Chapter 3 Lecture
advertisement

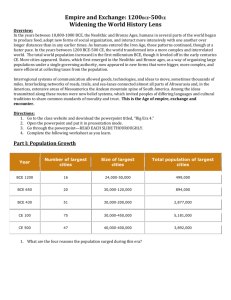
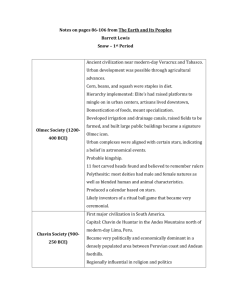
The Mediterranean and Middle East, 2000 – 500 BCE COSMOPOLITAN MIDDLE EAST Hittites • 1600 to 717 B.C.E. • Upper Mesopotamia/ Anatolia • Primarily a trading society • Polytheistic- Hattia, Battle god • Indo-European language family • IRON, 1300 B.C.E. Why Cosmopolitan? Relationship to Babylon • Same religion- Gods and goddesses of Babylon and Sumer • Changed Hammurabi’s law codes around- made them far less severe • Also had city-states • Hittites invade Babylon 1595 BCE Relationship to Egypt • First peace treaty in the world, 1285 BCE • Forged alliances with Egyptian Kings • Traded a lot New Kingdom Egypt • • • • • • • • 1532 - 1070 BCE Overthrew Hyksos (Bronze) 4M people Bureaucracy that separated gov’t Akhenaton – monotheism Rameses II - expansion Aggressive Conquered by Kushites then Assyrians (Iron) • What factors led to Egypt losing its isolationist perspective in the Near East? Aegean World • Minoan Crete • MINOANS: c. 2200 B.C.E. (very approximate) to about 1450/1400 B.C.E. • Europe’s first advanced civilization- CRETE • Very advanced culture, peaceful • Strong commercial ties (especially with Egypt and Sumer) • Mycenaean Greece • Migration to southern Greece c. 2,000 BCE of Indo-Europeans • Lots of contact with Minoans- traded, adapted parts of their culture • Attacked Crete (Knossus) c. 1,450 BCE • Very prosperous • • What are the similarities and differences between the rise of civilization in the Aegean Sea area with the rise of earlier world civilizations? What are the benefits and limitations of oral histories? Assyrian Empire • 911 to 612 BCE • BIGGEST EMPIRE WE’VE SEEN SO FAR • Would DESTROY those who opposed them/take into slavery • Transplant across empire BUT opportunities for conquered to rise within the military/government • Military • All powerful kings • Libraries • Why have historians called the Assyrian Empire of the first millennium BCE the first true empire? • How were the Assyrians able to conquer and control such a large and diverse empire? • How should the Assyrian Empire be judged? Israel • Existence CONFIRMED by outside sources (Egyptian steles) in second millennium • Pastoral nomads from Mesopotamia • Monotheistic • Many connections to other Middle Eastern civilizations • Monarchs- 1020-930 BCE- Saul, David, Solomon • TEMPLE • Role of prophets • North kingdom conquered by 722 BCE Judea conquered 586 BCE • • How reliable are religious documents as records of history? (Bible) What were the causes and consequences of the migrations of the people ultimately known as the Israelites? PHOENICIANS PHOENICIANS • 1200-800 BCE (Dominated trade) • Present-day Lebanon • Established the “Phoenician Triangle” • Similar in many ways to Mesopotamia • Carthage (monopoly/navy) • • • How would you describe the nature and extent of Phoenician expansion in the Mediterranean? What is meant by the description of Carthage as a commercial “empire”? Some civs still obviously very closely linked to rivers, but why are others not so directly centered on rivers?