course of study, include steps/activities needed for successful post school transition If there are transition services listed that are likely to be provided or paid for by an outside agency then you need to obtain written consent before inviting agency representative to the IEP meeting. South Dakota - Technical Assistance Guide For Transition in the IEP 1. 2. Incorporate into IEP: Requirements Enhanced Practices Predictor Activities Identify ‘practices’ AND/OR ‘policies’ that need to be put into place or changed to meet I-13 and enhanced practices. Is (are) there annual IEP goal(s) related to the student’s transition service needs? There is at least one annual goal or short-term objective included in the IEP that will reasonably help the student make progress towards each of the stated postsecondary goals. There is a reasonable link between the annual goals and the postsecondary goals. NOTE: It is not necessary that there be a separate single annual goal or short-term objective for each postsecondary goal. It is possible that a single annual goal could help the student make progress towards each of the stated postsecondary goals may qualify. N/A 1.6, 3.6, 4.9, 5.5, 6.1, 6.2, 7.2, 9.7, 11.4, 11.8 Step II: Present Levels of Academic Achievement and Functional Performance Step I Measurable Post-secondary Goals Step III: Transition Services Step IV: Measurable Annual Goals Includes: Courses of study Ageappropriate transition assessments •Training •Education •Employment •Independent Living Skills – where appropriate Includes: •Instruction •Related services •Community experiences •Employment and other postschool adult living objectives When appropriate: •Daily living skills •Functional vocational evaluation O’Leary, E., 2005 © Copyright Step II: Present Levels of Academic Achievement and Functional Performance Step I Measurable Post-secondary Goals Step III: Transition Services Step IV: Measurable Annual Goals Includes: Courses of study Ageappropriate transition assessments •Training •Education •Employment •Independent Living Skills – where appropriate Includes: •Instruction •Related services •Community experiences •Employment and other postschool adult living objectives When appropriate: •Daily living skills •Functional vocational evaluation O’Leary, E., 2005 © Copyright Education Strategy/activity Transition Services Strategy/activity All activities and services 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. Strategy/activity Strategy/activity Strategy/activity Strategy/activity Strategy/activity Strategy/activity Strategy/activity Strategy/activity Strategy/activity Strategy/activity Strategy/activity Strategy/activity General Education Strategies activities for current year 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Activity Activity Activity Activity Activity Activity Rehab Strategy/activity Student Strategy/activity Strategy/activity Parent Strategy/activity Others Strategy/activity O’Leary, E., 2005 © Copyright Special Education Annual Goals 1. 2. Incorporate into IEP: Requirements Enhanced Practices Predictor Activities Identify ‘practices’ AND/OR ‘policies’ that need to be put into place or changed to meet I-13 and enhanced practices. If appropriate, is there evidence that a representative of any participating agency was invited to the IEP Team meeting with the prior consent of the parent or student who has reached the age of majority? If appropriate, there is evidence that a representative of any participating agency was invited to the IEP team meeting with the prior consent of the parent or the student who has reached the age of majority. Invitations of outside agencies are documented in the student's IEP or file. For any outside agency that is likely to provide or pay for any transition services for the current and next IEP year the adult agency personnel are invited (e.g. phone call, written invitation, meeting or e-mail). The invitation states the name(s) of the agency personnel invited to the IEP meeting. Invited adult agency personnel attend the IEP meeting. Adult agency personnel attending the student's IEP meeting participate in the development of the needed transition services including the identification of the transition service activities they will provide and pay for. 3.5, 5.7, 13.2, 13.5, 14.1, 14.3, 15.2, 15.3, 15.5, 15.6, 15.7, 15.8, 15.9, 16.7 1. 2. Incorporate into IEP: Requirements Enhanced Practices Predictor Activities Identify ‘practices’ AND/OR ‘policies’ that need to be put into place or changed to meet I-13 and enhanced practices.